1 导入库
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "3" # 只暴露第3号 GPU
import unsloth
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
import torch
'''
🦥 Unsloth: Will patch your computer to enable 2x faster free finetuning.
🦥 Unsloth Zoo will now patch everything to make training faster!
'''
2 加载模型
max_seq_length = 2048
# 上下文总长上限(输入 + 生成之和)
dtype = None
# 让 Unsloth 自动根据硬件选择计算精度. Float16 for Tesla T4, V100, Bfloat16 for Ampere+
load_in_4bit = True
# 以 4-bit 量化加载权重(大幅降显存)
#加载模型
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = "unsloth/mistral-7b-v0.3", # "unsloth/mistral-7b" for 16bit loading
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
dtype = dtype,
load_in_4bit = load_in_4bit,
)
'''
==((====))== Unsloth 2025.9.1: Fast Mistral patching. Transformers: 4.56.1.
\\ /| NVIDIA RTX A5000. Num GPUs = 1. Max memory: 23.673 GB. Platform: Linux.
O^O/ \_/ \ Torch: 2.8.0+cu128. CUDA: 8.6. CUDA Toolkit: 12.8. Triton: 3.4.0
\ / Bfloat16 = TRUE. FA [Xformers = 0.0.32.post2. FA2 = False]
"-____-" Free license: http://github.com/unslothai/unsloth
Unsloth: Fast downloading is enabled - ignore downloading bars which are red colored!
'''
3 给模型套上PEFT
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = 128, # LoRA的rank
target_modules = ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj",
"embed_tokens", "lm_head",],
# 在哪些线性层上挂 LoRA
#q_proj、k_proj、v_proj、o_proj:注意力的 Q、K、V、O 投影层(几乎必挂)。
#gate_proj、up_proj、down_proj:FFN、MLP 的三层(常见也会挂,提升表达)。
#embed_tokens、lm_head:词嵌入层与输出头。
# 只做指令微调(SFT):通常不挂这两个(怕“忘词”或过拟合词分布)。
# 做持续预训练领域预训练(continual pretraining):可以挂,让词分布也跟着适配领域。
lora_alpha = 32,
#LoRA缩放系数
lora_dropout =
bias = "none",
use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth",
#梯度检查点(重算):用计算换显存。
# True:标准做法,省显存但会慢一点。
# "unsloth":Unsloth 自家优化版,更省显存/更适配超长上下文。
use_rslora = True, # We support rank stabilized LoRA
#一种改进版 LoRA,会对低秩分解做稳定化处理,在较小/较大 r 时输出分布更稳
#常常能提升收敛与泛化。开着一般是正收益。
loftq_config = None,
#LoftQ:一种把量化和 LoRA 结合来抵消量化误差的技术
)
4 加载数据集
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("roneneldan/TinyStories", split = "train[:2500]")
'''
这里加载的是 TinyStories 数据集(里面是一些简短的英文小故事)
split = "train[:2500]" 表示:只取训练集的前 2500 条样本
如果你有一个纯文本 list(比如自己读的 txt 文件),想转成 Hugging Face Dataset,可以先做:
from datasets import Dataset
data = ["第一句话", "第二句话", "第三句话"]
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"text": data})
'''
EOS_TOKEN = tokenizer.eos_token
'''
LLM(大模型)在训练时需要知道一句话/一个样本什么时候结束。
这个结束标记就是 EOS token(End Of Sequence)。
每个 tokenizer 都定义了自己的 eos_token(例如 <|endoftext|>)。
这里提前拿出来,方便后面加到每个样本结尾。
'''
def formatting_prompts_func(examples):
return { "text" : [example + EOS_TOKEN for example in examples["text"]] }
dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched = True,)
'''
对 examples["text"] 里的每一个字符串,都在末尾拼接上 EOS_TOKEN。
'''
for row in dataset[:5]["text"]:
print("=========================")
print(row)
'''
=========================
One day, a little girl named Lily found a needle in her room. She knew it was difficult to play with it because it was sharp. Lily wanted to share the needle with her mom, so she could sew a button on her shirt.
Lily went to her mom and said, "Mom, I found this needle. Can you share it with me and sew my shirt?" Her mom smiled and said, "Yes, Lily, we can share the needle and fix your shirt."
Together, they shared the needle and sewed the button on Lily's shirt. It was not difficult for them because they were sharing and helping each other. After they finished, Lily thanked her mom for sharing the needle and fixing her shirt. They both felt happy because they had shared and worked together.</s>
=========================
Once upon a time, there was a little car named Beep. Beep loved to go fast and play in the sun. Beep was a healthy car because he always had good fuel. Good fuel made Beep happy and strong.
One day, Beep was driving in the park when he saw a big tree. The tree had many leaves that were falling. Beep liked how the leaves fall and wanted to play with them. Beep drove under the tree and watched the leaves fall on him. He laughed and beeped his horn.
Beep played with the falling leaves all day. When it was time to go home, Beep knew he needed more fuel. He went to the fuel place and got more healthy fuel. Now, Beep was ready to go fast and play again the next day. And Beep lived happily ever after.</s>
=========================
One day, a little fish named Fin was swimming near the shore. He saw a big crab and wanted to be friends. "Hi, I am Fin. Do you want to play?" asked the little fish. The crab looked at Fin and said, "No, I don't want to play. I am cold and I don't feel fine."
Fin felt sad but wanted to help the crab feel better. He swam away and thought of a plan. He remembered that the sun could make things warm. So, Fin swam to the top of the water and called to the sun, "Please, sun, help my new friend feel fine and not freeze!"
The sun heard Fin's call and shone its warm light on the shore. The crab started to feel better and not so cold. He saw Fin and said, "Thank you, little fish, for making me feel fine. I don't feel like I will freeze now. Let's play together!" And so, Fin and the crab played and became good friends.</s>
=========================
Once upon a time, in a land full of trees, there was a little cherry tree. The cherry tree was very sad because it did not have any friends. All the other trees were big and strong, but the cherry tree was small and weak. The cherry tree was envious of the big trees.
One day, the cherry tree felt a tickle in its branches. It was a little spring wind. The wind told the cherry tree not to be sad. The wind said, "You are special because you have sweet cherries that everyone loves." The cherry tree started to feel a little better.
As time went on, the cherry tree grew more and more cherries. All the animals in the land came to eat the cherries and play under the cherry tree. The cherry tree was happy because it had many friends now. The cherry tree learned that being different can be a good thing. And they all lived happily ever after.</s>
=========================
Once upon a time, there was a little girl named Lily. Lily liked to pretend she was a popular princess. She lived in a big castle with her best friends, a cat and a dog.
One day, while playing in the castle, Lily found a big cobweb. The cobweb was in the way of her fun game. She wanted to get rid of it, but she was scared of the spider that lived there.
Lily asked her friends, the cat and the dog, to help her. They all worked together to clean the cobweb. The spider was sad, but it found a new home outside. Lily, the cat, and the dog were happy they could play without the cobweb in the way. And they all lived happily ever after.</s>
'''
5 创建 Trainer
from trl import SFTTrainer
from transformers import TrainingArguments
from unsloth import UnslothTrainer, UnslothTrainingArguments
#UnslothTrainer:省显存 / LoRA / 长上下文 的强化版 Trainer
trainer = UnslothTrainer(
model = model, #之前加了 LoRA/PEFT 的模型
tokenizer = tokenizer,#对应的分词器
train_dataset = dataset, # 已经处理好的 TinyStories 数据集
dataset_text_field = "text", #告诉 Trainer 用哪一列作为文本
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,#模型一次能看到的最大 token 长度
dataset_num_proc = 8,#用 8 个进程预处理数据(多核 CPU 加速)
#训练参数
args = UnslothTrainingArguments(
per_device_train_batch_size = 2, #每张 GPU 上一次放 2 条样本
gradient_accumulation_steps = 8,
#累积 8 次 mini-batch 的梯度再更新一次参数。→ 等效 总 batch size = 2 × 8 = 16
warmup_ratio = 0.1,
#前 10% 的训练步数只慢慢增加学习率(从 0 → 正常值)。防止模型一上来“炸掉”
num_train_epochs = 1,
#只训练 1 个 epoch(全数据走一遍)。常用于小实验;正式训练会设 3~5。
learning_rate = 5e-5,
#主干参数(LoRA adapter、MLP/attention 部分)的学习率
embedding_learning_rate = 5e-6,
#专门给嵌入层(embed_tokens)的学习率。 → 更小,避免词向量被破坏太快
#这是 Unsloth 的一个特色:可以分层控制学习率
logging_steps = 1,
#每一步训练都记录一次日志(loss 等)
optim = "adamw_8bit",
#用 bitsandbytes 的 8-bit AdamW 优化器 → 节省显存
weight_decay = 0.00,
#不做权重衰减(正则化),一般微调可以设 0
lr_scheduler_type = "cosine",
#学习率随训练进度按余弦曲线下降。比线性 decay 更平滑
seed = 3407,
output_dir = "outputs",
#模型、日志等会保存到这个文件夹
report_to = "none",
#不上报到 WandB、TensorBoard 等平台。如果要可视化训练过程,可以改成 "wandb" 或 "tensorboard"。
),
)
6 开Train
trainer_stats = trainer.train()
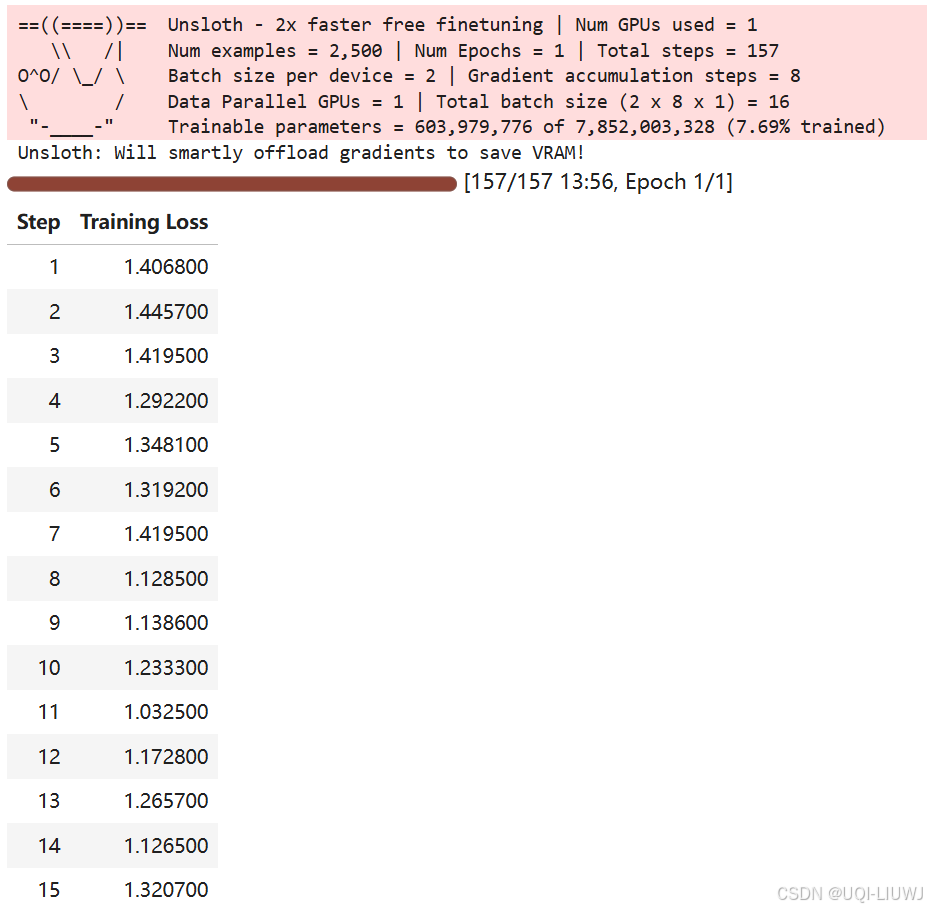
7 inference
FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model)
'''
这是 Unsloth 特有的 API。
它会把模型切到 推理模式,做一些优化(比如关掉 dropout、开启更高效的缓存),避免训练相关逻辑浪费资源。
'''
inputs = tokenizer(
[
"Once upon a time, in a galaxy, far far away,"
]*1, return_tensors = "pt").to("cuda")
'''
输入一条 prompt(也可以一次输入多条)。
tokenizer(..., return_tensors="pt"):转成 PyTorch 的 tensor。
.to("cuda"):放到 GPU 上。
'''
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens = 64, # Increase for longer outputs!
# Recommended Gemma-3 settings!
temperature = 1.0,
use_cache=True
)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs)[0])
'''
<s> Once upon a time, in a galaxy, far far away, there was a little girl named Lily. She loved to play with her toys and explore the universe. One day, she found a big, shiny rock. She picked it up and it was very heavy.
Lily's mom saw her and said, "Lily, that rock is too heavy for you
'''























&spm=1001.2101.3001.5002&articleId=151791817&d=1&t=3&u=0b5bcdaa83244858b224722bae7d1311)
 292
292

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










