DMA基本原理在此不介绍,请百度。
https://xilinx.github.io/embeddedsw.github.io/axidma/doc/html/api/index.html
BD组成
Within the ring, the driver maintains four groups of BDs. Each group consists of 0 or more adjacent BDs:
Free: The BDs that can be allocated by the application with XAxiDma_BdRingAlloc().
Pre-process: The BDs that have been allocated with XAxiDma_BdRingAlloc(). These BDs are under application control. The application modifies these BDs through driver API to prepare them for DMA transactions.
Hardware: The BDs that have been enqueued to hardware with XAxiDma_BdRingToHw(). These BDs are under hardware control and may be in a state of awaiting hardware processing, in process, or processed by hardware. It is considered an error for the application to change BDs while they are in this group. Doing so can cause data corruption and lead to system instability.
Post-process: The BDs that have been processed by hardware and have been extracted from the Hardware group with XAxiDma_BdRingFromHw(). These BDs are under application control. The application can check the transfer status of these BDs. The application use XAxiDma_BdRingFree() to put them into the Free group.
BDs are expected to transition in the following way for continuous DMA transfers:
XAxiDma_BdRingAlloc() XAxiDma_BdRingToHw()
Free ------------------------> Pre-process ----------------------> Hardware
|
/|\ |
| XAxiDma_BdRingFree() XAxiDma_BdRingFromHw() |
±-------------------------- Post-process <----------------------+
The following diagram shows the state transition for the DMA engine:
_____ XAxiDma_StartBdRingHw(), or XAxiDma_BdRingStart(), ______
| | or XAxiDma_Resume() | |
| H |----------------------------------------------------->| NH |
| |<-----------------------------------------------------| |
----- XAxiDma_Pause() or XAxiDma_Reset() ------
Software Initialization
To use the Simple mode DMA engine for transfers, the following setup is required:
DMA Initialization using XAxiDma_CfgInitialize() function. This step initializes a driver instance for the given DMA engine and resets the engine.
Enable interrupts if chosen to use interrupt mode. The application is responsible for setting up the interrupt system, which includes providing and connecting interrupt handlers and call back functions, before enabling the interrupts.
Set the buffer address and length field in respective channels to start the DMA transfer
To use the SG mode DMA engine for transfers, the following setup are required:
DMA Initialization using XAxiDma_CfgInitialize() function. This step initializes a driver instance for the given DMA engine and resets the engine.
BD Ring creation. A BD ring is needed per DMA channel and can be built by calling XAxiDma_BdRingCreate().
Enable interrupts if chose to use interrupt mode. The application is responsible for setting up the interrupt system, which includes providing and connecting interrupt handlers and call back functions, before enabling the interrupts.
Start a DMA transfer: Call XAxiDma_BdRingStart() to start a transfer for the first time or after a reset, and XAxiDma_BdRingToHw() if the channel is already started. Calling XAxiDma_BdRingToHw() when a DMA channel is not running will not put the BDs to the hardware, and the BDs will be processed later when the DMA channel is started through XAxiDma_BdRingStart().
Examples
We provide five examples to show how to use the driver API:
One for SG interrupt mode (xaxidma_example_sg_intr.c), multiple BD/packets transfer
One for SG polling mode (xaxidma_example_sg_poll.c), single BD transfer.
One for SG polling mode (xaxidma_poll_multi_pkts.c), multiple BD/packets transfer
One for simple polling mode (xaxidma_example_simple_poll.c)
One for simple Interrupt mode (xaxidma_example_simple_intr.c)
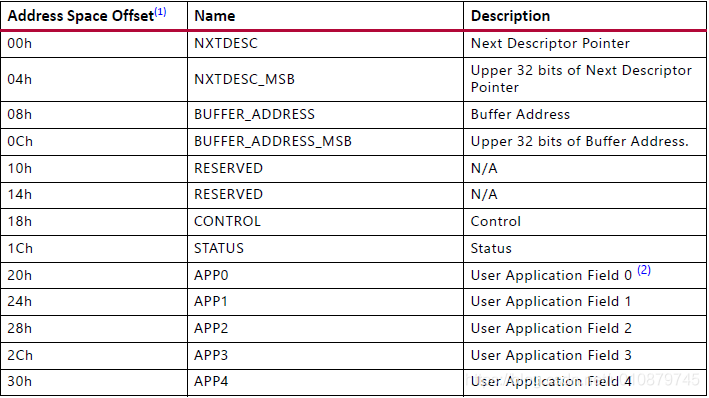
Scatter Gather Descriptor
This section defines the fields of the S2MM (Receive) and MM2S (Transmit) Scatter Gather
Descriptors for when the AXI DMA is configured for Scatter / Gather Mode. The descriptor
is made up of eight 32-bit base words and 0 or 5 User Application words. Multiple
descriptors per packet are supported through the Start of Frame and End of Frame flags.
Table 2-26: Descriptor Fields (Non-multichannel Mode)
We added XAxiDma_LookupConfig() so that user does not need to look for the hardware settings anymore. A helper function, XAxiDma_BdRingClone(), can speed up the BD ring setup if the BDs have same types of controls, for example, SOF and EOF. After using the XAxiDma_BdRingClone(), the application only needs to setup the buffer address and transfer length.
AXI DMA提供的demo,基于的Vivado设计中是将DMA的M_AXIS_MM2S和S_AXIS_S2MM通过AXIS DATA FIFO进行回环。
demo中完成如下过程:
初始化TxBuffer
将TxBuffer中数据通过DMA写入到FIFO
再将FIFO中数据通过DMA都回到RxBuffer
等待传输完成,比对TxBuffer和RxBuffer
上次过程循环多次
在这个demo中,其实两个没有顺序要求,因为有FIFO的存在,XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA要等待XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE向FIFO中写数据后才能真正开始传输。
在你实际应用中,就要根据你的应用要求进行操作了。
Configured in simple mode
简单中断方式
Status = SetupIntrSystem(&Intc, &AxiDma, TX_INTR_ID, RX_INTR_ID);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Failed intr setup\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Disable all interrupts before setup */
XAxiDma_IntrDisable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
XAxiDma_IntrDisable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/* Enable all interrupts */
XAxiDma_IntrEnable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
XAxiDma_IntrEnable(&AxiDma, XAXIDMA_IRQ_ALL_MASK,
XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
/* Initialize flags before start transfer test */
TxDone = 0;
RxDone = 0;
Error = 0;
Value = TEST_START_VALUE;
for(Index = 0; Index < MAX_PKT_LEN; Index ++) {
TxBufferPtr[Index] = Value;
Value = (Value + 1) & 0xFF;
}
/* Flush the buffers before the DMA transfer, in case the Data Cache
* is enabled
*/
Xil_DCacheFlushRange((UINTPTR)TxBufferPtr, MAX_PKT_LEN);
Xil_DCacheFlushRange((UINTPTR)RxBufferPtr, MAX_PKT_LEN);
/* Send a packet */
for(Index = 0; Index < Tries; Index ++) {
Status = XAxiDma_SimpleTransfer(&AxiDma,(UINTPTR) RxBufferPtr,
MAX_PKT_LEN, XAXIDMA_DEVICE_TO_DMA);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
Status = XAxiDma_SimpleTransfer(&AxiDma,(UINTPTR) TxBufferPtr,
MAX_PKT_LEN, XAXIDMA_DMA_TO_DEVICE);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/*
* Wait TX done and RX done
*/
while (!TxDone && !RxDone && !Error) {
/* NOP */
}
SG轮询方式
Status = TxSetup(&AxiDma);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
Status = RxSetup(&AxiDma);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Send a packet */
Status = SendPacket(&AxiDma);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
/* Check DMA transfer result */
Status = CheckDmaResult(&AxiDma);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("AXI DMA SG Polling Example Failed\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
xil_printf("Successfully ran AXI DMA SG Polling Example\r\n");
static int CheckDmaResult(XAxiDma * AxiDmaInstPtr)
{
XAxiDma_BdRing *TxRingPtr;
XAxiDma_BdRing *RxRingPtr;
XAxiDma_Bd *BdPtr;
int ProcessedBdCount;
int FreeBdCount;
int Status;
TxRingPtr = XAxiDma_GetTxRing(AxiDmaInstPtr);
RxRingPtr = XAxiDma_GetRxRing(AxiDmaInstPtr);
/* Wait until the one BD TX transaction is done */
while ((ProcessedBdCount = XAxiDma_BdRingFromHw(TxRingPtr,
XAXIDMA_ALL_BDS,
&BdPtr)) == 0) {
}
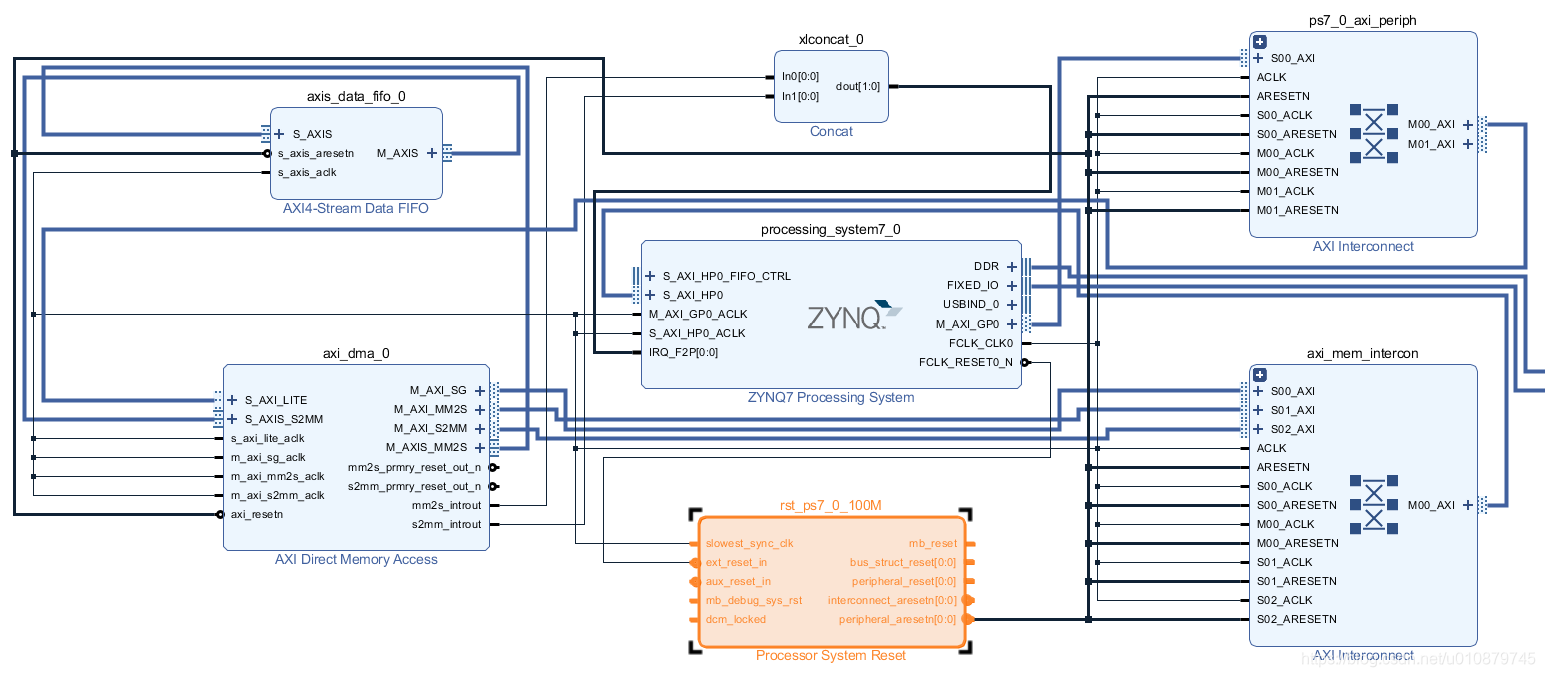
创建DMA项目


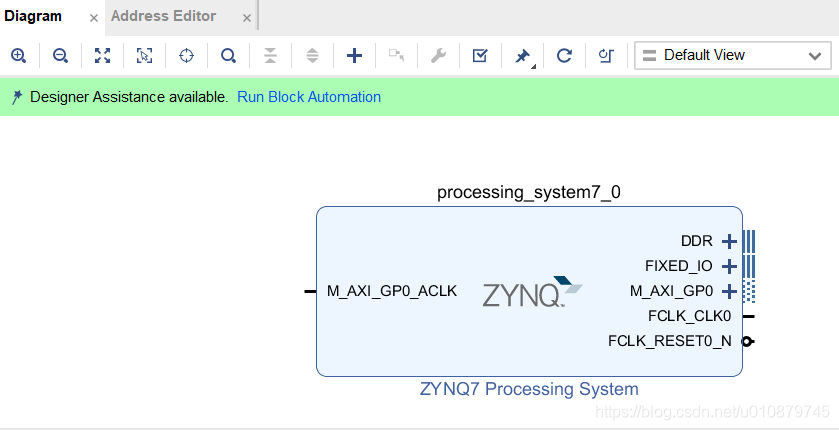



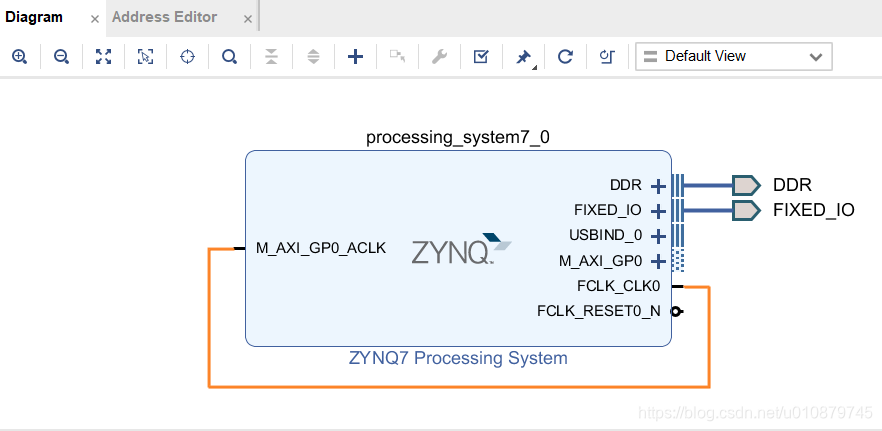


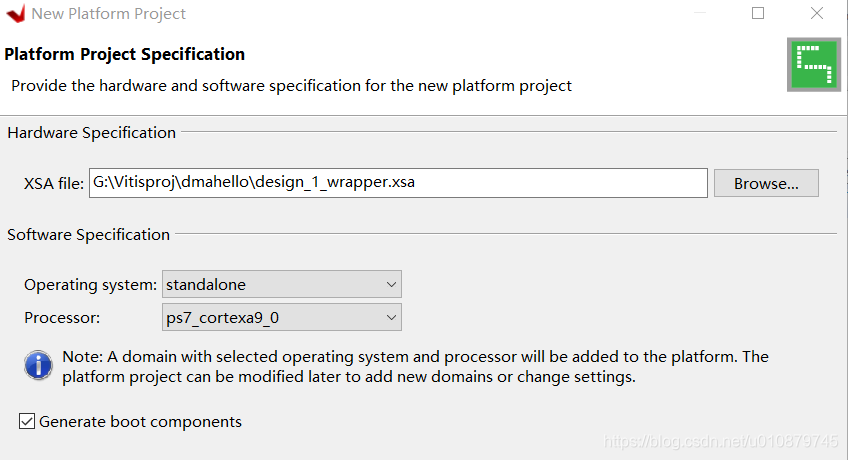



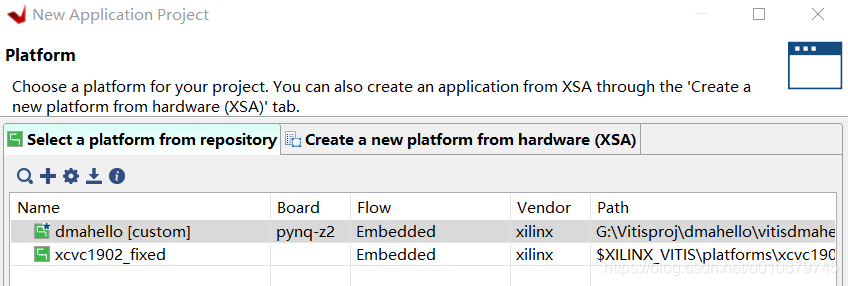

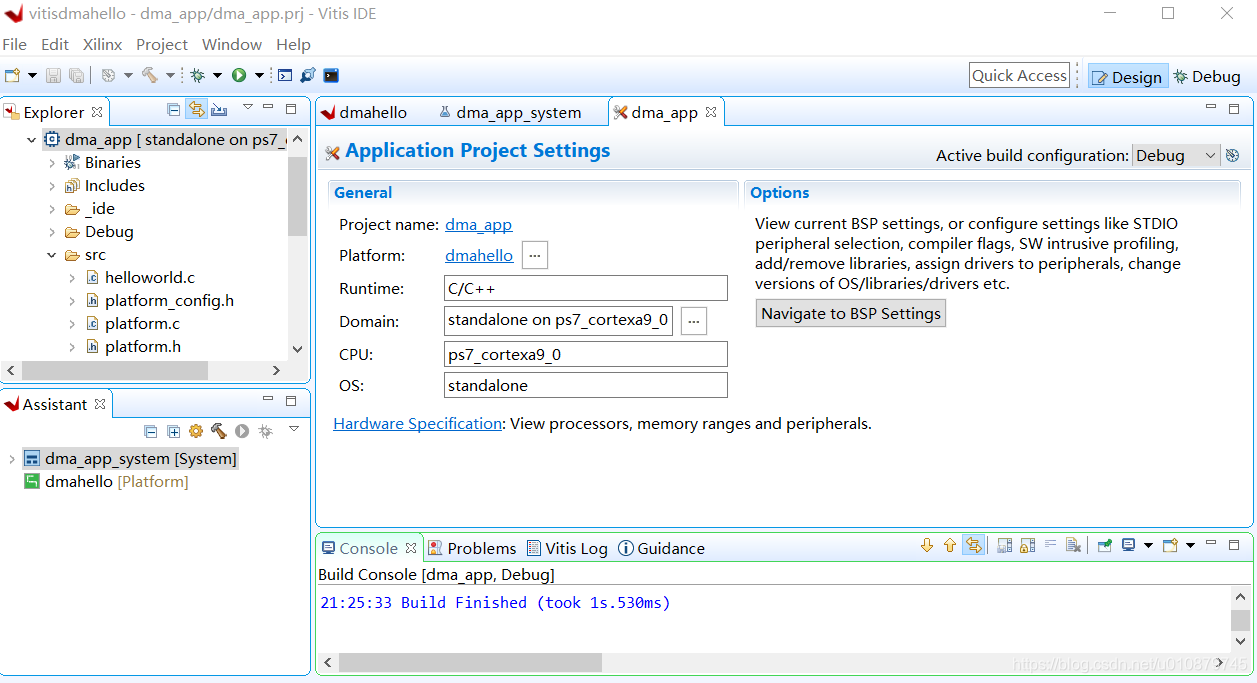

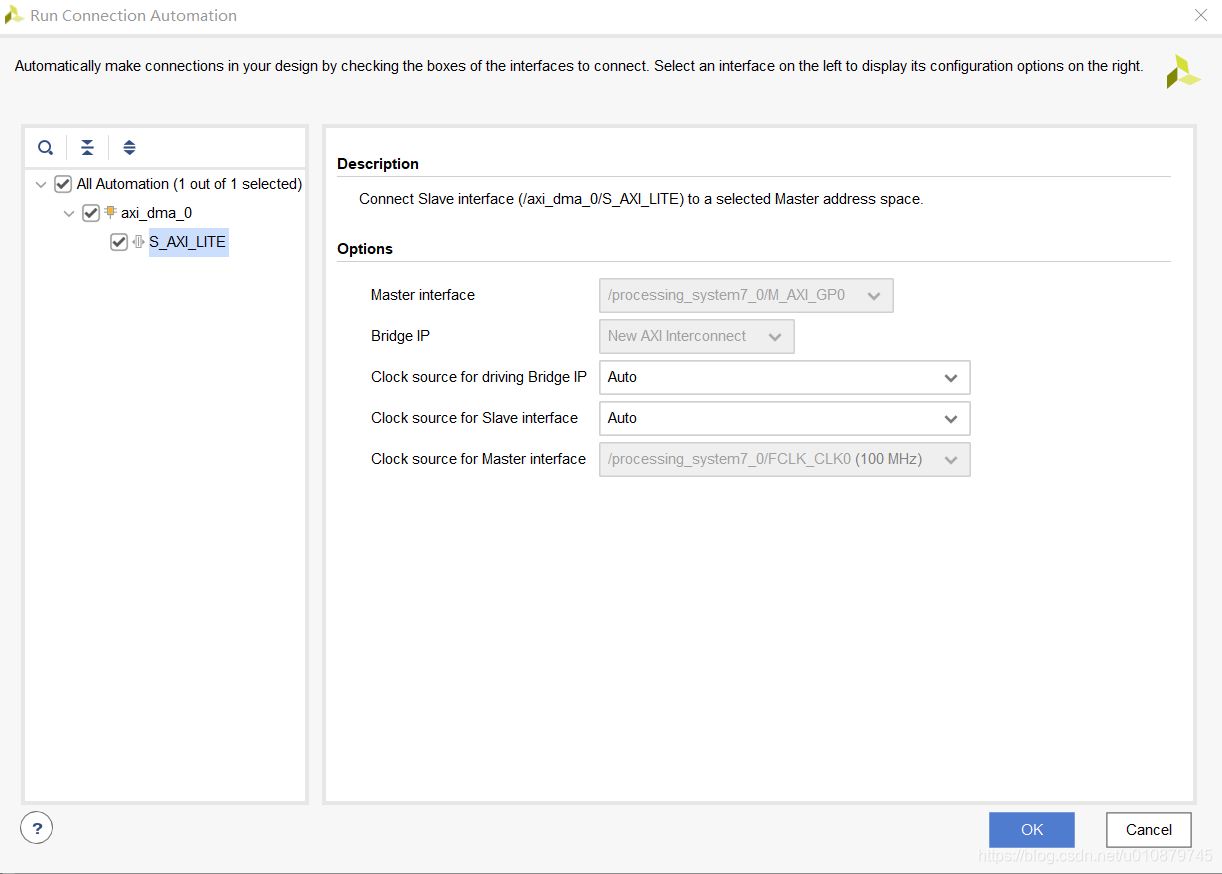






电路图
验证成功




























 5560
5560

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








