步骤:
1. 加载点云,显示,白色点云
2. 鼠标选取地面部分点云,作为校准标准
void pp_callback(const pcl::visualization::AreaPickingEvent& event, void* args)
{
std::vector< int > indices;
if (event.getPointsIndices(indices)==-1)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
{
clicked_points_3d->points.push_back(cloud->points.at(indices[i]));
}
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> red(clicked_points_3d, 255, 0, 0);
std::stringstream ss;
std::string cloudName;
ss << num++;
ss >> cloudName;
cloudName += "_cloudName";
viewer->addPointCloud(clicked_points_3d, red, cloudName);
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 10, cloudName);
}3.将选取的点云拟合平面,计算法向量
bool estimateGroundPlane(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr &in_cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr &out_cloud,
const float in_distance_thre)
{
//plane segmentation
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZRGB> plane_seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr plane_inliers ( new pcl::PointIndices );
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr plane_coefficients ( new pcl::ModelCoefficients );
plane_seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
plane_seg.setModelType ( pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE );
plane_seg.setMethodType ( pcl::SAC_RANSAC );
plane_seg.setDistanceThreshold ( in_distance_thre );
plane_seg.setInputCloud ( in_cloud );
plane_seg.segment ( *plane_inliers, *plane_coefficients );
pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZRGB> extract;
extract.setInputCloud (in_cloud);
extract.setIndices (plane_inliers);
extract.filter (*out_cloud);
cout<<"cloud size="<<out_cloud->size()<<endl;
return true;
}计算平面法向量
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr out_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGB>); // 创建点云(指针)
estimateGroundPlane(clicked_points_3d,out_cloud,0.1);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
//创建法线估计的对象
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZRGB,pcl::Normal> normalEstimation;
normalEstimation.setInputCloud(out_cloud);
//对于每一个点都用半径为10m的近邻搜索方式
normalEstimation.setRadiusSearch(10);
//Kd_tree是一种数据结构便于管理点云以及搜索点云,法线估计对象会使用这种结构来找到哦啊最近邻点
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>::Ptr kdtree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZRGB>);
normalEstimation.setSearchMethod(kdtree);
//计算法线
normalEstimation.compute(*normals);4.根据法向量,计算旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix4f CreateRotateMatrix(Eigen::Vector3f before,Eigen::Vector3f after)
{
before.normalize();
after.normalize();
float angle = acos(before.dot(after));
Eigen::Vector3f p_rotate =before.cross(after);
p_rotate.normalize();
Eigen::Matrix4f rotationMatrix = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
rotationMatrix(0, 0) = cos(angle) + p_rotate[0] * p_rotate[0] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(0, 1) = p_rotate[0] * p_rotate[1] * (1 - cos(angle) - p_rotate[2] * sin(angle));//这里跟公式比多了一个括号,但是看实验结果它是对的。
rotationMatrix(0, 2) = p_rotate[1] * sin(angle) + p_rotate[0] * p_rotate[2] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(1, 0) = p_rotate[2] * sin(angle) + p_rotate[0] * p_rotate[1] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(1, 1) = cos(angle) + p_rotate[1] * p_rotate[1] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(1, 2) = -p_rotate[0] * sin(angle) + p_rotate[1] * p_rotate[2] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(2, 0) = -p_rotate[1] * sin(angle) +p_rotate[0] * p_rotate[2] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(2, 1) = p_rotate[0] * sin(angle) + p_rotate[1] * p_rotate[2] * (1 - cos(angle));
rotationMatrix(2, 2) = cos(angle) + p_rotate[2] * p_rotate[2] * (1 - cos(angle));
return rotationMatrix;
}5.旋转点云,并显示,绿色点云
效果:
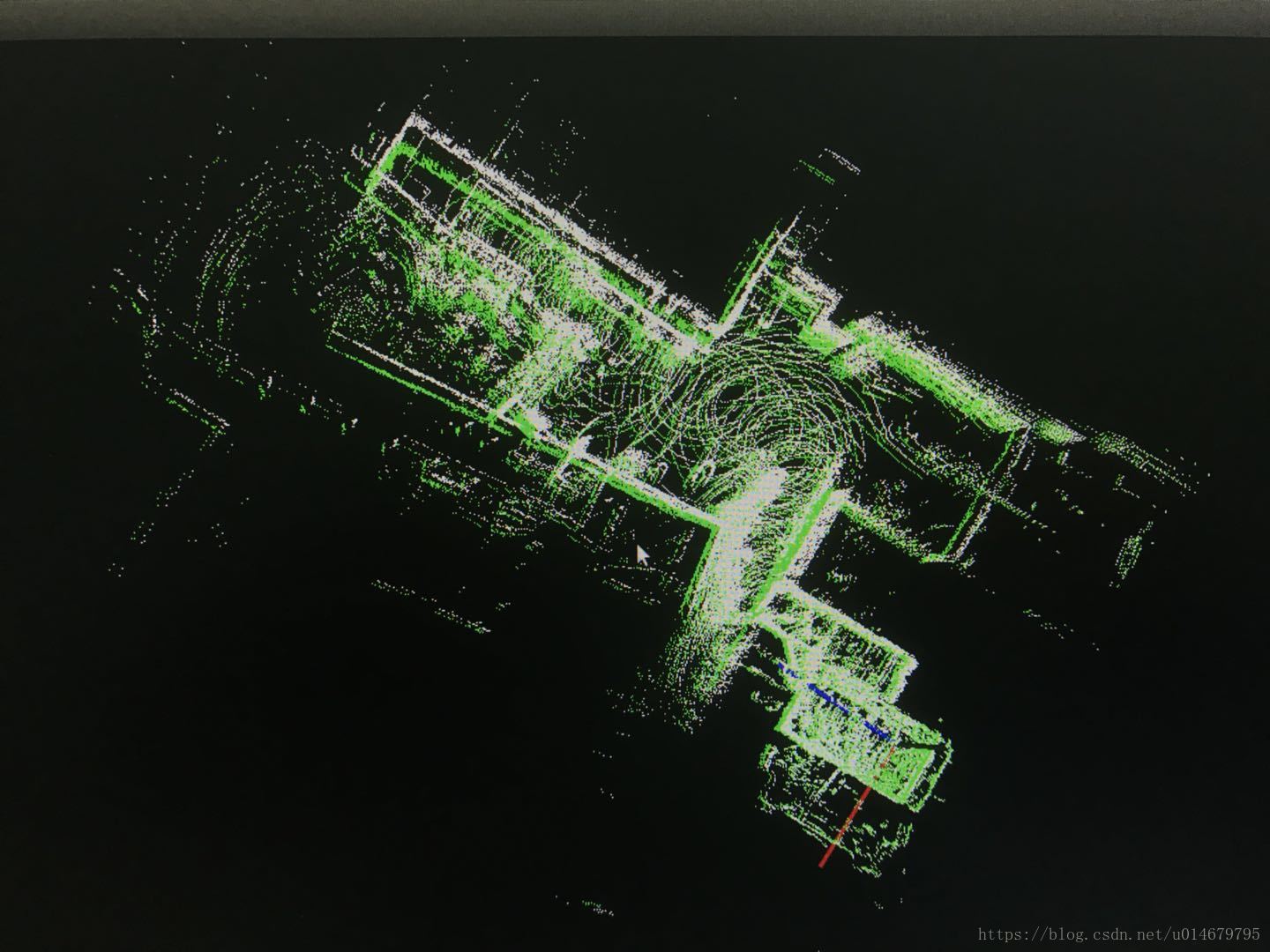

全部代码见链接 https://download.csdn.net/download/u014679795/10634354
























 492
492

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








