封装是C++面向对象的三大特性之一,“对象”包含属性和行为,具有相同属性和行为的对象即可抽象封装为一个“类”。
一、封装的规则
将属性和行为封装为一个类,再用类创建具体的对象,属性和行为均可被设置不同的访问权限,权限分为公共权限、保护权限和私有权限。
若为公共权限,类内可以访问 ,类外也可以访问;
若为保护权限,类内可以访问 ,类外不可以访问,继承时可以访问;
若为私有权限,类内可以访问 ,类外不可以访问,继承时不可以访问。
class Person
{//成员
//成员属性/成员变量
//公共权限
public:
string m_Nationality = "中国";
//保护权限
protected:
string m_Car = "比亚迪";
//私有权限
private:
string m_Phone = "华为";
//成员方法/成员函数
public:
void SetNationality(string nationality)
{
m_Nationality = nationality;
}
//展示国籍、汽车和手机
void Show()
{
cout << m_Nationality << endl;
cout << m_Car << endl;
cout << m_Phone << endl << endl;
}
protected:
void SetCar(string car)
{
m_Car = car;
}
private:
void SetPhone(string phone)
{
m_Phone = phone;
}
};
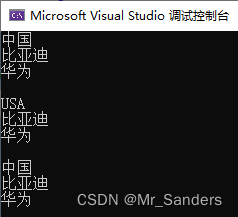
int main()
{
Person Chou;
Chou.Show();
Chou.m_Nationality = "USA";
//调试报错,成员不可访问
//Chou.m_Car = "Tesla";
//Chou.m_Phone = "iPhone";
Chou.Show();
Chou.SetNationality("中国");
//调试报错,成员不可访问
//Chou.SetCar("Tesla");
//Chou.SetPhone("iPhone");
Chou.Show();
return 0;
}
二、封装的意义
一般在封装类时会将成员属性都设置为私有权限,通过拥有公共权限的成员方法实现读写操作。封装的意义也正是在于此,即保护成员属性不被类外程序直接访问和修改,保护和隐藏成员方法的实现细节避免被无意中破坏,使代码模块化,仅通过保留的对外接口与外部程序交互。
//point.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class point
{
public:
//设置x坐标
void setx(int x);
//获取x坐标
int getx();
//设置y坐标
void sety(int y);
//获取y坐标
int gety();
private:
//点类的x,y坐标
int p_x;
int p_y;
};
//point.c
#include"point.h"
//设置x坐标
void point::setx(int x)//
{
p_x = x;
}
//获取x坐标
int point::getx()
{
return p_x;
}
//设置y坐标
void point::sety(int y)
{
p_y = y;
}
//获取y坐标
int point::gety()
{
return p_y;
}
//circle.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include"point.h"
class Circle
{
public:
void setr(int r);
double getr();
void setcenter(point center);
point getcenter();
private:
int c_r;
//另一个类也可做本类中的成员
point c_center;
};
//circle.c
#include"Circle.h"
void Circle::setr(int r)//设置半径
{
c_r = r;
}
double Circle::getr()//获取半径
{
return c_r;
}
void Circle::setcenter(point center)
{
c_center = center;
}
point Circle::getcenter()
{
return c_center;
}
//main.c
#include"circle.h"
#include"point.h"
//判断点和圆关系
void Isincircle(Circle& c, point& p)
{
//计算点和圆心距离的平方
int d =
(c.getcenter().getx() - p.getx()) * (c.getcenter().getx() - p.getx()) +
(c.getcenter().gety() - p.gety()) * (c.getcenter().gety() - p.gety());
//计算圆半径的平方
double R = c.getr() * c.getr();
//判断关系
if (d > R)
{
cout << "点在圆外" << endl;
}
else if (d < R)
{
cout << "点在圆内" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "点在圆上" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
//设置圆对象
Circle c;
c.setr(10);
//设置点对象
point p;
p.setx(10);
p.sety(0);
//设置圆对象中的圆心(点对象)
point center;
center.setx(0);
center.sety(0);
c.setcenter(center);
//判断关系
cout << "圆心为(0,0),半径为10" << endl;
cout << "点坐标为(10,0)" << endl;
Isincircle(c, p);
return 0;
}当圆半径为10时:

当圆半径为5时:

当圆半径为15时:

三、struct和class的区别
1.封装
struct中的成员默认为公共权限,class中的成员默认为私有权限。
class A
{
//默认为私有权限
int m_A;
};
struct B
{
//默认为公共权限
int m_B;
};
int main()
{
A a;
//报错
//a.m_A = 1;
//cout << a.m_A << endl;
//可执行
B b;
b.m_B = 2;
cout << b.m_B << endl;
return 0;
}
2.继承
在子类继承父类时,编译器默认的继承方式为私有继承;而子结构体继承父结构体时,编译器默认的继承方式为公有继承。
struct A
{
public:
int a1;
protected:
int a2;
private:
int a3;
};
//默认继承方式为公有继承
struct B :A
{
public:
int b;
//B对A为公有继承,因此在类B中可以访问A中的公有成员和保护成员,但不能访问私有成员
void func()
{
this->a1 = 1;
this->a2 = 2;
//this->a3 = 3;
cout << this->a1 << " ";
cout << this->a2 << " ";
}
};
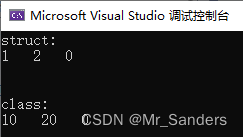
void test1()
{
B the_B;
//B对A为公有继承,因此通过B创建的对象可以访问A中的公有成员,但不能访问保护成员和私有成员
the_B.a1 = 0;
//the_B.a2 = 0;
//the_B.a3 = 0;
the_B.b = 0;
cout << "struct:" << endl;
the_B.func();
cout << the_B.b;
cout << endl << endl << endl;
}
class C
{
public:
int c1;
protected:
int c2;
private:
int c3;
};
//默认继承方式为私有继承
class D:C
{
public:
int d;
//D对C为私有继承,因此在类D中可以访问C中的公有成员和保护成员,但不能访问私有成员
void func()
{
this->c1 = 10;
this->c2 = 20;
//this->a3 = 30;
cout << this->c1 << " ";
cout << this->c2 << " ";
}
};
void test2()
{
D the_D;
//D对C为私有继承,因此通过D创建的对象不可以访问C中任何成员
//the_D.c1 = 0;
//the_D.c2 = 0;
//the_D.c3 = 0;
the_D.d = 0;
cout << "class:" << endl;
the_D.func();
cout << the_D.d;
cout << endl << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
test2();
return 0;
} 
3.总结
C++中仍然引入结构体,主要是为了保持和C语言的兼容性。无论是封装还是继承,class和struct之间的根本区别都是在于其默认的访问权限设置。而在使用时,如果用来存储数据集合等轻量级对象时,选择struct;如果用来表示数据量大、逻辑复杂的对象时,选择class。






















 1253
1253











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








