负责组内的定位导航也已经有一段时间了,HDL定位也用了一段时间,大部分情况下效果也还不错。但对其原理还是不是很清晰,只是大概知道用ukf融合了imu数据和匹配用的是ndt。最近要求优化定位效果,做一些自己的东西,因此需要了解原理进行增删改查。特此学习并记录HDL定位的原理及源码。
一,HDL原理
hdl的后端数据融合使用的UKF,与EKF相比较,UKF更好地拟合非线性的概率分布,而不是强行进行线性化,EKF由于要计算雅可比矩阵,更烧脑一些,UKF要对协方差矩阵做开方,也需要用到矩阵分解,两者计算量差不多。当然,如果一定要用EKF应该也能解决如今的低速定位问题。
在hdl中使用的ndt就像我们熟悉的pcl接口一样,只不过调用了多线程omp模式,它提供的是测量值。imu提供的是先验值,我们如果选择不用imu则先验值为原有的位姿。
参与融合的状态向量依然是p、v、q、ba、bg,一共16维,观测量则是7维,即p、q。和其它KF的接口一样,这里提供了predict和correct两个接口:
1.更新预测
control是传入的一帧imu数据,我们姑且看作是控制量,预测时首先判断协方差矩阵是否是方阵并且是否正定,因为我们在求sigma点的过程中要求协方差矩阵的逆,因此提取出它们的特征值和特征向量并再次相乘。接下来就是求解sigma点了:
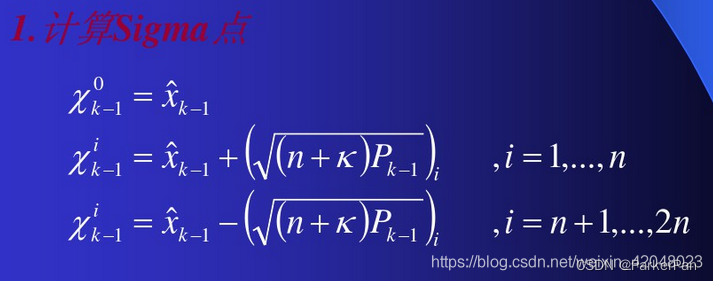
void computeSigmaPoints(const VectorXt& mean, const MatrixXt& cov, MatrixXt& sigma_points) {
const int n = mean.size();
assert(cov.rows() == n && cov.cols() == n);
//用llt分解求协方差的逆矩阵
Eigen::LLT<MatrixXt> llt;
llt.compute((n + lambda) * cov);
MatrixXt l = llt.matrixL();
sigma_points.row(0) = mean;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sigma_points.row(1 + i * 2) = mean + l.col(i);
sigma_points.row(1 + i * 2 + 1) = mean - l.col(i);
}
}
在计算到所有的sigma点之后,用这些点重新拟合一个正态分布,在这个过程中引入了权重weights,它的初始赋值在构造函数中:
weights[0] = lambda / (N + lambda);
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * N + 1; i++) {
weights[i] = 1 / (2 * (N + lambda));
}

void predict(const VectorXt& control)
{
// calculate sigma points
ensurePositiveFinite(cov);
computeSigmaPoints(mean, cov, sigma_points);
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
//状态转移方程
sigma_points.row(i) = system.f(sigma_points.row(i), control);
}
const auto& R = process_noise;
// unscented transform
VectorXt mean_pred(mean.size());
MatrixXt cov_pred(cov.rows(), cov.cols());
mean_pred.setZero();
cov_pred.setZero();
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
mean_pred += weights[i] * sigma_points.row(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
VectorXt diff = sigma_points.row(i).transpose() - mean_pred;
cov_pred += weights[i] * diff * diff.transpose();
}
cov_pred += R;
mean = mean_pred;
cov = cov_pred;
}
在每帧imu传入后都进行一次预测更新,在观测矫正之前我们得到了sigma点拟合的状态分布,而非状态转换矩阵,很像粒子滤波。
2.观测值估计真值
correct函数是观测矫正的过程,我们先拟合观测的sigma点,再用观测方程求解观测的均值,并加权计算扩增后的预测状态以及观测状态的协方差矩阵。

void correct(const VectorXt& measurement)
{
// create extended state space which includes error variances
//状态扩增,即先更新预测值的协方差矩阵,将上一部分用sigma点拟合的协方差加上测量噪声
VectorXt ext_mean_pred = VectorXt::Zero(N + K, 1);
MatrixXt ext_cov_pred = MatrixXt::Zero(N + K, N + K);
ext_mean_pred.topLeftCorner(N, 1) = VectorXt(mean);
ext_cov_pred.topLeftCorner(N, N) = MatrixXt(cov);
ext_cov_pred.bottomRightCorner(K, K) = measurement_noise;
//拟合状态扩增后的均值与协方差,也就是再算一遍sigma点
ensurePositiveFinite(ext_cov_pred);
computeSigmaPoints(ext_mean_pred, ext_cov_pred, ext_sigma_points);
// unscented transform
//UT变换,即拟合测量的均值和协方差
expected_measurements.setZero();
for (int i = 0; i < ext_sigma_points.rows(); i++) {
expected_measurements.row(i) = system.h(ext_sigma_points.row(i).transpose().topLeftCorner(N, 1));
expected_measurements.row(i) += VectorXt(ext_sigma_points.row(i).transpose().bottomRightCorner(K, 1));
}
//虽然叫expected,但这是7维的测量值,也就是用sigma点拟合的测量分布!
VectorXt expected_measurement_mean = VectorXt::Zero(K);
for (int i = 0; i < ext_sigma_points.rows(); i++) {
expected_measurement_mean += ext_weights[i] * expected_measurements.row(i);
}
//测量的协方差矩阵,即Pk+1
MatrixXt expected_measurement_cov = MatrixXt::Zero(K, K);
for (int i = 0; i < ext_sigma_points.rows(); i++) {
VectorXt diff = expected_measurements.row(i).transpose() - expected_measurement_mean;
expected_measurement_cov += ext_weights[i] * diff * diff.transpose();
}
// calculated transformed covariance
//那么,在这里的23*7的sigma矩阵就是状态扩增后的Pk|k+1
MatrixXt sigma = MatrixXt::Zero(N + K, K);
for (int i = 0; i < ext_sigma_points.rows(); i++) {
auto diffA = (ext_sigma_points.row(i).transpose() - ext_mean_pred);
auto diffB = (expected_measurements.row(i).transpose() - expected_measurement_mean);
sigma += ext_weights[i] * (diffA * diffB.transpose());
}
//计算卡尔曼增益K=Pk|k+1/Pk
kalman_gain = sigma * expected_measurement_cov.inverse();
const auto& K = kalman_gain;
//更新观测后的真值估计
VectorXt ext_mean = ext_mean_pred + K * (measurement - expected_measurement_mean);
MatrixXt ext_cov = ext_cov_pred - K * expected_measurement_cov * K.transpose();
mean = ext_mean.topLeftCorner(N, 1);
cov = ext_cov.topLeftCorner(N, N);
}
最后简单总结一下UKF的过程:
1.产生2n+1个sigma点,在状态向量的附近,有点像粒子滤波。
2.利用状态转移矩阵,预测观测量的sigma点,并根据权重计算状态向量的均值和协方差矩阵。
3.利用测量矩阵得到sigma点的预测测量值。
4.根据sigma点和权重得到状态向量的预测值。
5.根据KF公式,将状态向量的预测值和观测值进行真值估计。
因此hdl的逻辑就很清晰地显示出来了,在获取到估计值后,便将状态向量的前10维,也就是pvq取出得到位姿的估计值,实现了定位的迭代。
Eigen::Vector3f pos() const {
return Eigen::Vector3f(ukf->mean[0], ukf->mean[1], ukf->mean[2]);
}
Eigen::Vector3f vel() const {
return Eigen::Vector3f(ukf->mean[3], ukf->mean[4], ukf->mean[5]);
}
Eigen::Quaternionf quat() const {
return Eigen::Quaternionf(ukf->mean[6], ukf->mean[7], ukf->mean[8], ukf->mean[9]).normalized();
}
Eigen::Matrix4f matrix() const {
Eigen::Matrix4f m = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
m.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = quat().toRotationMatrix();
m.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = pos();
return m;
}
二、源代码解析
主要参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wyang9x/article/details/112464644;
点云数据的预处理:
一般下面这几种情况需要进行点云滤波处理:
(1)点云数据密度不规则需要平滑
(2)因为遮挡等问题造成离群点需要去除
(3)大量数据需要下采样
(4)噪声数据需要去除
前文提到HDL采用的是ndt进行匹配的,单其实代码里是有GICP_OMP(广义迭代最近点)可选的
void initialize_params() {
// intialize scan matching method
double downsample_resolution = private_nh.param<double>("downsample_resolution", 0.1);
std::string ndt_neighbor_search_method = private_nh.param<std::string>("ndt_neighbor_search_method", "DIRECT7");
double ndt_resolution = private_nh.param<double>("ndt_resolution", 1.0);
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT>> voxelgrid(new pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT>());
voxelgrid->setLeafSize(downsample_resolution, downsample_resolution, downsample_resolution);
downsample_filter = voxelgrid;
//定义了ndt和glcp
pclomp::NormalDistributionsTransform<PointT, PointT>::Ptr ndt(new pclomp::NormalDistributionsTransform<PointT, PointT>());
pclomp::GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint<PointT, PointT>::Ptr gicp(new pclomp::GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint<PointT, PointT>());
//ndt参数与搜索方法。默认DIRECT7,作者说效果不好可以尝试改为DIRECT1.
ndt->setTransformationEpsilon(0.01);
ndt->setResolution(ndt_resolution);
if(ndt_neighbor_search_method == "DIRECT1") {
NODELET_INFO("search_method DIRECT1 is selected");
ndt->setNeighborhoodSearchMethod(pclomp::DIRECT1);
registration = ndt;
} else if(ndt_neighbor_search_method == "DIRECT7") {
NODELET_INFO("search_method DIRECT7 is selected");
ndt->setNeighborhoodSearchMethod(pclomp::DIRECT7);
registration = ndt;
} else if(ndt_neighbor_search_method == "GICP_OMP"){
//GICP_OMP 需要在启动文件中的配置参数中配置;
NODELET_INFO("search_method GICP_OMP is selected");
registration = gicp;
}
else {
if(ndt_neighbor_search_method == "KDTREE") {
NODELET_INFO("search_method KDTREE is selected");
} else {
NODELET_WARN("invalid search method was given");
NODELET_WARN("default method is selected (KDTREE)");
}
ndt->setNeighborhoodSearchMethod(pclomp::KDTREE);
registration = ndt;
}
// initialize pose estimator
//设置起点用。
if(private_nh.param<bool>("specify_init_pose", true)) {
NODELET_INFO("initialize pose estimator with specified parameters!!");
pose_estimator.reset(new hdl_localization::PoseEstimator(registration,
ros::Time::now(),
Eigen::Vector3f(private_nh.param<double>("init_pos_x", 0.0), private_nh.param<double>("init_pos_y", 0.0), private_nh.param<double>("init_pos_z", 0.0)),
Eigen::Quaternionf(private_nh.param<double>("init_ori_w", 1.0), private_nh.param<double>("init_ori_x", 0.0), private_nh.param<double>("init_ori_y", 0.0), private_nh.param<double>("init_ori_z", 0.0)),
private_nh.param<double>("cool_time_duration", 0.5)
));
}
}
launch文件的更改:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<launch>
<!-- arguments -->
<arg name="nodelet_manager" default="velodyne_nodelet_manager" />
<arg name="points_topic" default="/velodyne_points" />
<!-- input clouds are transformed in odom_child_frame, and then localization is performed in that frame -->
<!-- this is useful to match the LIDAR and IMU coodinate systems -->
<arg name="odom_child_frame_id" default="velodyne" />
<!-- optional arguments -->
<arg name="use_imu" default="false" />
<arg name="invert_imu_acc" default="false" />
<arg name="invert_imu_gyro" default="false" />
<arg name="use_global_localization" default="true" />
<arg name="imu_topic" default="/imu/data" />
<arg name="enable_robot_odometry_prediction" value="false" />
<arg name="robot_odom_frame_id" value="odom" />
<arg name="plot_estimation_errors" value="false" />
<include file="$(find hdl_global_localization)/launch/hdl_global_localization.launch" if="$(arg use_global_localization)" />
<!-- in case you use velodyne_driver, comment out the following line -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="$(arg nodelet_manager)" args="manager" output="screen"/>
<!-- globalmap_server_nodelet -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="globalmap_server_nodelet" args="load hdl_localization/GlobalmapServerNodelet $(arg nodelet_manager)">
<param name="globalmap_pcd" value="$(find hdl_localization)/data/map.pcd" />
<param name="convert_utm_to_local" value="true" />
<param name="downsample_resolution" value="0.1" />
</node>
<!-- hdl_localization_nodelet -->
<node pkg="nodelet" type="nodelet" name="hdl_localization_nodelet" args="load hdl_localization/HdlLocalizationNodelet $(arg nodelet_manager)">
<remap from="/velodyne_points" to="$(arg points_topic)" />
<remap from="/gpsimu_driver/imu_data" to="$(arg imu_topic)" />
<!-- odometry frame_id -->
<param name="odom_child_frame_id" value="$(arg odom_child_frame_id)" />
<!-- imu settings -->
<!-- during "cool_time", imu inputs are ignored -->
<param name="use_imu" value="$(arg use_imu)" />
<param name="invert_acc" value="$(arg invert_imu_acc)" />
<param name="invert_gyro" value="$(arg invert_imu_gyro)" />
<param name="cool_time_duration" value="2.0" />
<!-- robot odometry-based prediction -->
<param name="enable_robot_odometry_prediction" value="$(arg enable_robot_odometry_prediction)" />
<param name="robot_odom_frame_id" value="$(arg robot_odom_frame_id)" />
<!-- ndt settings -->
<!-- available reg_methods: NDT_OMP, NDT_CUDA_P2D, NDT_CUDA_D2D-->
<param name="reg_method" value="NDT_OMP" />
<!-- if NDT is slow for your PC, try DIRECT1 serach method, which is a bit unstable but extremely fast -->
<!--param name="ndt_neighbor_search_method" value="DIRECT1 " --/>
<param name="ndt_neighbor_search_method" value="GICP_OMP" />
<param name="ndt_neighbor_search_radius" value="2.0" />
<param name="ndt_resolution" value="1.0" />
<param name="downsample_resolution" value="0.1" />
<!-- if "specify_init_pose" is true, pose estimator will be initialized with the following params -->
<!-- otherwise, you need to input an initial pose with "2D Pose Estimate" on rviz" -->
<param name="specify_init_pose" value="true" />
<param name="init_pos_x" value="0.0" />
<param name="init_pos_y" value="0.0" />
<param name="init_pos_z" value="0.0" />
<param name="init_ori_w" value="1.0" />
<param name="init_ori_x" value="0.0" />
<param name="init_ori_y" value="0.0" />
<param name="init_ori_z" value="0.0" />
<param name="use_global_localization" value="$(arg use_global_localization)" />
</node>
<node pkg="hdl_localization" type="plot_status.py" name="plot_estimation_errors" if="$(arg plot_estimation_errors)" />
</launch>


























 1346
1346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








