极限定律
- 假设
a
a
a是一个常量以及有极限
lim x → a f ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) x→alimf(x) lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) x→alimg(x)
那么
1. lim x → a [ f ( x ) + g ( x ) ] = lim x → a f ( x ) + lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}[f(x) + g(x)] = \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) + \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) limx→a[f(x)+g(x)]=limx→af(x)+limx→ag(x)
2. lim x → a [ f ( x ) − g ( x ) ] = lim x → a f ( x ) − lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}[f(x) - g(x)] = \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) - \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) limx→a[f(x)−g(x)]=limx→af(x)−limx→ag(x)
3. lim x → a [ c f ( x ) ] = c lim x → a f ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}[cf(x)] = c\lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) limx→a[cf(x)]=climx→af(x)
4. lim x → a [ f ( x ) g ( x ) ] = lim x → a f ( x ) ⋅ lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}[f(x)g(x)] = \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) \cdot \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) limx→a[f(x)g(x)]=limx→af(x)⋅limx→ag(x)
5. lim x → a f ( x ) g ( x ) = lim x → a f ( x ) lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \frac{\lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x)}{\lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x)} limx→ag(x)f(x)=limx→ag(x)limx→af(x)
6. lim x → a [ f ( x ) ] n = [ lim x → a f ( x ) ] n \lim_{x \rightarrow a}[f(x)]^n = [\lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x)]^n limx→a[f(x)]n=[limx→af(x)]n
7. lim x → a c = c \lim_{x \rightarrow a}c = c limx→ac=c
8. lim x → a x = a \lim_{x \rightarrow a}x = a limx→ax=a
9. lim x → a x n = a n \lim_{x \rightarrow a}x^n = a^n limx→axn=an
10. lim x → a x n = a n \lim_{x \rightarrow a}\sqrt[n]{x} = \sqrt[n]{a} limx→anx=na
11. lim x → a f ( x ) n = lim x → a f ( x ) n \lim_{x \rightarrow a}\sqrt[n]{f(x)} = \sqrt[n]{\lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x)} limx→anf(x)=nlimx→af(x) - 例一
已知函数 f f f和 g g g的图像,计算下面方程的极限。
(a) lim x → − 2 [ f ( x ) + 5 g ( x ) ] \lim_{x \rightarrow -2}[f(x) + 5g(x)] limx→−2[f(x)+5g(x)]
(b) lim x → 1 [ f ( x ) g ( x ) ] \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}[f(x)g(x)] limx→1[f(x)g(x)]
(c) lim x → 2 f ( x ) g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow 2}\frac{f(x)}{g(x)} limx→2g(x)f(x)

- 例二
计算下列方程的极限
(a) lim x → 5 ( 2 x 2 − 3 x + 4 ) \lim_{x \rightarrow 5}(2x^2 - 3x + 4) limx→5(2x2−3x+4)
(b) lim x → − 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 − 1 5 − 3 x \lim_{x \rightarrow -2}\frac{x^3 + 2x^2 - 1}{5 - 3x} limx→−25−3xx3+2x2−1
直接带入性质
- 如果函数
f
f
f是一个多项式或有理函数,并且
a
a
a属于
f
f
f的定义域,那么
lim x → a f ( x ) = f ( a ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) = f(a) x→alimf(x)=f(a) - 例三
求 lim x → 1 x 2 − 1 x − 1 \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{x^2 - 1}{x - 1} limx→1x−1x2−1。
解:首先将分子分解为平方差
x 2 − 1 x − 1 = ( x + 1 ) ( x − 1 ) x − 1 \frac{x^2 - 1}{x - 1} = \frac{(x + 1)(x - 1)}{x - 1} x−1x2−1=x−1(x+1)(x−1)
根据极限的定义,我们知道 x x x趋于 1 1 1但 x ≠ 1 x \neq 1 x=1。因此可以消除公因数 x − 1 x - 1 x−1,再使用直接带入进行计算:
lim x → 1 x 2 − 1 x − 1 = ( x + 1 ) ( x − 1 ) x − 1 = lim x → 1 ( x + 1 ) = 1 + 1 = 2 \begin{aligned}\lim_{x \rightarrow 1}\frac{x^2 - 1}{x - 1} &= \frac{(x + 1)(x - 1)}{x - 1}\\ &= \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}(x + 1) \\ &= 1 + 1 = 2\end{aligned} x→1limx−1x2−1=x−1(x+1)(x−1)=x→1lim(x+1)=1+1=2 - 例四
已知方程,求 lim x → 1 g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}g(x) limx→1g(x)
g ( x ) = { x + 1 ( x ≠ 1 ) π ( x = 1 ) g(x) = \left\{ \begin{aligned} & x + 1 & (x \neq 1) \\ & \pi & (x = 1)\\ \end{aligned} \right. g(x)={x+1π(x=1)(x=1)
解:虽然 g ( 1 ) = π g(1) = \pi g(1)=π,但是极限的值并不依赖函数在 1 1 1处的值,极限的值是取 x x x趋于 1 1 1但 x ≠ 1 x \neq 1 x=1的值,因此
lim x → 1 g ( x ) = lim x → 1 ( x + 1 ) = 2 \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}g(x) = \lim_{x \rightarrow 1}(x + 1) = 2 x→1limg(x)=x→1lim(x+1)=2
定理
- 1.
lim
x
→
a
f
(
x
)
=
L
\lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) = L
limx→af(x)=L,当且仅当
lim
x
→
a
−
f
(
x
)
=
L
=
lim
x
→
a
+
f
(
x
)
\lim_{x \rightarrow a^-}f(x) = L = \lim_{x \rightarrow a^+}f(x)
limx→a−f(x)=L=limx→a+f(x)
2. 如果 f ( x ) ≤ g ( x ) f(x) \leq g(x) f(x)≤g(x),并且它们在 x x x趋于 a a a处的极限都存在,那么
lim x → a f ( x ) ≤ lim x → a g ( x ) \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) \leq \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) x→alimf(x)≤x→alimg(x)
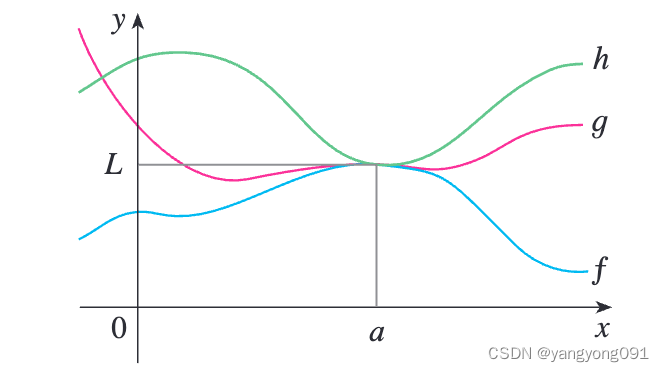
3. 如果 f ( x ) ≤ g ( x ) ≤ h ( x ) f(x) \leq g(x) \leq h(x) f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x),并且
lim x → a f ( x ) = lim x → a h ( x ) = L \lim_{x \rightarrow a}f(x) = \lim_{x \rightarrow a}h(x) = L x→alimf(x)=x→alimh(x)=L
那么
lim x → a g ( x ) = L \lim_{x \rightarrow a}g(x) = L x→alimg(x)=L
如图所示
- 举例
证明 lim x → 0 x 2 sin 1 x = 0 \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}x^2\sin\frac{1}{x} = 0 limx→0x2sinx1=0。
解:首先
− 1 ≤ sin 1 x ≤ 1 -1 \leq \sin\frac{1}{x} \leq 1 −1≤sinx1≤1
其次我们知道不等式两边同时乘以正数时,不等式关系依然成立。而 x 2 ≥ 0 x^2 \geq 0 x2≥0,所以两边同时乘以 x 2 x^2 x2,就有
− x 2 ≤ x 2 sin 1 x ≤ x 2 -x^2 \leq x^2\sin\frac{1}{x} \leq x^2 −x2≤x2sinx1≤x2
并且我们知道
lim x → 0 x 2 = 0 \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}x^2 = 0 x→0limx2=0
lim x → 0 − x 2 = 0 \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}-x^2 = 0 x→0lim−x2=0
所以,设 f ( x ) = − x 2 f(x) = -x^2 f(x)=−x2, g ( x ) = x 2 sin 1 x g(x) = x^2\sin\frac{1}{x} g(x)=x2sinx1和 h ( x ) = x 2 h(x) = x^2 h(x)=x2,根据定理3,可得
lim x → 0 x 2 sin 1 x = 0 \lim_{x \rightarrow 0}x^2\sin\frac{1}{x} = 0 x→0limx2sinx1=0
























 190
190

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








