一、新雀优化算法NOA求解带时间窗的车辆路径问题
1.1VRPTW模型如下:
带时间窗的车辆路径问题(Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows, VRPTW)
1.2新雀优化算法NOA求解VRPTW
close all
clear
clc
SearchAgents_no=30; % 种群大小
Function_name='F1';
Max_iteration=100; % 最大迭代次数
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);
[fMin,bestX,curve]=NOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); %算法求解
%% 显示最终结果
Pos=ShowResult(bestX);
%% 画图
figure
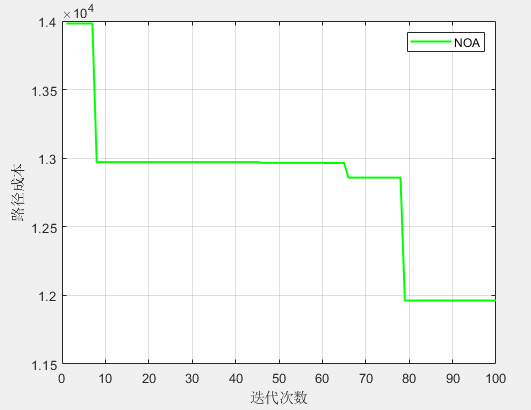
plot(curve,'Color','g','linewidth',1.5)%semilogy
xlabel('迭代次数');
ylabel('路径成本');
grid on
box on
legend('NOA')
%% 保存数据
save curve curve
save bestX bestX部分结果:

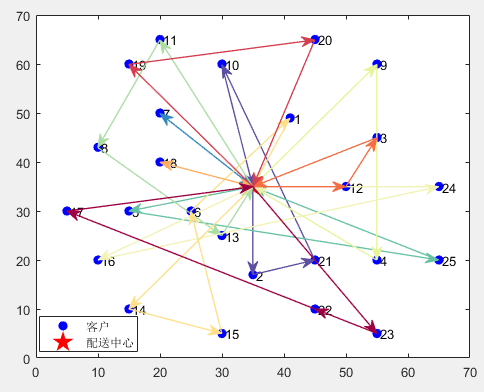
配送路线1:0->2->21->10->0 服务顾客数量:3 路径长度:96.65542 装载量:34
服务顾客2的起始时间:18.00000,结束时间:28.00000
服务顾客21的起始时间:38.44031,结束时间:48.44031
服务顾客10的起始时间:91.16033,结束时间:101.16033
抵达配送中心的时间:126.65542
配送路线2:0->7->0 服务顾客数量:1 路径长度:42.42641 装载量:5
服务顾客7的起始时间:21.21320,结束时间:31.21320
抵达配送中心的时间:52.42641
配送路线3:0->5->25->0 服务顾客数量:2 路径长度:105.14674 装载量:32
服务顾客5的起始时间:20.61553,结束时间:30.61553
服务顾客25的起始时间:81.60572,结束时间:91.60572
抵达配送中心的时间:125.14674
配送路线4:0->11->8->13->0 服务顾客数量:3 路径长度:95.79470 装载量:44
服务顾客11的起始时间:33.54102,结束时间:43.54102
服务顾客8的起始时间:67.70711,结束时间:77.70711
服务顾客13的起始时间:104.61436,结束时间:114.61436
抵达配送中心的时间:125.79470
配送路线5:0->9->4->0 服务顾客数量:2 路径长度:97.01562 装载量:35
服务顾客9的起始时间:32.01562,结束时间:42.01562
服务顾客4的起始时间:82.01562,结束时间:92.01562
抵达配送中心的时间:117.01562
配送路线6:0->16->24->0 服务顾客数量:2 路径长度:116.16353 装载量:22
服务顾客16的起始时间:29.15476,结束时间:39.15476
服务顾客24的起始时间:96.16353,结束时间:106.16353
抵达配送中心的时间:136.16353
配送路线7:0->14->15->6->1->0 服务顾客数量:4 路径长度:113.39314 装载量:41
服务顾客14的起始时间:32.01562,结束时间:42.01562
服务顾客15的起始时间:57.82701,结束时间:67.82701
服务顾客6的起始时间:93.32211,结束时间:103.32211
服务顾客1的起始时间:128.16159,结束时间:138.16159
抵达配送中心的时间:153.39314
配送路线8:0->18->0 服务顾客数量:1 路径长度:31.62278 装载量:12
服务顾客18的起始时间:15.81139,结束时间:25.81139
抵达配送中心的时间:41.62278
配送路线9:0->12->3->0 服务顾客数量:2 路径长度:48.54102 装载量:32
服务顾客12的起始时间:15.00000,结束时间:25.00000
服务顾客3的起始时间:36.18034,结束时间:46.18034
抵达配送中心的时间:68.54102
配送路线10:0->19->20->0 服务顾客数量:2 路径长度:94.05221 装载量:26
服务顾客19的起始时间:32.01562,结束时间:42.01562
服务顾客20的起始时间:72.42943,结束时间:82.42943
抵达配送中心的时间:114.05221
配送路线11:0->23->22->17->0 服务顾客数量:3 路径长度:122.37102 装载量:49
服务顾客23的起始时间:36.05551,结束时间:46.05551
服务顾客22的起始时间:57.23585,结束时间:67.23585
服务顾客17的起始时间:111.95721,结束时间:121.95721
抵达配送中心的时间:152.37102
配送路线总长度:963.18259


























 299
299

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








