系列文章目录
前言
本作业为旧版的深蓝学院高飞的路径规划课程作业,第二章。具体内容详见课程移动机器人运动规划-深蓝学院 - 专注人工智能与自动驾驶的学习平台
一、课程知识
c空间的概念,为了简化问题,将机器人抽象成一个质点对障碍物进行膨胀,膨胀的半径则为机器人半径

多种图,对应不同的算法,



不同的图都要涉及遍历的算法,广度和深度优先算法,不再赘述。
广度优先算法会一定得找到最优解,而深度优先第一次找到的解则不一定最优
Heuristic search

就是去猜!you guess!怎么走会离终点更近。是直线距离更近就会更近吗?不一定,这种贪心就是所述的倾向性,倾向于直线距离更近的,如果是无障碍任意行动的图是这样的。但是如果中间有障碍物呢?此时不一定了。如何去设计一个启发式函数,则是遍历的魅力。

更快!

更慢!
Dijkstra’s Algorithm 和 A star
如果是权重图呢?此时,先去遍历谁?
遍历周围邻居,再遍历最近点的邻居,在所有点中找到新的最近点,以确定下一步从哪点开始,循环往复。

从所有遍历的点中找到最近点是很慢的,故使用优先队列的容器,即最大(小)堆,底层是完全二叉树。
dijkstra算法也可以引入启发式函数,即最终的权重f(n) = 该步代价h(n) + 估计接下来的代价g(n),这就是A star算法。而普通珊格图 + 估计函数 = 权重图 以适应 Dij算法。
估计占比越大,倾向性越大
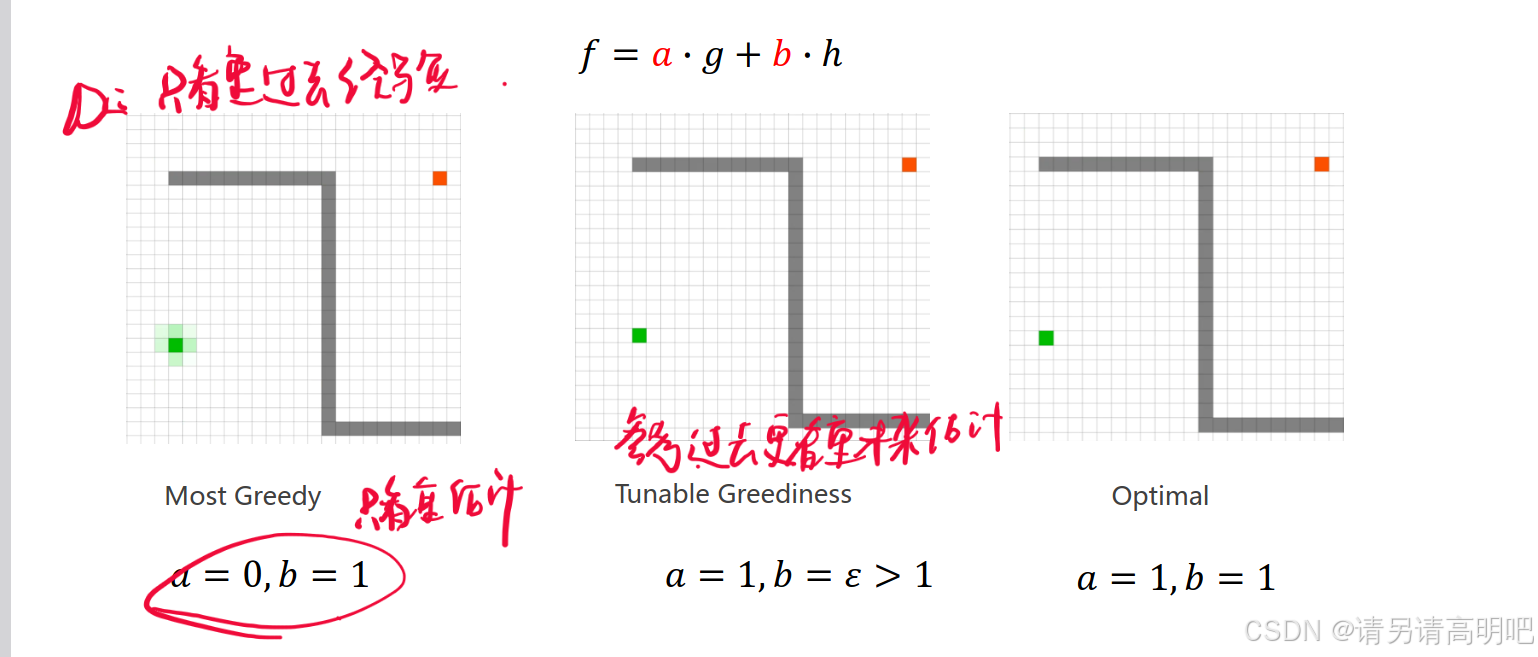
Engineering Considerations
什么是最好的估计?

越接近实际情况的估计就是最好的估计!
Tie Breaker
启发式就是为倾向性而生的,左右摇摆则会极大的影响它的性能,对称性的地图对于它就是灾难

因为出现很多相同的f的珊格,导致算法难以贪心的坚定的选择一条路。
我把它看作是启发式的微调,加剧了倾向性以遍历更少的点(如果人人平等那与bfs还有什么区别)
一般的:

或者:

倾向性的算法有一些问题,太过偏激,撞了墙才知道了拐

对于路径生成造成过大难度。
Jump Point Search
基于tie breaker 的方法,针对对称性的解决方法


个人看法,该方法的规则是我来到这一格那就只做这一格能做到的最好的事,优先水平,垂直,跳跃。只理解到这一步。
二、作业代码解析

节点属性头文件:

index和coord的关系,后者是x,y,z前者是一维存储方式
STEP 1: finish the AstarPathFinder::getHeu , which is the heuristic function
index和coord的关系,后者是x,y,z坐标,前者是整数x,y,z坐标存储方式
设计一个启发式函数,可以使用曼哈顿和欧式距离

解释其中的启发式距离:
step 3: Remove the node with lowest cost function from open set to closed set please write your code below
利用大小堆的优先级队列来将最小代价节点弹出遍历
while ( !openSet.empty() ){
/*
*
*
step 3: Remove the node with lowest cost function from open set to closed set
please write your code below
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
This part you should use the C++ STL: multimap, more details can be find in Homework description
*
*
*/
currentPtr = openSet.begin()->second;
openSet.erase(openSet.begin());
currentPtr->id = -1; //put current node in closed set
// if the current node is the goal
if( currentPtr->index == goalIdx ){
ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();
terminatePtr = currentPtr;
ROS_WARN("[A*]{sucess} Time in A* is %f ms, path cost if %f m", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() * 1000.0, currentPtr->gScore * resolution );
return;
}
//get the succetion
AstarGetSucc(currentPtr, neighborPtrSets, edgeCostSets);STEP 4: finish AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc
完成遍历邻居节点的函数

注意:其中为遍历为id 0,遍历加入openset id 1,遍历后加入closeset id -1
STEP 5: For all unexpanded neigbors "m" of node "n", please finish this for loop
其中,对26个邻居节点遍历根据id ,若为0则加入开集,若为1则判断权重是否最小,若为-1则条过
/*
*
*
STEP 5: For all unexpanded neigbors "m" of node "n", please finish this for loop
please write your code below
*
*/
for(int i = 0; i < (int)neighborPtrSets.size(); i++){
neighborPtr = neighborPtrSets[i];
/*
*
*
Judge if the neigbors have been expanded
please write your code below
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = -1 : unexpanded
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = 1 : expanded, equal to this node is in close set
*
*/
if(neighborPtr -> id == 0){ //discover a new node, which is not in the closed set and open set
/*
*
*
STEP 6: As for a new node, do what you need do ,and then put neighbor in open set and record it
please write your code below
*
*/
neighborPtr -> cameFrom = currentPtr;
neighborPtr -> gScore = currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr);
neighborPtr -> id = 1;
openSet.insert(make_pair(neighborPtr->fScore, neighborPtr));
}
else if(neighborPtr -> id == 1){ //this. node is in open set and need to judge if it needs to update, the "0" should be deleted when you are coding
/*
*
*
STEP 7: As for a node in open set, update it , maintain the openset ,and then put neighbor in open set and record it
please write your code below
*
*/
if(neighborPtr -> gScore > currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i]){
neighborPtr -> cameFrom = currentPtr;
neighborPtr -> gScore = currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr, endPtr);
}
}
else{//this node is in closed set 已经找到到该邻居节点的最优路径,可忽略
/*
*
please write your code below
*
*/
continue;
}
}
}
step 8:trace back from the curretnt nodePtr to get all nodes along the path please write your code below
确定最短路径,此时gridnode中的comefrom就派上了用场

参考:
1.【A*算法】c++ ros 深蓝学院 移动机器人运动规划第二章作业 编程思路 代码_深蓝学院移动机器人运动规划第二章代码-CSDN博客


























 1704
1704

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








