http://blog.csdn.net/zyh821351004/article/details/52421005
cartographer与karto的比较
1. 两者采取的都是图优化框架。 采取的优化库不一致, karto采取的是spa(karto_slam)或g2o(nav2d), cartographer采取的是google的ceres构建problem优化。 karto的前端与后端采取的是单线程进行,cartographer按paper说明,采取的是4线程后端优化,还在进一步确定。
2. 运动预测部分:tracker
karto利用的是odom进行初始位置的预测, cartographer部分利用imu构建预测模型,scanmatcher与odom(可选)构建观测模型,采取UKF进行运动预测, cartographer带有tracker的说法。
// Implementation of a Kalman filter. We follow the nomenclature from Thrun, S. et al., Probabilistic Robotics, 2006.
// Extended to handle non-additive noise/sensors inspired by Kraft, E., A // Quaternion-based Unscented Kalman Filter for Orientation Tracking.
3. scanMatcher 部分
3.1 karto 采取的的是real-time correlative scan matcher(三维窗口遍历寻优)的方式进行的。 采取的是双分辨率的低分辨率和高分辨率的两次搜索。
This is an implementation of the algorithm described in "Real-Time Correlative Scan Matching" by Olson. The correlative scan matching algorithm is exhaustively evaluating the scan matching search space. As described by the paper, the basic steps are: // 1) Evaluate the probability p(z|xi, m) over the entire 3D search window using the low-resolution table. // 2) Find the best voxel in the low-resolution 3D space that has not already been considered. Denote this value as Li. If Li < Hbest, terminate: Hbest is the best scan matching alignment. // 3) Evaluate the search volume inside voxel i using the high resolution table. Suppose the log-likelihood of this voxel is Hi. Note that Hi <= Li since the low-resolution map overestimates the log likelihoods. If Hi > Hbest, set Hbest = Hi. This can be made even faster by transforming the scan exactly once over some discretized range.
3.2 cartoGrapher也是采取的双搜索的方式进行的, 先用一次real-time correlative scan matcher(三维窗口遍历寻优),再构建优化等式,利用ceres优化求解。(栅格概率, T的偏差,R的偏差)
occupied_space_cost_functor_weight TranslationDeltaCostFunctor RotationDeltaCostFunctor
4. submap的说明
4.1 karto没有submap的概念,全部以keyScan的形式存储在sensorManager。 无地图缓存,但每次计算地图有计算消耗。
采取的是scan-map的匹配方式,每次keyScan进入主动的依据pose的距离窗口生成localMap进行匹配。 local 与 gloal的loop closure依据graph的结构和sensorManage顺序存储分配的ID信息,选择候选scans,生成localMap,进行匹配,依据score进一步确定闭环。
4.2 . cartographer采用了submap的概念, 依据一定数量的scan初始一个submap, 依据窗口大小, 插入newScan,更新submap. 有子图缓存,会占用内存。
// An individual submap, which has an initial position 'origin', keeps track of which laser fans where inserted into it, and sets the 'finished_probability_grid' to be used for loop closing once the map no longer changes.
// Submaps is a sequence of maps to which scans are matched and into which scans are inserted. // Except during initialization when only a single submap exists, there are // always two submaps into which scans are inserted: an old submap that is used // for matching, and a new one, which will be used for matching next, that is // being initialized. // // Once a certain number of scans have been inserted, the new submap is // considered initialized: the old submap is no longer changed, the "new" submap // is now the "old" submap and is used for scan-to-map matching. Moreover, // a "new" submap gets inserted.
5. loopCheck
5.1 karto grapher主要依据pose 和 distance信息创建localMap,scanMatcher(real-time correlative scan matcher)确定。
1) 依据当前的Vertex, 从Graph中找到与之相邻的所有vertex(一定距离范围内). 2) 采取广度优先搜索的方式,将相邻(next)与相连(adjacentVertices)添加进nearLinkedScans. 3) 从sensorManager中取从前到后,依据id序号挑选与当前在一定距离范围内,且不在nearLinkedScans中的candidateScans, 当数量达到一定size,返回。 4)loopScanMatcher进行scanTomap的匹配,当匹配response 和covariance达到一定要求认为闭环检测到。得到调整的correct pose. 5)Add link to loop : 调整边(全局闭环) 6) 触发correctPose: spa优化
5.2 cartogapher 类似((real-time correlative scan matcher)),引入了branch and bound的方式, 加快了闭环的查找。
依据多分辨率多层的树型结构,单枝生长的方式(branch),及时剪枝操作(bound),深度优先搜索确定闭环。 (Intra-submap Inter-submap )
添加相应的闭环约束。构建优化问题,利用ceres优化。
// Current optimization problem.
sparse_pose_graph::OptimizationProblem optimization_problem_; sparse_pose_graph::ConstraintBuilder constraint_builder_ GUARDED_BY(mutex_);
// This is an implementation of the algorithm described in "Real-Time Correlative Scan Matching" by Olson.
// It is similar to the RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher but has a different trade-off: Scan matching is faster because more effort is put into the
// precomputation done for a given map. However, this map is immutable after construction.
[原文:http://blog.csdn.NET/zyh821351004/article/details/52421005 ]
demo_video:
cartographer 3d http://v.qq.com/x/page/n0334yt1tt1.html
cartographer 2d http://v.qq.com/x/page/z03346p134v.html
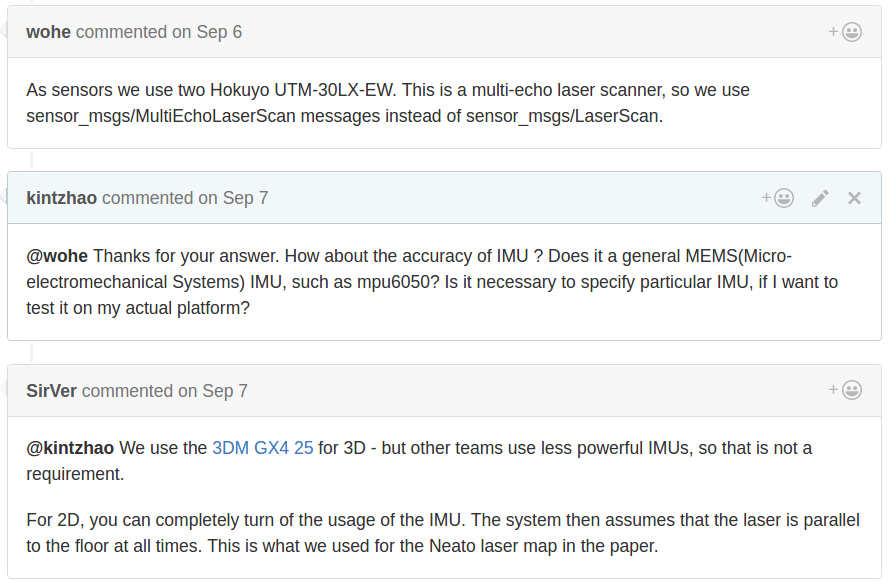
https://github.com/googlecartographer/cartographer_ros/issues/41 sensor: two Hokuyo UTM-30LX-EW + 3DM GX4 25
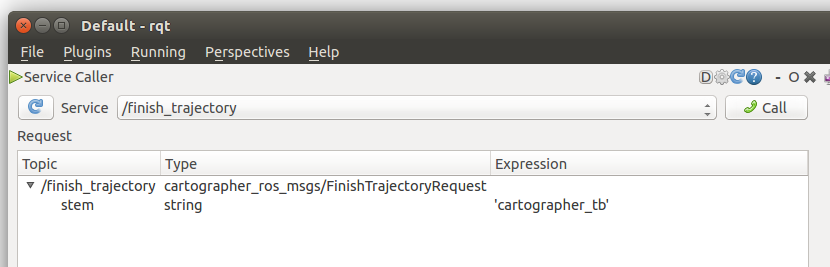
地图保存接口(srv): 保存位置:~/.ros/cartographer_tb.pgm
rosservice call /finish_trajectory "stem: 'cartographer_tb'"

最早调试遇到的bug,issue贴的图片。























 2266
2266

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








