
摘要
本文介绍了基于Autoware平台的路径规划系统,使用MATLAB/Simulink实现了自动驾驶车辆的路径规划算法。该系统集成了激光雷达传感器、车道检测和路径规划模块,为自动驾驶技术提供了一个灵活的开发和仿真环境。通过结合Autoware和MATLAB/Simulink,能够模拟和验证不同环境下自动驾驶车辆的路径规划性能。
理论
自动驾驶的路径规划是自动驾驶技术的关键组件,涉及到车辆如何从起点导航至终点,并避开可能的障碍物。路径规划通常分为三类:
-
全局路径规划:生成从起点到终点的理想路径,通常基于地图数据(例如HD地图)。
-
局部路径规划:根据传感器信息(例如激光雷达或相机),调整全局路径,避开动态或静态障碍物。
-
路径跟踪:控制器通过调整车辆的速度和方向,使其跟随规划的路径,通常采用纯跟踪算法(Pure Pursuit)或模型预测控制(MPC)。
在本示例中,Autoware作为自动驾驶软件栈,提供了路径规划的基础,而MATLAB/Simulink则用于实现和仿真路径跟踪算法。
-
Autoware模块:集成了激光雷达传感器(如Velodyne)、SLAM定位、路径规划与控制等功能,允许自动驾驶车辆在复杂的环境中自适应行驶。
-
MATLAB/Simulink实现:Simulink中的路径跟踪控制模块采用纯跟踪算法,通过接收Autoware生成的轨迹点,实时调整车辆的转向和速度。
实验结果
实验在虚拟环境中使用Autoware平台进行了模拟,结合MATLAB/Simulink对路径跟踪控制算法进行了验证。实验展示了车辆在复杂道路条件下的路径跟踪效果。如下图所示,自动驾驶车辆在仿真环境中沿着规划好的路径平稳行驶,且能够应对动态障碍物。
实验环境:
-
Autoware版本:1.14.0
-
Matlab版本:R2023a
-
控制算法:纯跟踪(Pure Pursuit)
实验结果显示,通过结合Autoware路径规划和MATLAB/Simulink的控制算法,能够实现精准的路径跟踪,且在面对复杂路况时具备良好的稳定性和适应性。
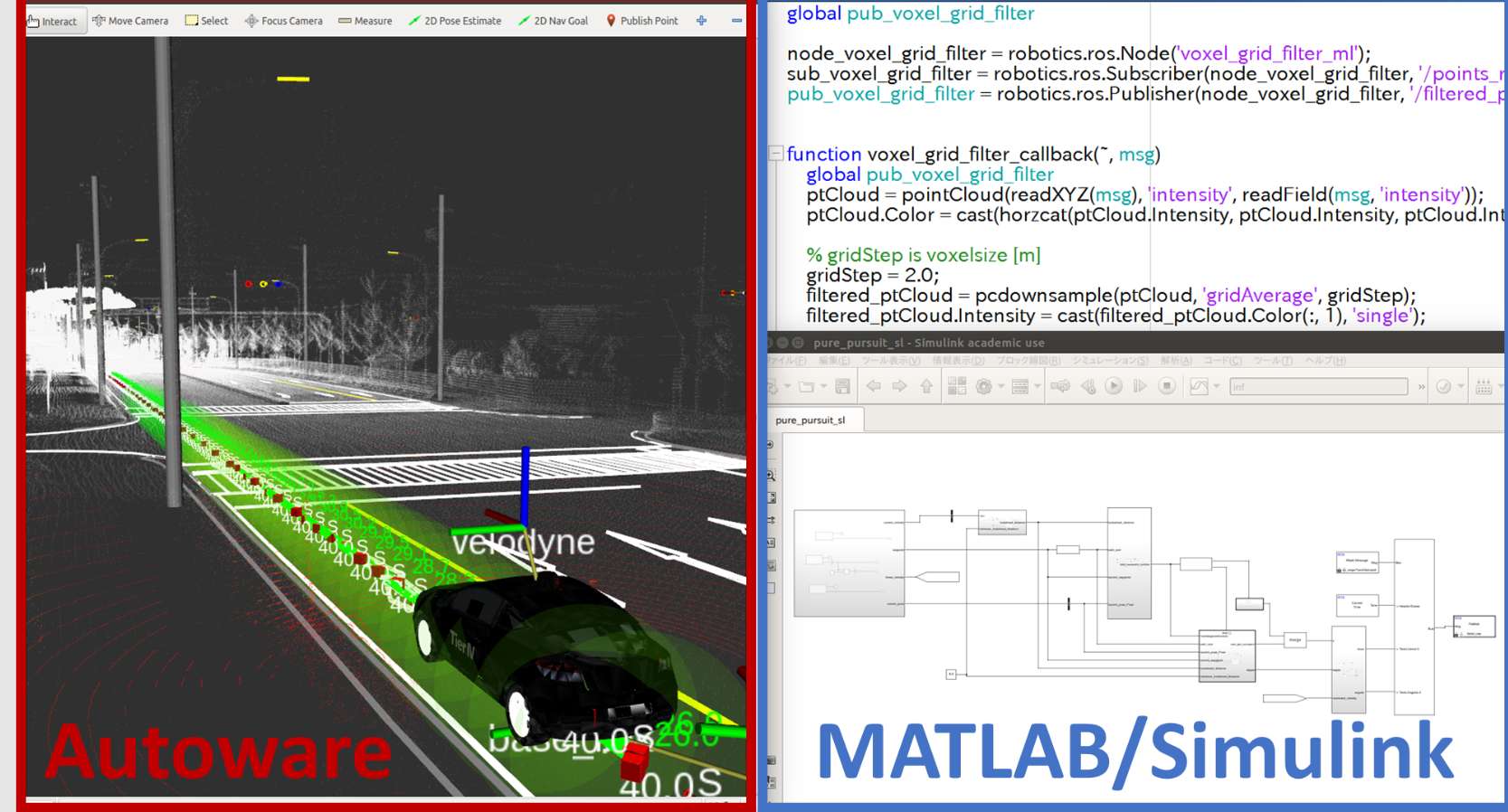
部分代码
以下是用于纯跟踪算法的MATLAB代码示例:
% Pure Pursuit Path Following Algorithm
% Vehicle parameters
L = 2.5; % Wheelbase [m]
max_steering_angle = pi/4; % Max steering angle [rad]
velocity = 10; % Constant velocity [m/s]
% Waypoints (generated from Autoware)
waypoints = [0, 0; 10, 10; 20, 5; 30, -10]; % Example waypoints
% Initialize position
position = [0, 0];
orientation = 0; % Initial orientation [rad]
% Time parameters
T = 0:0.1:20; % Time vector
% Preallocation for results
trajectory = zeros(length(T), 2); % Store position over time
% Loop through each time step
for i = 1:length(T)
% Compute the nearest waypoint
distances = sqrt(sum((waypoints - position).^2, 2));
[~, nearest_idx] = min(distances);
% Get the target waypoint
target_wp = waypoints(nearest_idx, :);
% Compute the desired steering angle using pure pursuit
alpha = atan2(target_wp(2) - position(2), target_wp(1) - position(1)) - orientation;
steering_angle = atan(2 * L * sin(alpha) / distances(nearest_idx));
% Limit steering angle
steering_angle = max(min(steering_angle, max_steering_angle), -max_steering_angle);
% Update orientation and position
orientation = orientation + velocity * tan(steering_angle) / L * 0.1; % Update orientation
position = position + velocity * [cos(orientation), sin(orientation)] * 0.1; % Update position
% Store the current position
trajectory(i, :) = position;
end
% Plot the results
figure;
plot(waypoints(:,1), waypoints(:,2), 'rx', 'MarkerSize', 10); % Waypoints
hold on;
plot(trajectory(:,1), trajectory(:,2), 'b-', 'LineWidth', 2); % Vehicle path
xlabel('X [m]');
ylabel('Y [m]');
title('Pure Pursuit Path Following');
legend('Waypoints', 'Vehicle Path');
grid on;
参考文献
❝
Kato, S., & Nishimura, T. (2015). Autoware: An open autonomous driving platform. Journal of Robotics and Mechatronics, 27(5), 1-6.
Thrun, S., Burgard, W., & Fox, D. (2005). Probabilistic Robotics. MIT Press.
Coulter, R. C. (1992). Implementation of the Pure Pursuit Path Tracking Algorithm. Carnegie Mellon University, Technical Report CMU-RI-TR-92-01.
(文章内容仅供参考,具体效果以图片为准)





















 1333
1333

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








