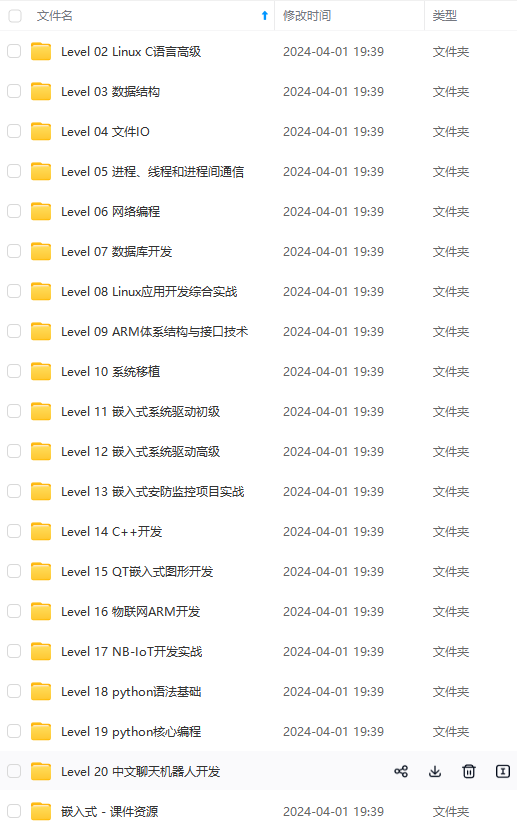
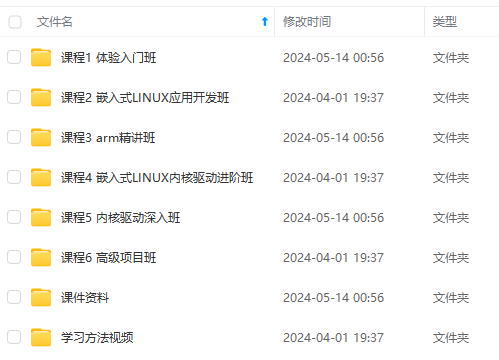
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上物联网嵌入式知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、电子书籍、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
需要这些体系化资料的朋友,可以加我V获取:vip1024c (备注嵌入式)
delta = 5;
[vertices, edges, path] = rrt(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p);
path_smooth = smooth(map, path, vertices, delta);
imshow(int32(1 - map), []);
title('RRT (Rapidly-Exploring Random Trees) - Smooth');
% imagesc(1 - map);
% colormap(gray);
hold on;
[edgesRowCount, ~] = size(edges);
for ii = 1 : edgesRowCount
plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(edges(ii, 1), 1), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 1)], ...
[vertices(edges(ii, 1), 2), vertices(edges(ii, 2), 2)], ...
'b', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
plot(q_start(1), q_start(2), 'g*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot(q_goal(1), q_goal(2), 'r*', 'linewidth', 1);
[~, pathCount] = size(path);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path(ii), 1), vertices(path(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path(ii), 2), vertices(path(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'r', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
[~, pathCount] = size(path_smooth);
for ii = 1 : pathCount - 1
%plot(vertices(ii, 1), vertices(ii, 2), 'cyan*', 'linewidth', 1);
plot([vertices(path_smooth(ii), 1), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 1)], ...
[vertices(path_smooth(ii), 2), vertices(path_smooth(ii + 1), 2)], ...
'black', 'LineWidth', 2);
end
//rrt.m
function [vertices, edges, path] = rrt(map, q_start, q_goal, k, delta_q, p)
%Algorithm to build a tree to solve map
% that goes from the start position till the goal position and to generate a path that connects
% both vertices
%
% map: matrix that you can obtain loading the mat files.
%
% q_start: coordinates x and y of the start position. You can find the coordinates below the figures
% of the environmentin the previous page.
%
% q_goal: coordinates x and y of the goal position. You can find the coordinates below the figures
% of the environment in the previous page.
%
% k: maximum number of samples that will be considered to generate the tree, if the goal is not
% found before.
%
% delta_q: distance between q_new and q_near.
%
% p: probability (between 0 and 1) of choosing q_goal as q_random.
%
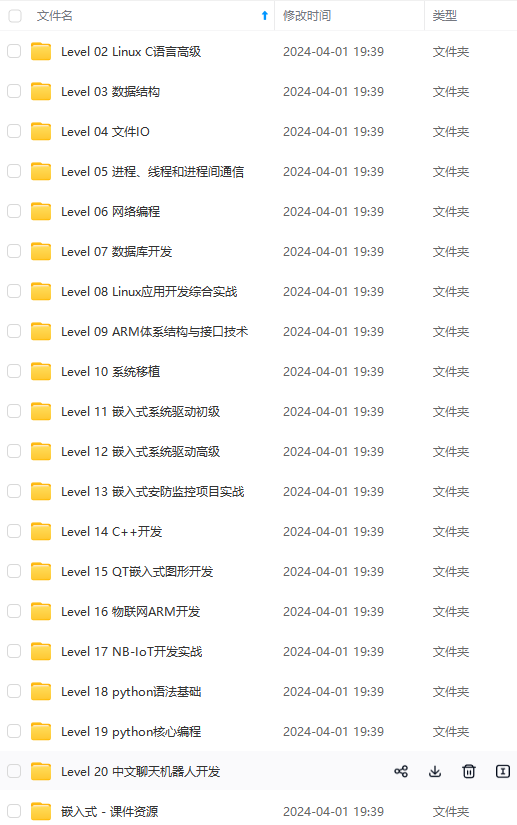
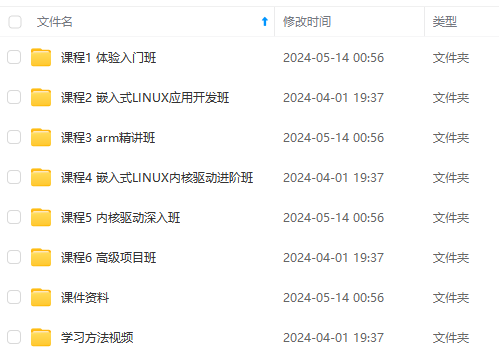
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上物联网嵌入式知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、电子书籍、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
需要这些体系化资料的朋友,可以加我V获取:vip1024c (备注嵌入式)
友,可以加我V获取:vip1024c (备注嵌入式)**






















 1037
1037

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








