Author
Shaoqing Ren, Kaiming He, Ross Girshick, and Jian Sun

Shaoqing Ren
Abstract
In this work , it introduces a Region Proposal Network(RPN) that shares full-image convolutional features with the detection net work, thus enabling nearly cost-free region proposals.An RPN is a fully convolutional network that simultaneously predicts object bounds and objectness scores at each position. The RPN is trained end-to-end to generate high-quality region proposals, which are used by Fast R CNN for detection. We further merge RPN and Fast RCNN into a single net work by sharing their convolutional features, the RPN component tells the unified network where to look.
1 Introduction
Now, proposals are the test-time computational bottleneck in state-of-the-art detection systems.
The RPN is thus a kind of fully convolutional network and can be trained end to end specifically for the task for generating detection proposals.
RPNs are designed to efficiently predict region proposals with a wide range of scales and aspect rations.
our scheme can be thought of as pyramid of regression referrences, which avoids enumerating images or filters of multipe scales or aspect ratios.
To unify RPNs with Fast R-CNN object detection neet works, we propose a training scheme that alternates between fine-tuning for the region proposal task and then fine-tuning for object detection, while keeping the proposals fixed.
The frameworks of RPN and Faster Rcnn have been adopted and generalized to other methods, such as 3D object detection, part-based detction,instance segmentation and image captioning.
#fcn
J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell, “Fully convolutional
networks for semantic segmentation,” in IEEE Conference on
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015.
#3D object detection
S. Song and J. Xiao, “Deep sliding shapes for amodal 3d object
detection in rgb-d images,” arXiv:1511.02300, 2015.2 related work
2.1 object proposals
J. Hosang, R. Benenson, and B. Schiele, “How good are detection
proposals, really?” in British Machine Vision Conference
(BMVC), 2014.
J. Hosang, R. Benenson, P. Doll´ar, and B. Schiele, “What makes
for effective detection proposals?” IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2015.
N. Chavali, H. Agrawal, A. Mahendru, and D. Batra,
“Object-Proposal Evaluation Protocol is ’Gameable’,” arXiv:
1505.05836, 2015.deep networks for object detection
Multibox does not share features between the proposal and detection networks. concurrent with our work, the deepmask method is developed for learning segmentation proposal.
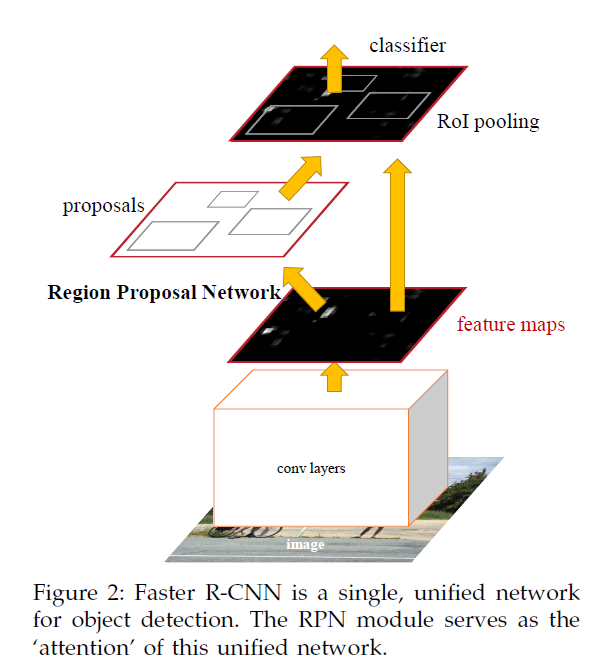
3 Faster r-cnn
faster r-cnn=RPN+detector=fast r-cnn + rpn
3.1 RPN
RPN takes an image of any size as input and outputs a set of rectangular object proposals, each with an objectness score.
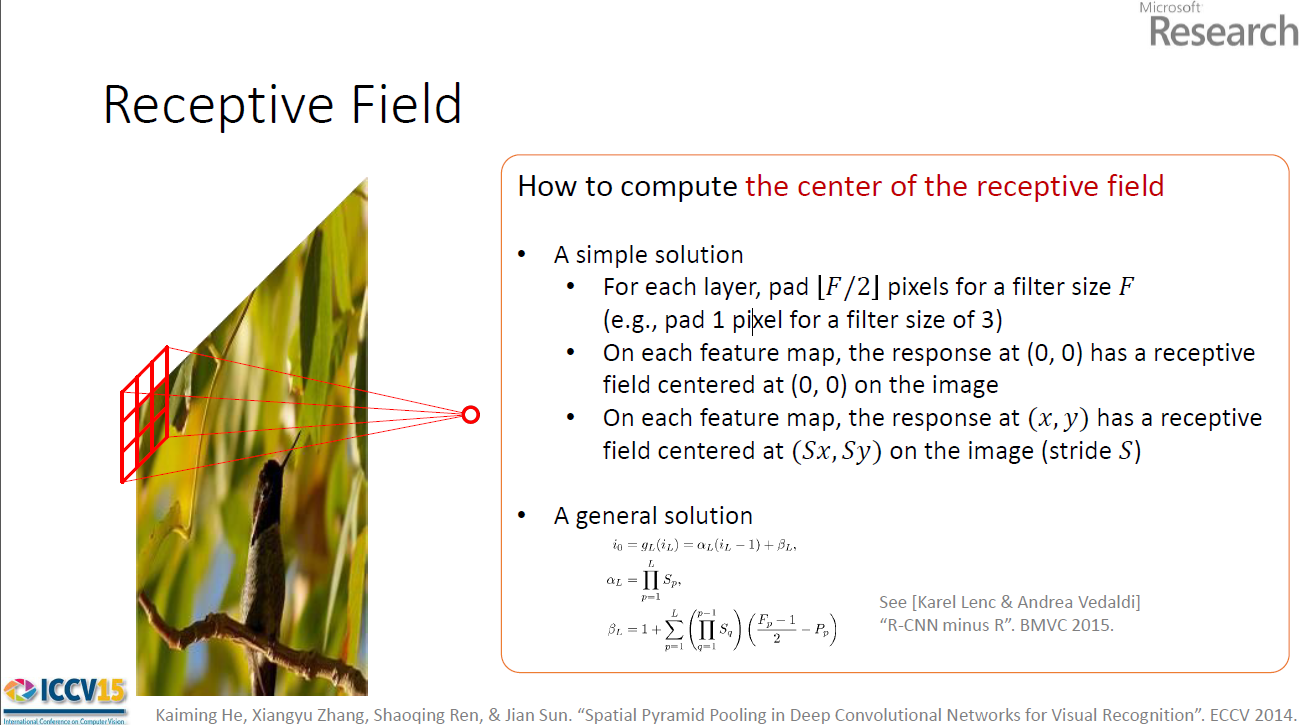
To generate region proposals , we slide a small network over the convolutional feture map , this small network takes as input an nxn (3x3 here, but the receptive field is large171 or 228) spatial window of the input convolutional feature map.
Each sliding window is mapped to a lower-dimmensional feature. then is fed into two sibling fullyconnected layer.
Note that because the mini-network operates in a sliding-windo fashion, the fully-connected layers are shared across all spatial locations.
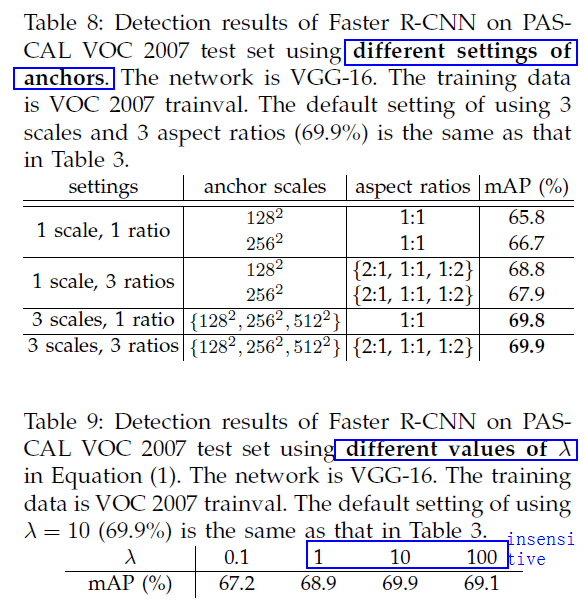
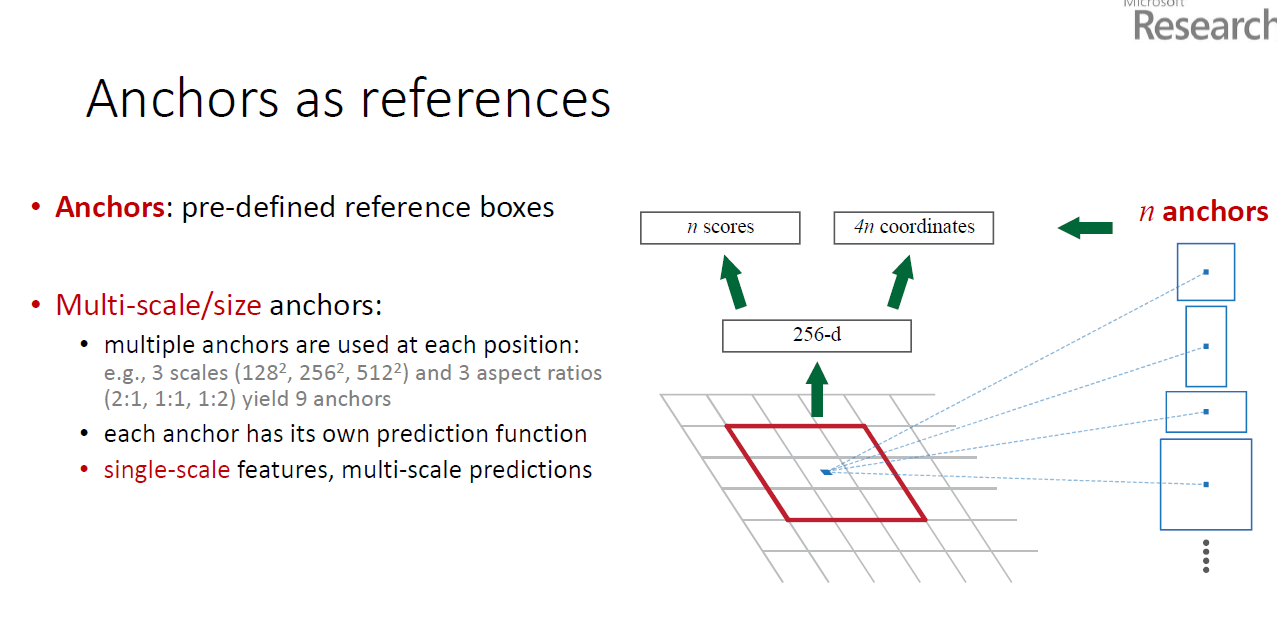
3.1.1 Anchors
At each sliding-window location, we simulataneously predict multiple region proposals,
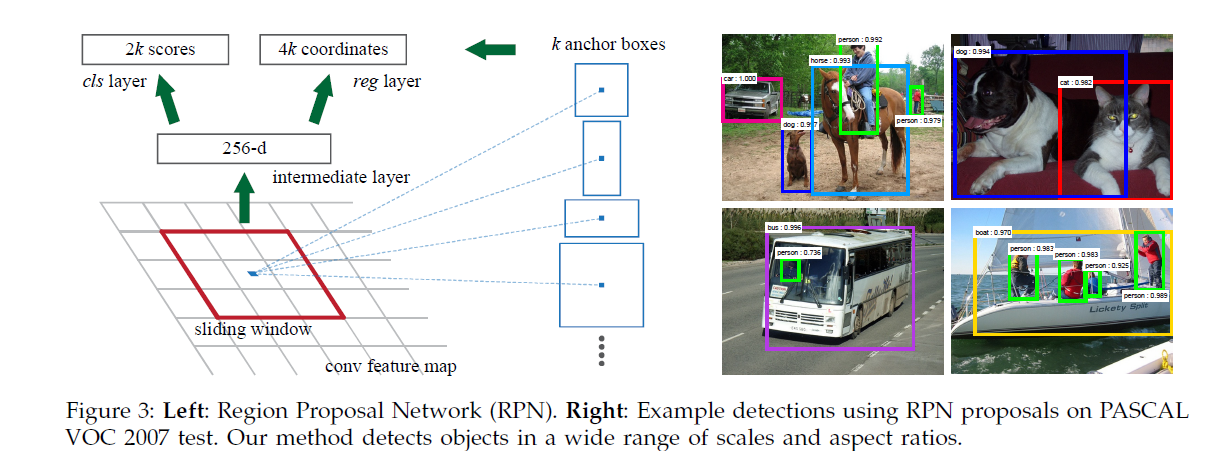
An anchor is centered at the sliding window, and is associated with a scale and apect ratio(fig.3 left).
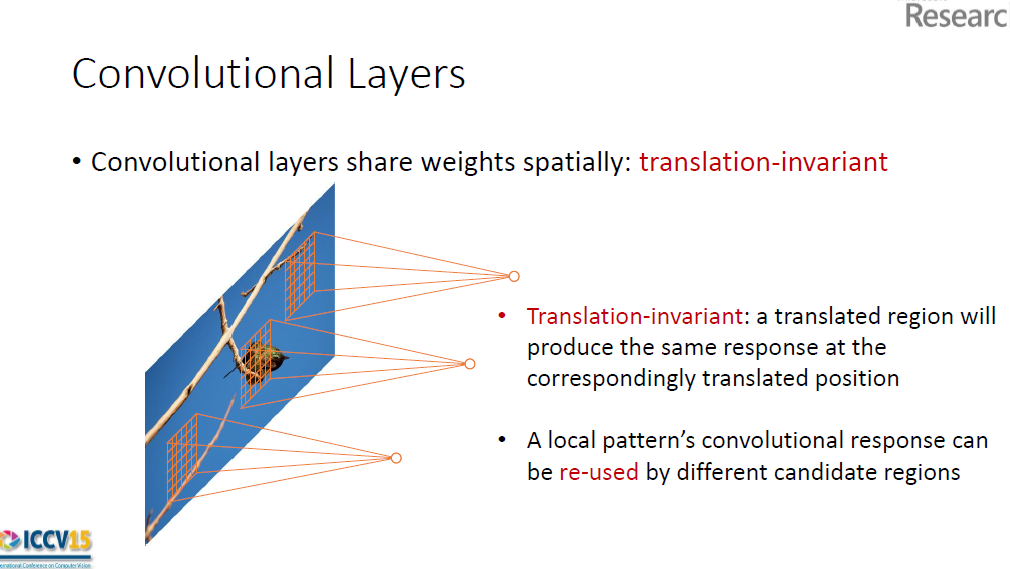
3.1.1.1 Translation-invariant anchors
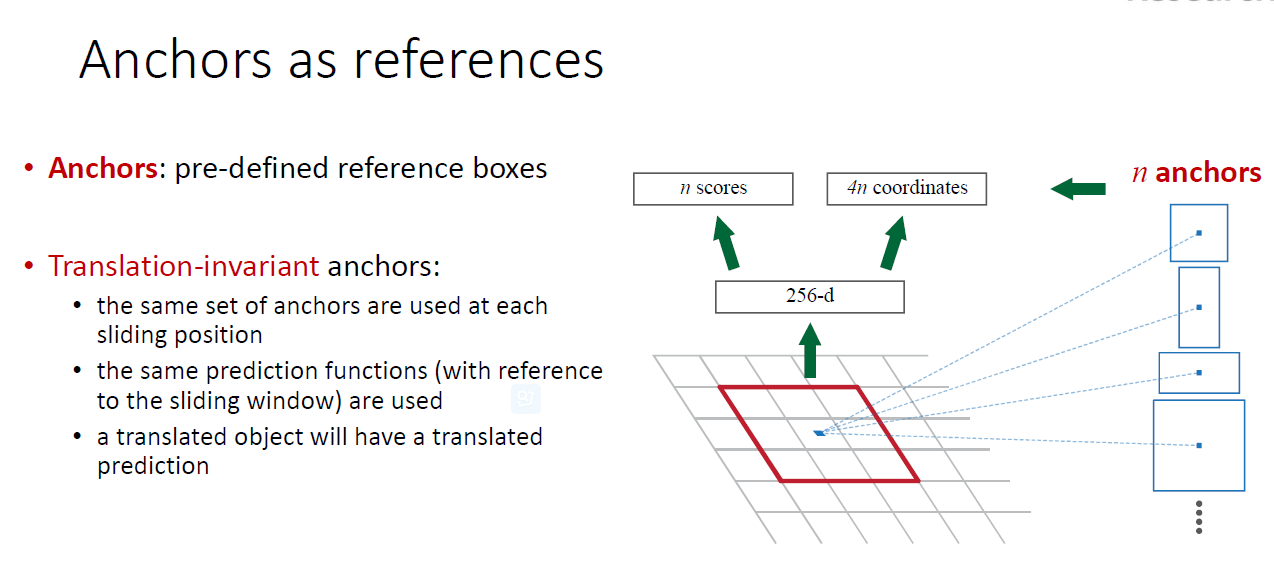
3.1.1.2 Multi-scale Anchors as Regression Refrence
3.1.2 Loss Function
For training RPNs, we assign a binary class label (of being an object or not )to each ancher. we assign a positive label to two kinds of anchors:
1. the achor with the highest IoU overlop with a groound-truth box
2. IoU >0.7
negative label <0.3 IoU
loss function:
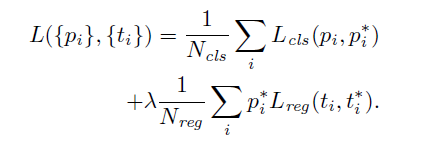
i is the index of an ancor
two terms are normalized by Ncls and Nreg, and weight by a balancing parameter
λ
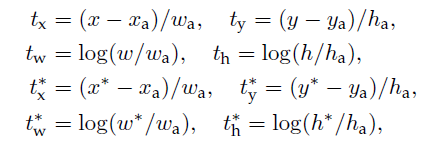
bounding-box regression is performed on features pooled from arbitrarily size RoIs, and the regression weights are shared by all region sizes,. In our formulation, the features used for regression are of the same spatial size(3x3) on the feature maps. To account for varying sizes, a set f k boundign box regressors are learned . each regressor is responsible forone sacle and one aspect ration, and the k regressors do not share weights.
As such , it is still possible to predict boxes of various sizes even though the features are of a fixed size scale, thanks to the design of anchors.
3.1.3 Training RPNs
We randomly sample 256 anchors in an image to compute the loss function of a mini-batch, where the sampled positive and negative anchors anchors have a ratio of up to 1:1.
initialize new layer mean 0, standard deviation 0.01 Gaussian distribution.
3.2 Sharing Features for RPN and Fast R-cnn
Three ways for training network with features share:
1. alternating training

2. approximate joint training
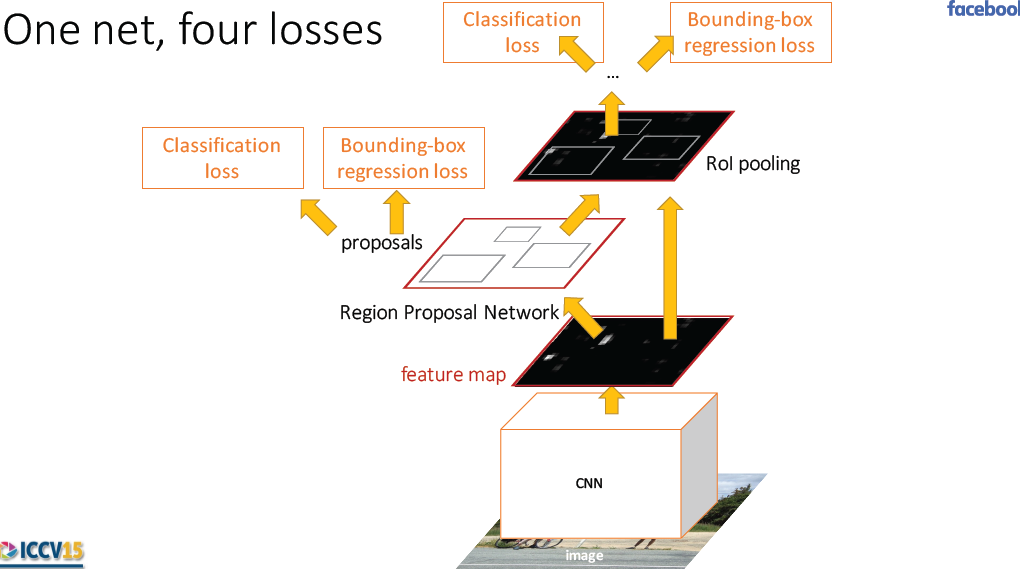
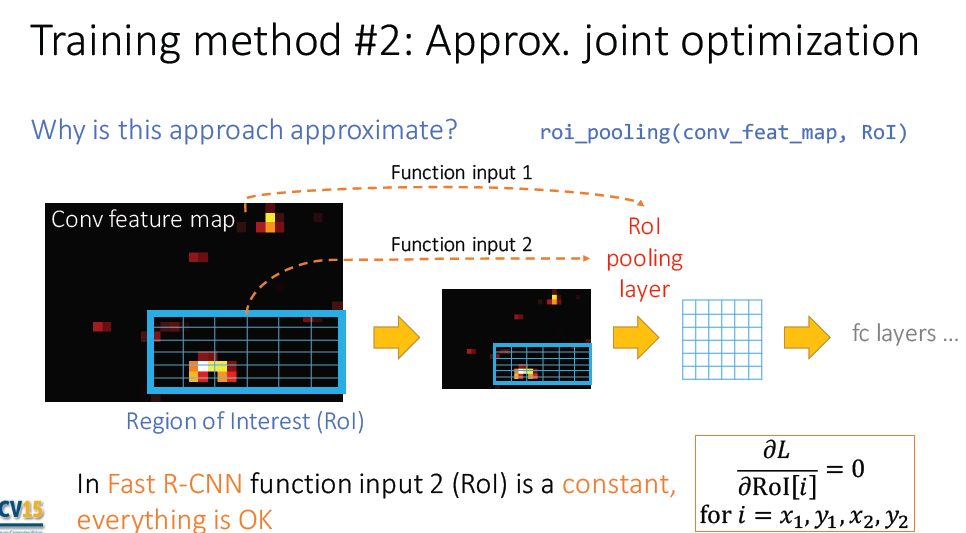
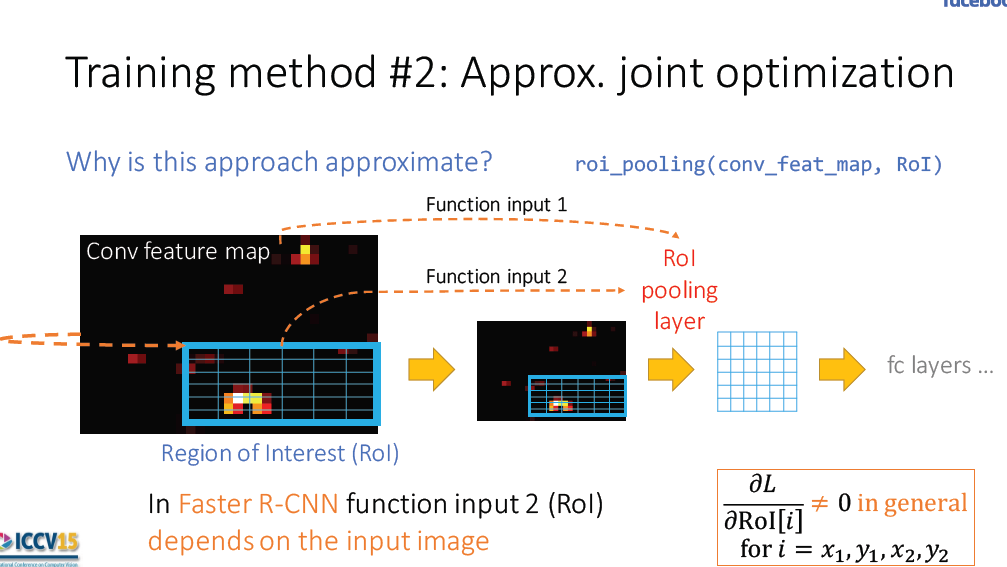
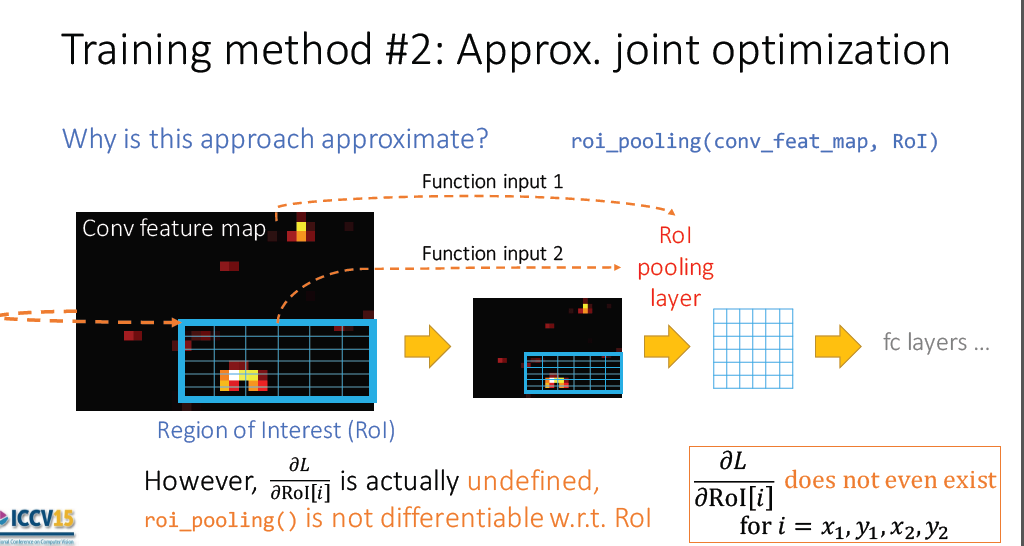

3. Non-approximate jiont training
J. Dai, K. He, and J. Sun, “Instance-aware semantic segmentation
via multi-task network cascades,” arXiv:1512.04412, 20153.3 Implementation Details
Some RPN proposals highly overlap with each other. To reduce redundancy , we adopt non-maximun suppression on the proposal regions based on their cls scores.We fix the IoU threshold for NMS at 0.7 , which leaves us about 2000 proposal regions per image. as we will show, NMS does not harm the ultimate detection accuracy , but substantially reduces the number of proposals. We train fast r-cnn using 2000 rpn proposals ,but evaluate different numbers of proposals at test time.
4 Experiments

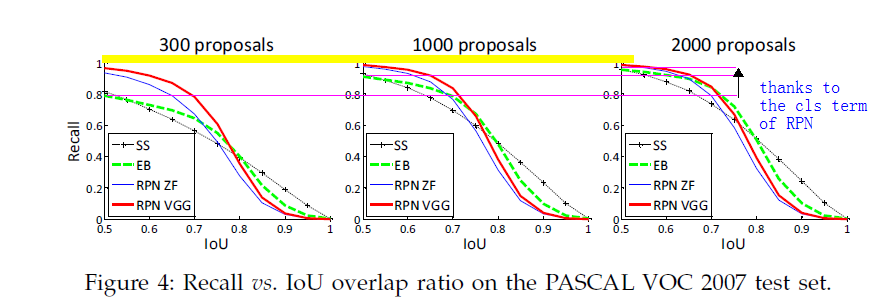
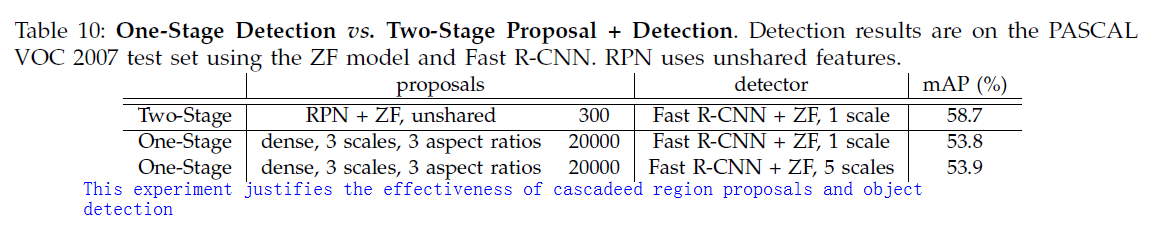
One stage detection vs.Two stage proposal + detection























 2151
2151

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








