1.Agents for self-driving laboratories applied to quantum computing
Authors: Shuxiang Cao, Zijian Zhang, Mohammed Alghadeer, Simone D Fasciati, Michele Piscitelli, Mustafa Bakr, Peter Leek, Alán Aspuru-Guzik
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.07978
论文摘要
Fully automated self-driving laboratories are promising to enable high-throughput and large-scale scientific discovery by reducing repetitive labor. However, effective automation requires deep integration of laboratory knowledge, which is often unstructured, multimodal, and difficult to incorporate into current AI systems. This paper introduces the \textit{k-agents} framework, designed to support experimentalists in organizing laboratory knowledge and automating experiments with agents. Our framework employs large language model-based agents to encapsulate laboratory knowledge, including available laboratory operations and methods for analyzing experiment results. To automate experiments, we introduce execution agents that break multi-step experimental procedures into state machines, interact with other agents to execute each step, and analyze the experiment results. The analyzed results are then utilized to drive state transitions, enabling closed-loop feedback control. To demonstrate its capabilities, we applied the agents to calibrate and operate a superconducting quantum processor, where they autonomously planned and executed experiments for hours, successfully producing and characterizing entangled quantum states at the level achieved by human scientists. Our knowledge-based agent system opens up new possibilities for managing laboratory knowledge and accelerating scientific discovery.
论文简评
这篇关于使用大型语言模型为基础的智能体自动化实验室实验的论文非常出色。它介绍了k-代理框架,该框架利用大规模语言模型来自动执行复杂的实验室工作流。这种创新的应用不仅与快速发展的人工智能领域密切相关,而且对实际应用具有重要意义,特别是在量子计算领域。此外,论文通过详细描述框架及其组件,为未来实验室自动化的发展奠定了坚实的基础。总之,这篇论文不仅展示了其技术潜力,也提供了宝贵的经验教训,对于推动科学研究的进步具有深远的影响。

2.Proactive Agents for Multi-Turn Text-to-Image Generation Under Uncertainty
Authors: Meera Hahn, Wenjun Zeng, Nithish Kannen, Rich Galt, Kartikeya Badola, Been Kim, Zi Wang
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.06771
论文摘要
User prompts for generative AI models are often underspecified, leading to sub-optimal responses. This problem is particularly evident in text-to-image (T2I) generation, where users commonly struggle to articulate their precise intent. This disconnect between the user’s vision and the model’s interpretation often forces users to painstakingly and repeatedly refine their prompts. To address this, we propose a design for proactive T2I agents equipped with an interface to (1) actively ask clarification questions when uncertain, and (2) present their understanding of user intent as an understandable belief graph that a user can edit. We build simple prototypes for such agents and verify their effectiveness through both human studies and automated evaluation. We observed that at least 90% of human subjects found these agents and their belief graphs helpful for their T2I workflow. Moreover, we develop a scalable automated evaluation approach using two agents, one with a ground truth image and the other tries to ask as few questions as possible to align with the ground truth. On DesignBench, a benchmark we created for artists and designers, the COCO dataset (Lin et al., 2014), and ImageInWords (Garg et al., 2024), we observed that these T2I agents were able to ask informative questions and elicit crucial information to achieve successful alignment with at least 2 times higher VQAScore(Linet al., 2024) than thestandardsingle-turn T2I generation. Demo: https://github.com/google-deepmind/proactive_t2i_agents.
论文简评
该篇论文旨在提出一种主动文本到图像(T2I)生成方法,以更好地表达和细化用户意图,并通过清晰的问题澄清和信念图与用户互动。作者通过人类研究和自动评估验证了他们方法的有效性,提高了用户体验和图像质量。此外,他们还创建了一个专门针对T2I任务的新基准数据集(DesignBench),为未来的研究提供了有价值的资源。综上所述,该文在解决文本到图像生成中遇到的主要问题方面提出了创新的概念,并且其有效性得到了充分证明,值得进一步深入研究。

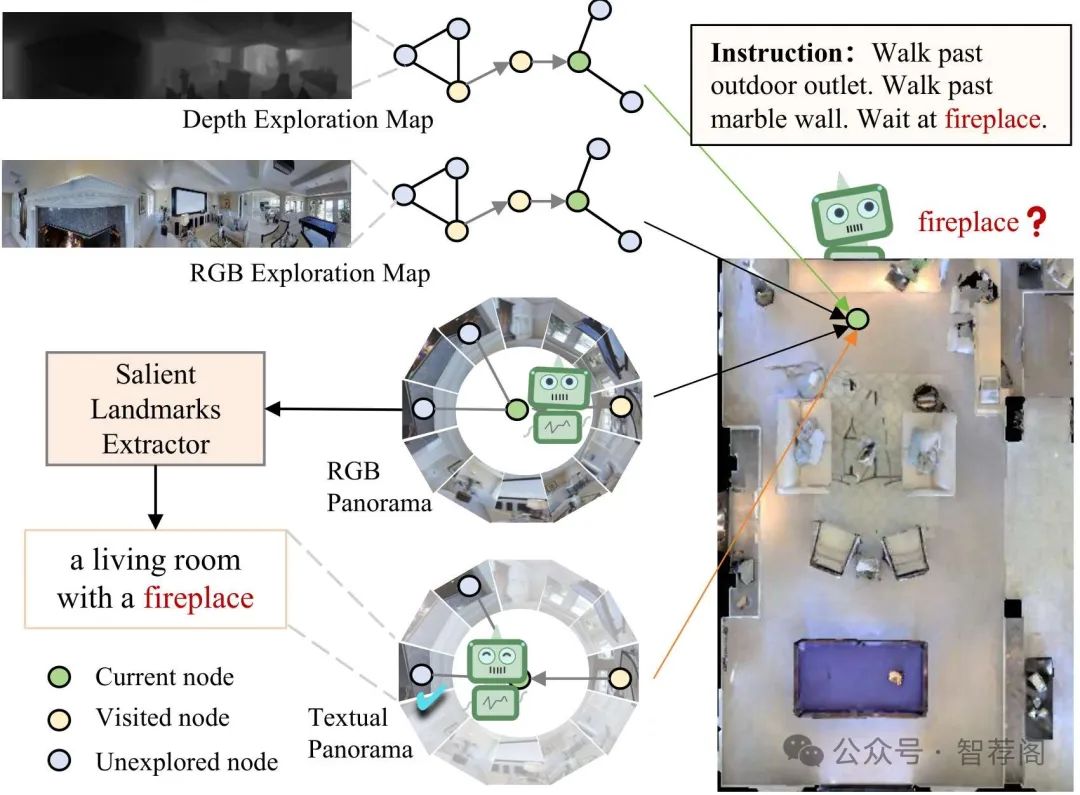
3.Agent Journey Beyond RGB: Unveiling Hybrid Semantic-Spatial Environmental Representations for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Authors: Xuesong Zhang, Yunbo Xu, Jia Li, Zhenzhen Hu, Richnag Hong
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.06465
论文摘要
Navigating unseen environments based on natural lan guage instructions remains difficult for egocentric agents in Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN). While recent advancements have yielded promising outcomes, they pri marily rely on RGB images for environmental representa tion, often overlooking the underlying semantic knowledge and spatial cues. Intuitively, humans inherently ground textual semantics within the spatial layout during indoor navigation. Inspired by this, we propose a versatile Se mantic Understanding and Spatial Awareness (SUSA) ar chitecture to facilitate navigation. SUSA includes a Tex tual Semantic Understanding (TSU) module, which nar rows the modality gap between instructions and environ ments by generating and associating the descriptions of en vironmental landmarks in the agent’s immediate surround ings. Additionally, a Depth-based Spatial Perception (DSP) module incrementally constructs a depth exploration map, enabling a more nuanced comprehension of environmen tal layouts. Experimental results demonstrate that SUSA’s hybrid semantic-spatial representations effectively enhance navigation performance, setting new state-of-the-art per formance across three VLN benchmarks (REVERIE, R2R, and SOON). The source code are publicly available at https://github.com/HCI-LMC/VLN-SUSA.
论文简评
综上所述,该论文提出了SUSA架构,用于增强视觉-语言导航(VLN)任务的表现,成功解决了视觉信息与语义理解之间的挑战。通过引入文本语义理解和深度感知,该方法能够提供比传统RGB图像更多的环境信息,从而显著提升了VLN的性能。实验结果表明,SUSA在多个VLN基准测试中取得了领先的成绩,证明了其在解决此类问题上的有效性。此外,该研究还针对实际应用中的一个关键问题进行了深入探讨,为未来的研究提供了有价值的启示。总之,这篇论文是一个重要的研究成果,对于推动VLN领域的发展具有重要意义。
4.From Lived Experience to Insight: Unpacking the Psychological Risks of Using AI Conversational Agents
Authors: Mohit Chandra, Suchismita Naik, Denae Ford, Ebele Okoli, Munmun De Choudhury, Mahsa Ershadi, Gonzalo Ramos, Javier Hernandez, Ananya Bhattacharjee, Shahed Warreth, Jina Suh
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.07951
论文摘要
Recent gain in popularity of AI conversational agents has led to their increased use for improving productivity and supportingwell-being. While previous research has aimed to understand the risks associ ated with interactions with AI conversational agents, these studies often fall short in capturing the lived experiences. Additionally, psy chological risks have often been presented as a sub-category within broader AI-related risks in past taxonomy works, leading to under representation of the impact of psychological risks of AI use. To address these challenges, our work presents a novel risk taxonomy focusing on psychological risks of using AI gathered through lived experience of individuals. We employed a mixed-method approach, involving a comprehensive survey with 283 individuals with lived mentalhealth experience and workshops involving lived experience experts to develop a psychological risk taxonomy. Our taxonomy features 19 AI behaviors, 21 negative psychological impacts, and 15 contexts related to individuals. Additionally, we propose a novel multi-path vignette based framework for understanding the com plex interplay between AI behaviors, psychological impacts, and individual user contexts. Finally, based on the feedback obtained from the workshop sessions, we present design recommendations for developing safer and more robust AI agents. Our work offers an in-depth understanding of the psychological risks associated with AI conversational agents and provides actionable recommendations for policymakers, researchers, and developers.
论文简评
该篇论文采用混合研究方法,综合了问卷调查与工作坊数据收集,旨在深入探讨人工智能对话代理的心理学风险。论文提出了一种新的风险分类体系,重点关注AI行为、负面心理影响以及用户情境,并强调了生活经验对这些洞察的重要性。此外,作者还提出了一个多路径情景框架,用于理解AI行为与心理影响之间的互动,最终给出了设计建议以确保更加安全的人工智能代理。综上所述,该文不仅解决了当前心理学界对于人工智能对话代理心理健康问题的关注,而且通过创新的研究方法和理论构建,为人工智能的发展提供了有益的参考。

5.Asynchronous Agents with Perfect Recall: Model Reductions, Knowledge-Based Construction, and Model Checking for Coalitional Strategies
Authors: Dilian Gurov, Filip Jamroga, Wojciech Jamroga, Mateusz Kamiński, Damian Kurpiewski, Wojciech Penczek, Teofil Sidoruk
如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
























 3365
3365

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








