简介
Qwen3 是阿里云开发的大型语言模型家族的一部分,Qwen 系列最初于 2023 年发布,经历了多次迭代,包括 Qwen1、Qwen2 和最新版 Qwen3。Qwen3 于 2025 年 4 月 29 日临晨正式发布,阿里强势开源Qwen3,并一次放出八款同系列模型。标志着阿里巴巴在 AI 领域的又一里程碑。

核心亮点
-
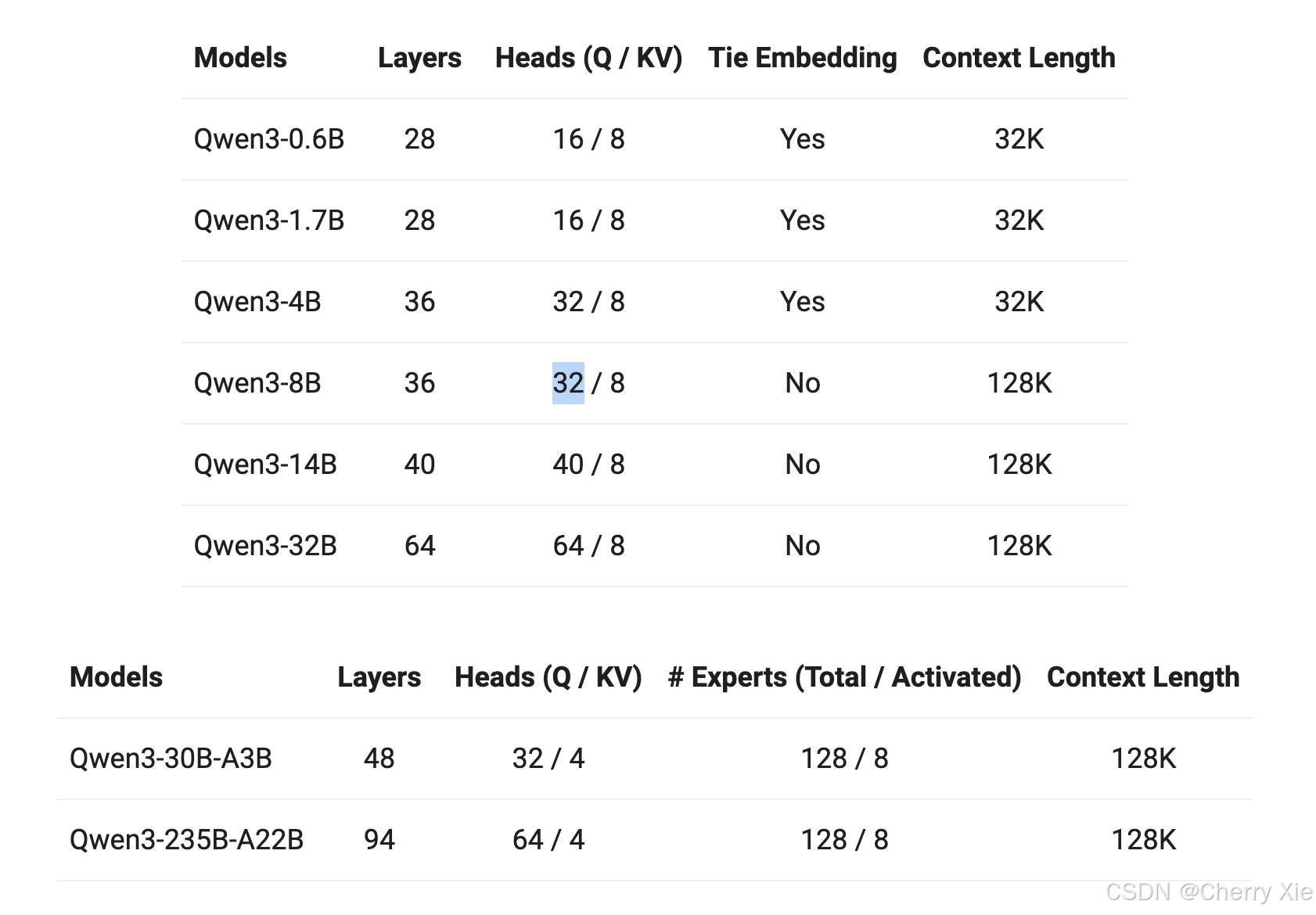
模型类型与参数规模:Qwen3 包括密集模型(Dense)和专家混合模型(Mixture of Experts, MoE)。参数规模从 0.6 亿到 2350 亿,涵盖小型模型(如 Qwen3-0.6B)和大型模型(如 Qwen3-235B-A22B)。GitHub 页面提供了详细的模型大小列表 (Qwen3 GitHub 页面)。

-
推理能力:支持“思考模式”和“非思考模式”,通过参数控制(如 enable_thinking 参数)或指令切换(如 /think, /nothink),实现灵活的推理能力。研究表明,这类似于 OpenAI 的 o3,但可能伴随更高的延迟。旗舰模型 Qwen3-235B-A22B 在代码、数学和通用能力等基准测试中,与 DeepSeek-R1、o1、o3-mini、Grok-3 和 Gemini-2.5-Pro 等顶级模型相比,表现出极具竞争力的结果。

-
训练数据与架构设计:使用超过 36 万亿个令牌的数据集,包括教科书、问答对、代码片段和 AI 生成数据,确保模型的多样性和泛化能力。部分模型采用 MoE 架构,提高计算效率,同时支持长上下文处理,采用 NTK-aware 插值、窗口注意力、LogN 注意力缩放和 RoPE(旋转位置编码)等技术。
-
支持框架与性能:支持多种框架,包括 Transformers(需要版本 >=4.51.0)、ModelScope、llama.cpp(需要 b5092)、Ollama(需要 v0.6.6)、LMStudio、MLX LM(需要 >=0.24.0)、SGLang(需要 >=0.4.6.post1)、vLLM(推荐 >=0.8.5)、MindIE 等。在 Codeforces、AIME 和 BFCL 等基准测试中,Qwen3-235B-A22B 超过了 OpenAI 的 o3-mini 和 Google 的 Gemini 2.5 Pro,Qwen3-32B 在 LiveCodeBench 上超越了 OpenAI 的 o1。
-
小型模型表现:小型 MoE 模型 Qwen3-30B-A3B 的激活参数数量仅为 QwQ-32B 的 10%,但表现更胜一筹;即使是 Qwen3-4B 这样的小型模型,也能与 Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct 的性能相媲美。GitHub 页面提到,Qwen3-30B-A3B 出色地超越了 QwQ-32B,而 Qwen3-4B 的性能与 Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct 相当 (Qwen3 GitHub 页面)。
-
多语言:Qwen3 模型支持 119 种语言和方言。这一广泛的多语言能力为国际应用开辟了新的可能性,让全球用户都能受益于这些模型的强大功能。
预训练
在预训练方面,Qwen3 的数据集相比 Qwen2.5 有了显著扩展。Qwen2.5是在 18 万亿个 token 上进行预训练的,而 Qwen3 使用的数据量几乎是其两倍,达到了约 36 万亿个 token,涵盖了 119 种语言和方言。为了构建这个庞大的数据集,我们不仅从网络上收集数据,还从 PDF 文档中提取信息。我们使用 Qwen2.5-VL 从这些文档中提取文本,并用 Qwen2.5 改进提取内容的质量。为了增加数学和代码数据的数量,我们利用 Qwen2.5-Math 和 Qwen2.5-Coder 这两个数学和代码领域的专家模型合成数据,合成了包括教科书、问答对以及代码片段等多种形式的数据。
预训练过程分为三个阶段。在第一阶段(S1),模型在超过 30 万亿个 token 上进行了预训练,上下文长度为 4K token。这一阶段为模型提供了基本的语言技能和通用知识。在第二阶段(S2),我们通过增加知识密集型数据(如 STEM、编程和推理任务)的比例来改进数据集,随后模型又在额外的 5 万亿个 token 上进行了预训练。在最后阶段,我们使用高质量的长上下文数据将上下文长度扩展到 32K token,确保模型能够有效地处理更长的输入。

由于模型架构的改进、训练数据的增加以及更有效的训练方法,Qwen3 Dense 基础模型的整体性能与参数更多的Qwen2.5基础模型相当。例如,Qwen3-1.7B/4B/8B/14B/32B-Base 分别与 Qwen2.5-3B/7B/14B/32B/72B-Base 表现相当。特别是在 STEM、编码和推理等领域,Qwen3 Dense 基础模型的表现甚至超过了更大规模的 Qwen2.5 模型。对于 Qwen3 MoE 基础模型,它们在仅使用 10% 激活参数的情况下达到了与 Qwen2.5 Dense 基础模型相似的性能。这带来了训练和推理成本的显著节省。
后训练
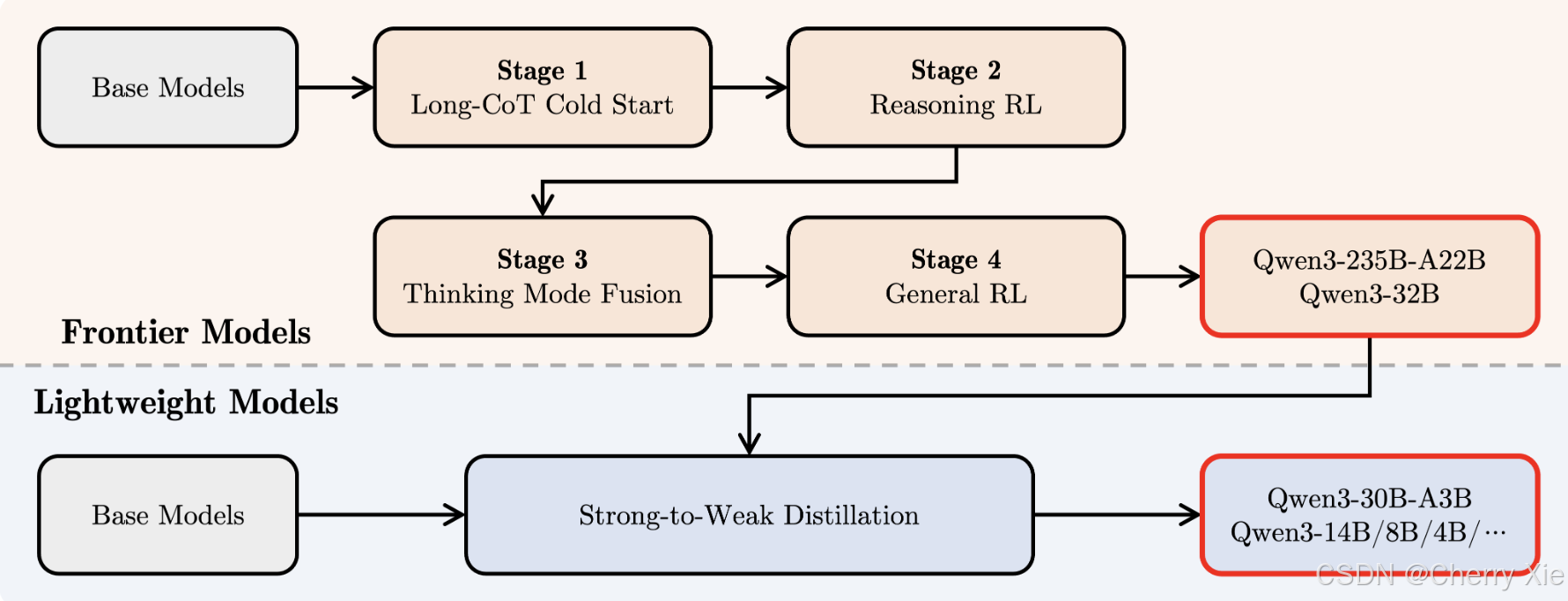
为了开发能够同时具备思考推理和快速响应能力的混合模型,我们实施了一个四阶段的训练流程。该流程包括:(1)长思维链冷启动,(2)长思维链强化学习,(3)思维模式融合,以及(4)通用强化学习。
在第一阶段,我们使用多样的的长思维链数据对模型进行了微调,涵盖了数学、代码、逻辑推理和 STEM 问题等多种任务和领域。这一过程旨在为模型配备基本的推理能力。第二阶段的重点是大规模强化学习,利用基于规则的奖励来增强模型的探索和钻研能力。
在第三阶段,我们在一份包括长思维链数据和常用的指令微调数据的组合数据上对模型进行微调,将非思考模式整合到思考模型中。确保了推理和快速响应能力的无缝结合。最后,在第四阶段,我们在包括指令遵循、格式遵循和 Agent 能力等在内的 20 多个通用领域的任务上应用了强化学习,以进一步增强模型的通用能力并纠正不良行为。
使用实例
普通实例
from modelscope import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B"
# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True # Switch between thinking and non-thinking modes. Default is True.
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=32768
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
# parsing thinking content
try:
# rindex finding 151668 (</think>)
index = len(output_ids) - output_ids[::-1].index(151668)
except ValueError:
index = 0
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print("thinking content:", thinking_content)
print("content:", content)
要禁用思考模式,只需对参数 enable_thinking 进行如下修改:
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=False # True is the default value for enable_thinking.
)
对于部署,您可以使用 sglang>=0.4.6.post1 或 vllm>=0.8.4 来创建一个与 OpenAI API 兼容的 API endpoint:
SGLang:
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B --reasoning-parser qwen3
vLLM:
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen3-30B-A3B --enable-reasoning --reasoning-parser deepseek_r1
要禁用思考模式,您可以移除参数 --reasoning-parser(以及 --enable-reasoning)。
如果用于本地开发,您可以通过运行简单的命令 ollama run qwen3:30b-a3b 来使用 ollama 与模型进行交互。您也可以使用 LMStudio 或者 llama.cpp 以及 ktransformers 等代码库进行本地开发。
多轮对话
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
class QwenChatbot:
def __init__(self, model_name="Qwen3-30B-A3B/Qwen3-30B-A3B"):
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
self.history = []
def generate_response(self, user_input):
messages = self.history + [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]
text = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
inputs = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
response_ids = self.model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=32768)[0][len(inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
response = self.tokenizer.decode(response_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# Update history
self.history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
self.history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
return response
# Example Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
chatbot = QwenChatbot()
# First input (without /think or /no_think tags, thinking mode is enabled by default)
user_input_1 = "How many r's in strawberries?"
print(f"User: {user_input_1}")
response_1 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_1)
print(f"Bot: {response_1}")
print("----------------------")
# Second input with /no_think
user_input_2 = "Then, how many r's in blueberries? /no_think"
print(f"User: {user_input_2}")
response_2 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_2)
print(f"Bot: {response_2}")
print("----------------------")
# Third input with /think
user_input_3 = "Really? /think"
print(f"User: {user_input_3}")
response_3 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_3)
print(f"Bot: {response_3}")
agent实例
from qwen_agent.agents import Assistant
# Define LLM
llm_cfg = {
'model': 'Qwen3-30B-A3B',
# Use the endpoint provided by Alibaba Model Studio:
# 'model_type': 'qwen_dashscope',
# 'api_key': os.getenv('DASHSCOPE_API_KEY'),
# Use a custom endpoint compatible with OpenAI API:
'model_server': 'http://localhost:8000/v1', # api_base
'api_key': 'EMPTY',
# Other parameters:
# 'generate_cfg': {
# # Add: When the response content is `<think>this is the thought</think>this is the answer;
# # Do not add: When the response has been separated by reasoning_content and content.
# 'thought_in_content': True,
# },
}
# Define Tools
tools = [
{'mcpServers': { # You can specify the MCP configuration file
'time': {
'command': 'uvx',
'args': ['mcp-server-time', '--local-timezone=Asia/Shanghai']
},
"fetch": {
"command": "uvx",
"args": ["mcp-server-fetch"]
}
}
},
'code_interpreter', # Built-in tools
]
# Define Agent
bot = Assistant(llm=llm_cfg, function_list=tools)
# Streaming generation
messages = [{'role': 'user', 'content': 'https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/ Introduce the latest developments of Qwen'}]
for responses in bot.run(messages=messages):
pass
print(responses)
相关文献
github地址:https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen3
模型下载:https://modelscope.cn/organization/qwen
demo online:https://huggingface.co/spaces/Qwen/Qwen3-Demo
官方体验:https://chat.qwen.ai/




























 1207
1207

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










