BBOX投影
首先在mmdetection3d/tools/data_converter/nuscenes_converter.py中,get_2d_boxes()可以直接从nuscenes原始sample数据中获取已标注的3D box信息,因此该函数就可以实现整体投影过程。
投影原理
投影过程分为以下几步:
-
世界坐标系 ——> Ego坐标系(自身)
- 这里需要世界坐标系原点变换到自身的 平移 T+旋转 R;

- 这里需要世界坐标系原点变换到自身的 平移 T+旋转 R;
-
Ego坐标系 ——> 相机坐标系
- 这里需要自身原点位置变换到相机位置的 平移 T+旋转 R(即相机外参) ;

- 这里需要自身原点位置变换到相机位置的 平移 T+旋转 R(即相机外参) ;
-
相机坐标系 ——> 像素坐标系
- 此处需要相机内参即可;

- 此处需要相机内参即可;
重要概念
- box坐标点的
origin:
在Nuscenes中,默认get_box()函数获取到的中心点为
代码重构
- 重构
get_2d_boxes()函数如下:(改动处均已标注出)
def get_2d_boxes(nusc,
sample_data_token: str,
visibilities: List[str],
mono3d=True):
"""Get the 2D annotation records for a given `sample_data_token`.
Args:
sample_data_token (str): Sample data token belonging to a camera
keyframe.
visibilities (list[str]): Visibility filter.
mono3d (bool): Whether to get boxes with mono3d annotation.
Return:
list[dict]: List of 2D annotation record that belongs to the input
`sample_data_token`.
"""
# Get the sample data and the sample corresponding to that sample data.
sd_rec = nusc.get('sample_data', sample_data_token)
assert sd_rec[
'sensor_modality'] == 'camera', 'Error: get_2d_boxes only works' \
' for camera sample_data!'
if not sd_rec['is_key_frame']:
raise ValueError(
'The 2D re-projections are available only for keyframes.')
s_rec = nusc.get('sample', sd_rec['sample_token'])
# --------------------------------------------
# 获取图像,用于可视化
cam_rec = nusc.get('sample_data', s_rec['data']['CAM_FRONT'])
imgname = os.path.join('/home/pc/Workspaces/Reaserch/mmdetection3d/data/nuscenes/trainval', \
cam_rec['filename'])
# --------------------------------------------
# Get the calibrated sensor and ego pose
# record to get the transformation matrices.
cs_rec = nusc.get('calibrated_sensor', sd_rec['calibrated_sensor_token'])
pose_rec = nusc.get('ego_pose', sd_rec['ego_pose_token'])
camera_intrinsic = np.array(cs_rec['camera_intrinsic'])
# Get all the annotation with the specified visibilties.
ann_recs = [
nusc.get('sample_annotation', token) for token in s_rec['anns']
]
ann_recs = [
ann_rec for ann_rec in ann_recs
if (ann_rec['visibility_token'] in visibilities)
]
repro_recs = []
box_list = [] # visualization
for ann_rec in ann_recs:
# Augment sample_annotation with token information.
ann_rec['sample_annotation_token'] = ann_rec['token']
ann_rec['sample_data_token'] = sample_data_token
# Get the box in global coordinates.
box = nusc.get_box(ann_rec['token'])
# Move them to the ego-pose frame.
box.translate(-np.array(pose_rec['translation']))
box.rotate(Quaternion(pose_rec['rotation']).inverse)
# Move them to the calibrated sensor frame.
box.translate(-np.array(cs_rec['translation']))
box.rotate(Quaternion(cs_rec['rotation']).inverse)
# Filter out the corners that are not in front of the calibrated
# sensor.
corners_3d = box.corners()
in_front = np.argwhere(corners_3d[2, :] > 0).flatten()
corners_3d = corners_3d[:, in_front]
# Project 3d box to 2d.
corner_coords = view_points(corners_3d, camera_intrinsic,
True).T[:, :2].tolist()
# Keep only corners that fall within the image.
final_coords = post_process_coords(corner_coords)
# Skip if the convex hull of the re-projected corners
# does not intersect the image canvas.
if final_coords is None:
continue
else:
min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y = final_coords
# Generate dictionary record to be included in the .json file.
repro_rec = generate_record(ann_rec, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y,
sample_data_token, sd_rec['filename'])
# If mono3d=True, add 3D annotations in camera coordinates
if mono3d and (repro_rec is not None):
loc = box.center.tolist()
dim = box.wlh
dim[[0, 1, 2]] = dim[[1, 2, 0]] # convert wlh to our lhw
dim = dim.tolist()
rot = box.orientation.yaw_pitch_roll[0]
rot = [-rot] # convert the rot to our cam coordinate
global_velo2d = nusc.box_velocity(box.token)[:2]
global_velo3d = np.array([*global_velo2d, 0.0])
e2g_r_mat = Quaternion(pose_rec['rotation']).rotation_matrix
c2e_r_mat = Quaternion(cs_rec['rotation']).rotation_matrix
cam_velo3d = global_velo3d @ np.linalg.inv(
e2g_r_mat).T @ np.linalg.inv(c2e_r_mat).T
velo = cam_velo3d[0::2].tolist()
repro_rec['bbox_cam3d'] = loc + dim + rot
repro_rec['velo_cam3d'] = velo
center3d = np.array(loc).reshape([1, 3])
center2d = points_cam2img(
center3d, camera_intrinsic, with_depth=False)
repro_rec['center2d'] = center2d.squeeze().tolist()
# normalized center2D + depth
# if samples with depth < 0 will be removed
# --------------------------------------------
# if repro_rec['center2d'][2] <= 0:
# continue
# --------------------------------------------
ann_token = nusc.get('sample_annotation',
box.token)['attribute_tokens']
if len(ann_token) == 0:
attr_name = 'None'
else:
attr_name = nusc.get('attribute', ann_token[0])['name']
attr_id = nus_attributes.index(attr_name)
repro_rec['attribute_name'] = attr_name
repro_rec['attribute_id'] = attr_id
# --------------------------------------------
box_list.append(torch.tensor(repro_rec['bbox_cam3d']))
# --------------------------------------------
repro_recs.append(repro_rec)
# --------------------------------------------
from mmdet3d.core.visualizer.image_vis import draw_camera_bbox3d_on_img
import cv2
img = cv2.imread(imgname)
from mmdet3d.core.bbox.structures.cam_box3d import CameraInstance3DBoxes
bbox_cam3d = torch.stack(box_list, dim=0) # repro_rec['bbox_cam3d']
bbox_cam3d = CameraInstance3DBoxes(bbox_cam3d,origin=(0.5,0.5,0.5))
draw_camera_bbox3d_on_img(bbox_cam3d,
raw_img=img,
cam2img=camera_intrinsic,
img_metas=None,
color=(0, 255, 0),
thickness=1)
# --------------------------------------------
投影效果
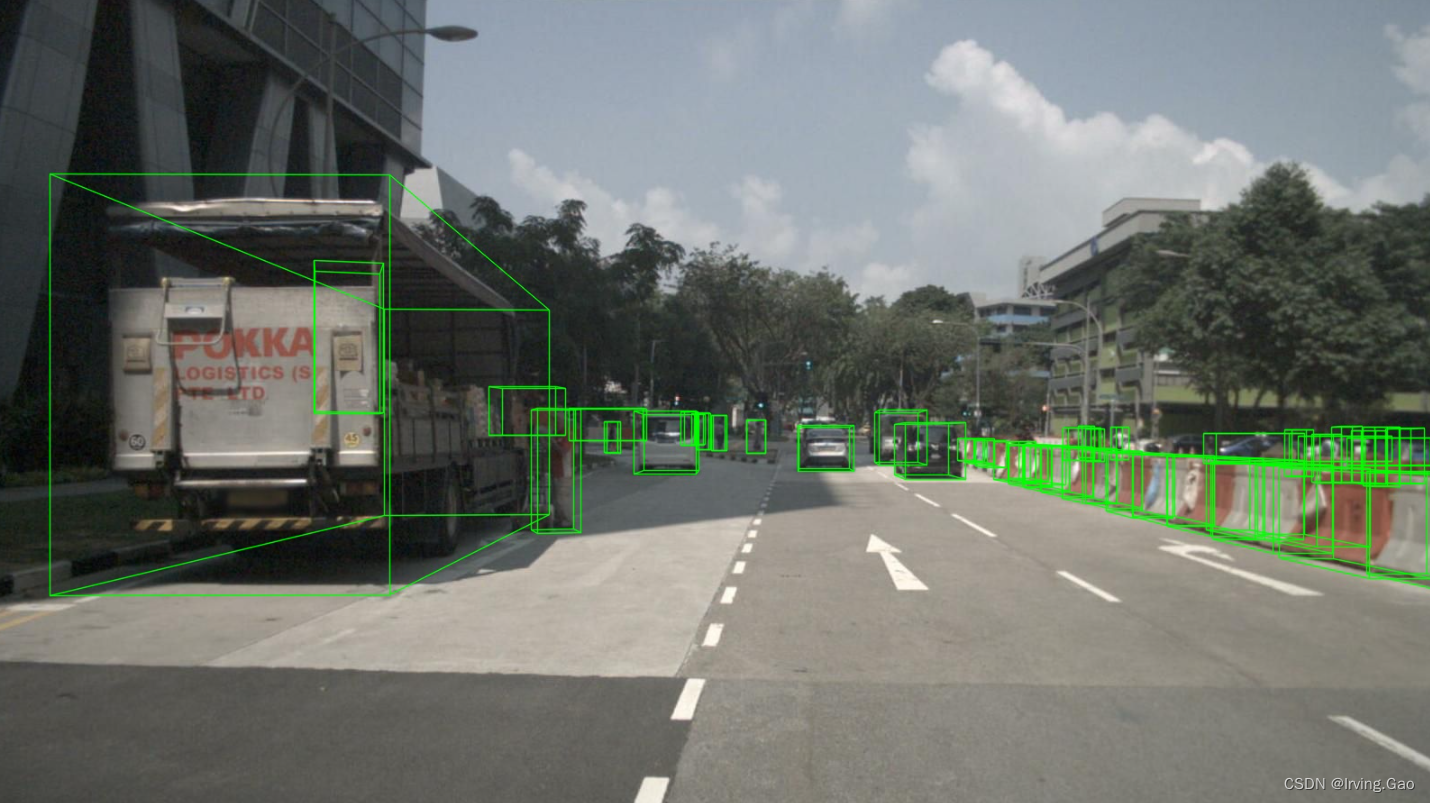
点投影











 本文介绍了如何在mmdetection3d中实现3D目标检测框的2D投影过程,详细解析了从世界坐标系到像素坐标系的转换步骤,并通过代码示例展示了具体的实现方法。
本文介绍了如何在mmdetection3d中实现3D目标检测框的2D投影过程,详细解析了从世界坐标系到像素坐标系的转换步骤,并通过代码示例展示了具体的实现方法。
















 1493
1493

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








