赵虚左老师讲的很详细,这里只是理一下思路,说下突然出现“新”概念之间的关系。
urdf文件:里面是配置模型的,既有模型的位置、尺寸、颜色,也包含复杂的物理模型信息比如:转动惯量,碰撞box大小等等,总之是定义模型的。
xacro文件: 也是配置模型的,就是urdf的高级版。
总流程就是:定义模型-》组装模型-》在launch文件启动-》加载Gazebo里-》打开自带的ros-control键盘控车
总结:
1:link里的 fame是相对于可视化模型的偏移,如果为0,0,0。那两坐标系重合,坐标系原点在模型左下角。有时候想让坐标系在模型里面,就要改link里的
joint里的 是坐标系位置,在rviz里就表示模型放在哪里的位置,比如雷达放在高1m,则:joint里的 z=1,这里的高是相对于谁高呢? 所以要在joint里写parent,是child相对于parent的高
 在xacro或urdf文件里添加下代码,表示使用ros插件将罗列的jointName(之前自己定义的)的tf发出来,当然也有其他方法
在xacro或urdf文件里添加下代码,表示使用ros插件将罗列的jointName(之前自己定义的)的tf发出来,当然也有其他方法
<gazebo>
<plugin name="joint_state_publisher" filename="libgazebo_ros_joint_state_publisher.so">
<jointName>rear_left_wheel_joint, rear_right_wheel_joint, front_left_steering_joint, front_right_steering_joint, front_right_wheel_joint, front_left_wheel_joint,base_link_to_fork_right_horizontal,fork_right_horizontal_to_fork_right_vertical,fork_left_horizontal_to_fork_left_vertical,base_link_to_fork_left_horizontal</jointName>
<updateRate>100</updateRate>
<robotNamespace>/$(arg roboname)</robotNamespace>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
说的问题是:选择不同的frame_id时候,就不显示其他的图像在rviz里,本质原因是,坐标系没统一变换,不在一棵TF数下,导致不会全部显示


Start.sh同时启动雷达、相机、地盘
<!-- 机器人启动文件:
1.启动底盘
2.启动激光雷达
3.启动摄像头
-->
<launch>
<include file="$(find ros_arduino_python)/launch/arduino.launch" />
<include file="$(find usb_cam)/launch/usb_cam-test.launch" />
<include file="$(find rplidar_ros)/launch/rplidar.launch" />
</launch>
静态坐标变换,指定了相机、雷达相对于底盘footprint关系
args="0.08 0 0.1 0 0 0 /base_footprint /camera_link"表示:xyz和欧拉角,父级坐标系和子坐标系。
父级坐标系和子坐标系和之前launch的对应
<!-- 机器人启动文件:
当不包含机器人模型时,需要发布坐标变换
-->
<launch>
<include file="$(find mycar_start)/launch/start.launch" />
<node name="camera2basefootprint" pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" args="0.08 0 0.1 0 0 0 /base_footprint /camera_link"/>
<node name="rplidar2basefootprint" pkg="tf2_ros" type="static_transform_publisher" args="0 0 0.1 0 0 0 /base_footprint /laser"/>
</launch>

实例:
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<!-- 形状 -->
<geometry>
<!-- 长方体的长宽高 -->
<!-- <box size="0.5 0.3 0.1" /> -->
<!-- 圆柱,半径和长度 -->
<!-- <cylinder radius="0.5" length="0.1" /> -->
<!-- 球体,半径-->
<!-- <sphere radius="0.3" /> -->
</geometry>
<!-- xyz坐标 rpy翻滚俯仰与偏航角度(3.14=180度 1.57=90度) -->
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<!-- 颜色: r=red g=green b=blue a=alpha -->
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.7 0.5 0 0.5" />
</material>
</visual>
</link>

赵老师的说明写的太好复制不过来了
我的理解:先在urdf设置一堆link,表示定义模型的尺寸大小啥的,先把东西捏好,然后再设置一堆joint来连接刚刚定义的link.
我理解link里的 可以都是000,表示开始放在的位置 ,joint里的 表示parent和child相对位置。
<!-- 添加摄像头 --> 表示摄像头放在0,0,0
<link name="camera">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="0.02 0.05 0.05" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<material name="red">
<color rgba="1 0 0 0.5" />
</material>
</visual>
</link>
<!-- 关节 --> 摄像头 作为child相对于base移动0.2 0 0.075
<joint name="camera2baselink" type="continuous">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="camera" />
<origin xyz="0.2 0 0.075" rpy="0 0 0" />
<axis xyz="0 0 1" />
</joint>

说人话就是:对于有parent的link(对应图里就是绿色的Child椭圆),它的joint位置决定的该link的绝对安装位置。(对应图中紫色箭头的意思)
紫色箭头要深刻理解,为啥上图child刚好安装在Parent屁股后,因为Joint的位置决定了它连带的Child的位置,且这个位置是相对的(相对于Joint parent的link位置)
此时Child中link origin=0,0,0,所以Child frame=Joint frame。若有时我们想让模型Frame在模型中心,则此时就要改Child link的 Origin
如何键盘控制小车在Gazebo里运动??
- 下载库 sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-teleop-twist-keyboard
- Launch 文件中添加 Gazebo 键盘控制程序
<launch>
<node name="twist_keyboard" pkg="teleop_twist_keyboard"
type="teleop_twist_keyboard.py" output="screen" />
</launch>
- 添加Gazebo控制器插件 (使用Gazebo自带的控制程序控制,我们只需要发对应的信号)
开启Gazebo后会订阅/cmd_vel等待被控制,之前的键盘控制程序会发布/cmd_vel话题。
我们只需新建一个xacro 类似于:
<robot name="my_car_move" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<!-- 传动实现:用于连接控制器与关节 -->
<xacro:macro name="joint_trans" params="joint_name">
<!-- Transmission is important to link the joints and the controller -->
<transmission name="${joint_name}_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${joint_name}">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${joint_name}_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</xacro:macro>
<!-- 每一个驱动轮都需要配置传动装置 -->
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="left_wheel2base_link" />
<xacro:joint_trans joint_name="right_wheel2base_link" />
<!-- 控制器 -->
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<rosDebugLevel>Debug</rosDebugLevel>
<publishWheelTF>true</publishWheelTF>
<robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace>
<publishTf>1</publishTf>
<publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>100.0</updateRate>
<legacyMode>true</legacyMode>
<leftJoint>left_wheel2base_link</leftJoint> <!-- 左轮 -->
<rightJoint>right_wheel2base_link</rightJoint> <!-- 右轮 -->
<wheelSeparation>${base_link_radius * 2}</wheelSeparation> <!-- 车轮间距 -->
<wheelDiameter>${wheel_radius * 2}</wheelDiameter> <!-- 车轮直径 -->
<broadcastTF>1</broadcastTF>
<wheelTorque>30</wheelTorque>
<wheelAcceleration>1.8</wheelAcceleration>
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic> <!-- 运动控制话题 -->
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic> <!-- 里程计话题 -->
<robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame> <!-- 根坐标系 -->
</plugin>
</gazebo>
</robot>

base_footprint设置controler所控制的机器人的坐标系是哪个坐标系
然后集成,启动launch即可:

显示里程计的方法:

2 urdf再次理解
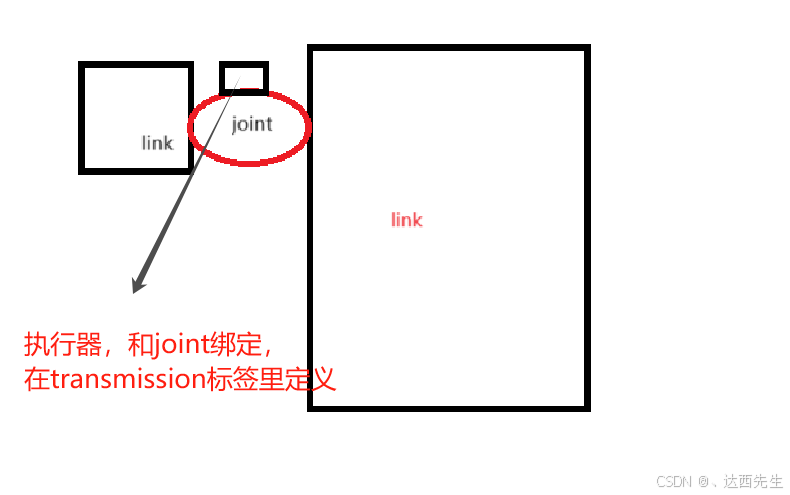
<transmission name="wheel_left_transmission">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="wheel_left_joint">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="wheel_left_motor">
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
hardware_interface/PositionJointInterface 是一种接口类型,它定义了如何通过位置控制来驱动关节,除此之外还包括 VelocityJointInterface 和 EffortJointInterface,它们分别用于速度控制和力矩控制。
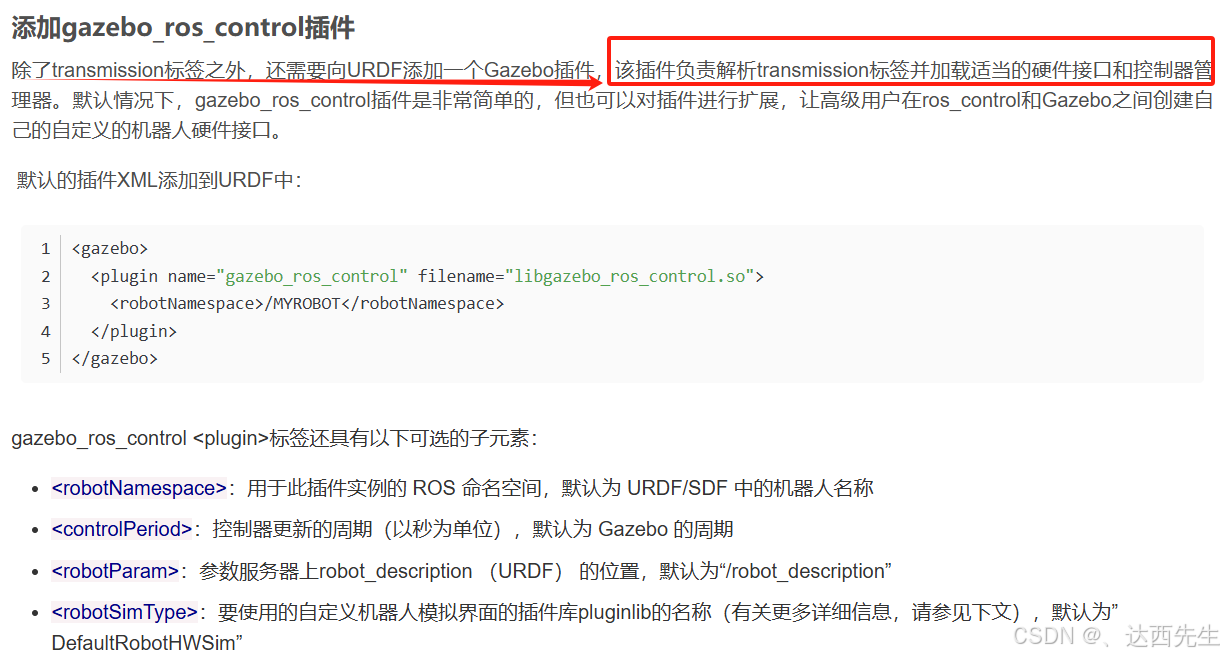
说白了就是:添加的plugin,libgazebo_ros_control.so将读取所有标签中的内容
下面举例解释:
<link name="base_footprint"></link>
<joint name="robot_footprint_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 0.07" rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent link="base_footprint" />
<child link="base_link" />
</joint> 这是我.xacro文件部分内容
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
<gazebo> 这是添加插件
<plugin name="object_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_planar_move.so">
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic>
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<odometryRate>30.0</odometryRate>
<robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
robotBaseFrame作为机器人的基座坐标系,用于表示机器人的位置和姿态。说人话就是:你机器人变成了质点,你定位,速度,里程计,以及发布cmd_vel控制的就是这个点
因为添加的每个link就含坐标系,所以这里写的名字就是你link的名字
将 odometryFrame设置为 base_footprint,在RVIZ中选择base_footprint坐标系就可以看见里程计信息
odometryTopic为odom,表示会有/odom话题发布里程计信息





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








