上一篇博客对数据处理的部分进行解读:Pointpillars代码解读——数据处理-CSDN博客
接下来对整个网络架构代码部分进行解读。
参考博客:(四)PointPillars论文的MMDetection3D代码解读——网络结构篇_mmdetection3d pointpillars-CSDN博客
目录

这个网络主要是将来自激光雷达(Lidar)的点云转换为稀疏伪图像(Pseduo image)。这个阶段又可以分成三个步骤(如图序号所示)。
1、点云离散化
原始点云是三维的,具有(x,y,z)三个坐标轴的坐标,这一步将三维空间中的点云沿着z轴的方向离散到x-y平面上均匀分布的网格中,形成了一组pillars(也就是柱状体),并拥有相对应的索引向量(图中对应的pillar index),引入索引向量之后可以解决点云无序性的问题。需要注意的是:这里pillar是在z轴方向上具有无限范围空间的体素(体积像素 voxel),故而不需要超参数控制z反向的融合/合并。
此时原始点云中的点由三维(x,y,z)扩展成九维(x,y,z,r,xc,yc,zc,xp,yp),其中xyz仍然是空间中的xyz轴坐标,r表示该点的反射强度(reflection),下标c表示该点到整个pillar中所有点的算术平均值的距离,即,x0表示每个点原始的坐标值;下标p表示该点距离pillar中心xy的偏移量。
由于点云的稀疏性,绝大部分的pillar中都是空的,并且非空的pillar中通常也就只有几个点,而作者采用了非常巧妙的方法解决这个问题:通过加强每一个样本(P)中非空pillars的数量和每一个pillar(N)中点数的限制,构造了一个(D,P,N)的密集向量用于减少稀疏性。【即P为样本中非空pillars数量、N为每个pillar中点的数量、D为维度】pillar中点数大于N则随机采样,反之则使用零进行填充来限制点数的数量。
2、生成向量
将1中生成的pillars采用简易版的PointNet,对于每一个点使用线性层,接下来是BatchNorm和Relu,生成规格为(C,P,N)的向量,之后再对N个通道进行最大池化操作(maxpooling)生成一个规格为(C,P)的输出向量。线性层可以表示为跨向量的1x1卷积故而可以实现高效率的计算。此时对N个点进行最大池化用于代表整个pillar的信息。
3、特征向量融合
将1中生成的索引和2中得到的规格为(C,P)的输出向量进行特征向量融合,形成伪图像。
即(P,C)+Pillar_index ——> (H,W,C),得到的是一个通道数位C的伪图像,从而可以使用最经典的图像网络进行处理。H和W分别代表图像的宽度和高度。
下面进行代码的解读:
一、点云数据预处理
代码存放位置:mmdetection3d/mmdet3d/models/data_preprocessors/data_preprocessor.py

# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
import math
from numbers import Number
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Sequence, Tuple, Union
import numpy as np
import torch
from mmdet.models import DetDataPreprocessor
from mmdet.models.utils.misc import samplelist_boxtype2tensor
from mmengine.model import stack_batch
from mmengine.utils import is_seq_of
from torch import Tensor
from torch.nn import functional as F
from mmdet3d.registry import MODELS
from mmdet3d.structures.det3d_data_sample import SampleList
from mmdet3d.utils import OptConfigType
from .utils import multiview_img_stack_batch
from .voxelize import VoxelizationByGridShape, dynamic_scatter_3d
@MODELS.register_module()
class Det3DDataPreprocessor(DetDataPreprocessor):
"""Points / Image pre-processor for point clouds / vision-only / multi-
modality 3D detection tasks.
It provides the data pre-processing as follows
- Collate and move image and point cloud data to the target device.
- 1) For image data:
- Pad images in inputs to the maximum size of current batch with defined
``pad_value``. The padding size can be divisible by a defined
``pad_size_divisor``.
- Stack images in inputs to batch_imgs.
- Convert images in inputs from bgr to rgb if the shape of input is
(3, H, W).
- Normalize images in inputs with defined std and mean.
- Do batch augmentations during training.
- 2) For point cloud data:
- If no voxelization, directly return list of point cloud data.
- If voxelization is applied, voxelize point cloud according to
``voxel_type`` and obtain ``voxels``.
Args:
voxel (bool): Whether to apply voxelization to point cloud.
Defaults to False.
voxel_type (str): Voxelization type. Two voxelization types are
provided: 'hard' and 'dynamic', respectively for hard voxelization
and dynamic voxelization. Defaults to 'hard'.
voxel_layer (dict or :obj:`ConfigDict`, optional): Voxelization layer
config. Defaults to None.
batch_first (bool): Whether to put the batch dimension to the first
dimension when getting voxel coordinates. Defaults to True.
max_voxels (int, optional): Maximum number of voxels in each voxel
grid. Defaults to None.
mean (Sequence[Number], optional): The pixel mean of R, G, B channels.
Defaults to None.
std (Sequence[Number], optional): The pixel standard deviation of
R, G, B channels. Defaults to None.
pad_size_divisor (int): The size of padded image should be divisible by
``pad_size_divisor``. Defaults to 1.
pad_value (float or int): The padded pixel value. Defaults to 0.
pad_mask (bool): Whether to pad instance masks. Defaults to False.
mask_pad_value (int): The padded pixel value for instance masks.
Defaults to 0.
pad_seg (bool): Whether to pad semantic segmentation maps.
Defaults to False.
seg_pad_value (int): The padded pixel value for semantic segmentation
maps. Defaults to 255.
bgr_to_rgb (bool): Whether to convert image from BGR to RGB.
Defaults to False.
rgb_to_bgr (bool): Whether to convert image from RGB to BGR.
Defaults to False.
boxtype2tensor (bool): Whether to convert the ``BaseBoxes`` type of
bboxes data to ``Tensor`` type. Defaults to True.
non_blocking (bool): Whether to block current process when transferring
data to device. Defaults to False.
batch_augments (List[dict], optional): Batch-level augmentations.
Defaults to None.
"""
def __init__(self,
voxel: bool = False,
voxel_type: str = 'hard',
voxel_layer: OptConfigType = None,
batch_first: bool = True,
max_voxels: Optional[int] = None,
mean: Sequence[Number] = None,
std: Sequence[Number] = None,
pad_size_divisor: int = 1,
pad_value: Union[float, int] = 0,
pad_mask: bool = False,
mask_pad_value: int = 0,
pad_seg: bool = False,
seg_pad_value: int = 255,
bgr_to_rgb: bool = False,
rgb_to_bgr: bool = False,
boxtype2tensor: bool = True,
non_blocking: bool = False,
batch_augments: Optional[List[dict]] = None) -> None:
super(Det3DDataPreprocessor, self).__init__(
mean=mean,
std=std,
pad_size_divisor=pad_size_divisor,
pad_value=pad_value,
pad_mask=pad_mask,
mask_pad_value=mask_pad_value,
pad_seg=pad_seg,
seg_pad_value=seg_pad_value,
bgr_to_rgb=bgr_to_rgb,
rgb_to_bgr=rgb_to_bgr,
boxtype2tensor=boxtype2tensor,
non_blocking=non_blocking,
batch_augments=batch_augments)
self.voxel = voxel
self.voxel_type = voxel_type
self.batch_first = batch_first
self.max_voxels = max_voxels
if voxel:
self.voxel_layer = VoxelizationByGridShape(**voxel_layer)
def forward(self,
data: Union[dict, List[dict]],
training: bool = False) -> Union[dict, List[dict]]:
"""Perform normalization, padding and bgr2rgb conversion based on
``BaseDataPreprocessor``.
Args:
data (dict or List[dict]): Data from dataloader. The dict contains
the whole batch data, when it is a list[dict], the list
indicates test time augmentation.
training (bool): Whether to enable training time augmentation.
Defaults to False.
Returns:
dict or List[dict]: Data in the same format as the model input.
"""
if isinstance(data, list):
num_augs = len(data)
aug_batch_data = []
for aug_id in range(num_augs):
single_aug_batch_data = self.simple_process(
data[aug_id], training)
aug_batch_data.append(single_aug_batch_data)
return aug_batch_data
else:
return self.simple_process(data, training)
def simple_process(self, data: dict, training: bool = False) -> dict:
"""Perform normalization, padding and bgr2rgb conversion for img data
based on ``BaseDataPreprocessor``, and voxelize point cloud if `voxel`
is set to be True.
Args:
data (dict): Data sampled from dataloader.
training (bool): Whether to enable training time augmentation.
Defaults to False.
Returns:
dict: Data in the same format as the model input.
"""
if 'img' in data['inputs']:
batch_pad_shape = self._get_pad_shape(data)
data = self.collate_data(data)
inputs, data_samples = data['inputs'], data['data_samples']
batch_inputs = dict()
if 'points' in inputs:
batch_inputs['points'] = inputs['points']
if self.voxel:
voxel_dict = self.voxelize(inputs['points'], data_samples)
batch_inputs['voxels'] = voxel_dict
if 'imgs' in inputs:
imgs = inputs['imgs']
if data_samples is not None:
# NOTE the batched image size information may be useful, e.g.
# in DETR, this is needed for the construction of masks, which
# is then used for the transformer_head.
batch_input_shape = tuple(imgs[0].size()[-2:])
for data_sample, pad_shape in zip(data_samples,
batch_pad_shape):
data_sample.set_metainfo({
'batch_input_shape': batch_input_shape,
'pad_shape': pad_shape
})
if self.boxtype2tensor:
samplelist_boxtype2tensor(data_samples)
if self.pad_mask:
self.pad_gt_masks(data_samples)
if self.pad_seg:
self.pad_gt_sem_seg(data_samples)
if training and self.batch_augments is not None:
for batch_aug in self.batch_augments:
imgs, data_samples = batch_aug(imgs, data_samples)
batch_inputs['imgs'] = imgs
return {'inputs': batch_inputs, 'data_samples': data_samples}
def preprocess_img(self, _batch_img: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# channel transform
if self._channel_conversion:
_batch_img = _batch_img[[2, 1, 0], ...]
# Convert to float after channel conversion to ensure
# efficiency
_batch_img = _batch_img.float()
# Normalization.
if self._enable_normalize:
if self.mean.shape[0] == 3:
assert _batch_img.dim() == 3 and _batch_img.shape[0] == 3, (
'If the mean has 3 values, the input tensor '
'should in shape of (3, H, W), but got the '
f'tensor with shape {_batch_img.shape}')
_batch_img = (_batch_img - self.mean) / self.std
return _batch_img
def collate_data(self, data: dict) -> dict:
"""Copy data to the target device and perform normalization, padding
and bgr2rgb conversion and stack based on ``BaseDataPreprocessor``.
Collates the data sampled from dataloader into a list of dict and list
of labels, and then copies tensor to the target device.
Args:
data (dict): Data sampled from dataloader.
Returns:
dict: Data in the same format as the model input.
"""
data = self.cast_data(data) # type: ignore
if 'img' in data['inputs']:
_batch_imgs = data['inputs']['img']
# Process data with `pseudo_collate`.
if is_seq_of(_batch_imgs, torch.Tensor):
batch_imgs = []
img_dim = _batch_imgs[0].dim()
for _batch_img in _batch_imgs:
if img_dim == 3: # standard img
_batch_img = self.preprocess_img(_batch_img)
elif img_dim == 4:
_batch_img = [
self.preprocess_img(_img) for _img in _batch_img
]
_batch_img = torch.stack(_batch_img, dim=0)
batch_imgs.append(_batch_img)
# Pad and stack Tensor.
if img_dim == 3:
batch_imgs = stack_batch(batch_imgs, self.pad_size_divisor,
self.pad_value)
elif img_dim == 4:
batch_imgs = multiview_img_stack_batch(
batch_imgs, self.pad_size_divisor, self.pad_value)
# Process data with `default_collate`.
elif isinstance(_batch_imgs, torch.Tensor):
assert _batch_imgs.dim() == 4, (
'The input of `ImgDataPreprocessor` should be a NCHW '
'tensor or a list of tensor, but got a tensor with '
f'shape: {_batch_imgs.shape}')
if self._channel_conversion:
_batch_imgs = _batch_imgs[:, [2, 1, 0], ...]
# Convert to float after channel conversion to ensure
# efficiency
_batch_imgs = _batch_imgs.float()
if self._enable_normalize:
_batch_imgs = (_batch_imgs - self.mean) / self.std
h, w = _batch_imgs.shape[2:]
target_h = math.ceil(
h / self.pad_size_divisor) * self.pad_size_divisor
target_w = math.ceil(
w / self.pad_size_divisor) * self.pad_size_divisor
pad_h = target_h - h
pad_w = target_w - w
batch_imgs = F.pad(_batch_imgs, (0, pad_w, 0, pad_h),
'constant', self.pad_value)
else:
raise TypeError(
'Output of `cast_data` should be a list of dict '
'or a tuple with inputs and data_samples, but got '
f'{type(data)}: {data}')
data['inputs']['imgs'] = batch_imgs
data.setdefault('data_samples', None)
return data
def _get_pad_shape(self, data: dict) -> List[Tuple[int, int]]:
"""Get the pad_shape of each image based on data and
pad_size_divisor."""
# rewrite `_get_pad_shape` for obtaining image inputs.
_batch_inputs = data['inputs']['img']
# Process data with `pseudo_collate`.
if is_seq_of(_batch_inputs, torch.Tensor):
batch_pad_shape = []
for ori_input in _batch_inputs:
if ori_input.dim() == 4:
# mean multiview input, select one of the
# image to calculate the pad shape
ori_input = ori_input[0]
pad_h = int(
np.ceil(ori_input.shape[1] /
self.pad_size_divisor)) * self.pad_size_divisor
pad_w = int(
np.ceil(ori_input.shape[2] /
self.pad_size_divisor)) * self.pad_size_divisor
batch_pad_shape.append((pad_h, pad_w))
# Process data with `default_collate`.
elif isinstance(_batch_inputs, torch.Tensor):
assert _batch_inputs.dim() == 4, (
'The input of `ImgDataPreprocessor` should be a NCHW tensor '
'or a list of tensor, but got a tensor with shape: '
f'{_batch_inputs.shape}')
pad_h = int(
np.ceil(_batch_inputs.shape[1] /
self.pad_size_divisor)) * self.pad_size_divisor
pad_w = int(
np.ceil(_batch_inputs.shape[2] /
self.pad_size_divisor)) * self.pad_size_divisor
batch_pad_shape = [(pad_h, pad_w)] * _batch_inputs.shape[0]
else:
raise TypeError('Output of `cast_data` should be a list of dict '
'or a tuple with inputs and data_samples, but got '
f'{type(data)}: {data}')
return batch_pad_shape
@torch.no_grad()
def voxelize(self, points: List[Tensor],
data_samples: SampleList) -> Dict[str, Tensor]:
"""Apply voxelization to point cloud.
Args:
points (List[Tensor]): Point cloud in one data batch.
data_samples: (list[:obj:`Det3DDataSample`]): The annotation data
of every samples. Add voxel-wise annotation for segmentation.
Returns:
Dict[str, Tensor]: Voxelization information.
- voxels (Tensor): Features of voxels, shape is MxNxC for hard
voxelization, NxC for dynamic voxelization.
- coors (Tensor): Coordinates of voxels, shape is Nx(1+NDim),
where 1 represents the batch index.
- num_points (Tensor, optional): Number of points in each voxel.
- voxel_centers (Tensor, optional): Centers of voxels.
"""
voxel_dict = dict()
if self.voxel_type == 'hard':
voxels, coors, num_points, voxel_centers = [], [], [], []
for i, res in enumerate(points):
res_voxels, res_coors, res_num_points = self.voxel_layer(res)
res_voxel_centers = (
res_coors[:, [2, 1, 0]] + 0.5) * res_voxels.new_tensor(
self.voxel_layer.voxel_size) + res_voxels.new_tensor(
self.voxel_layer.point_cloud_range[0:3])
res_coors = F.pad(res_coors, (1, 0), mode='constant', value=i)
voxels.append(res_voxels)
coors.append(res_coors)
num_points.append(res_num_points)
voxel_centers.append(res_voxel_centers)
voxels = torch.cat(voxels, dim=0)
coors = torch.cat(coors, dim=0)
num_points = torch.cat(num_points, dim=0)
voxel_centers = torch.cat(voxel_centers, dim=0)
voxel_dict['num_points'] = num_points
voxel_dict['voxel_centers'] = voxel_centers
elif self.voxel_type == 'dynamic':
coors = []
# dynamic voxelization only provide a coors mapping
for i, res in enumerate(points):
res_coors = self.voxel_layer(res)
res_coors = F.pad(res_coors, (1, 0), mode='constant', value=i)
coors.append(res_coors)
voxels = torch.cat(points, dim=0)
coors = torch.cat(coors, dim=0)
elif self.voxel_type == 'cylindrical':
voxels, coors = [], []
for i, (res, data_sample) in enumerate(zip(points, data_samples)):
rho = torch.sqrt(res[:, 0]**2 + res[:, 1]**2)
phi = torch.atan2(res[:, 1], res[:, 0])
polar_res = torch.stack((rho, phi, res[:, 2]), dim=-1)
min_bound = polar_res.new_tensor(
self.voxel_layer.point_cloud_range[:3])
max_bound = polar_res.new_tensor(
self.voxel_layer.point_cloud_range[3:])
try: # only support PyTorch >= 1.9.0
polar_res_clamp = torch.clamp(polar_res, min_bound,
max_bound)
except TypeError:
polar_res_clamp = polar_res.clone()
for coor_idx in range(3):
polar_res_clamp[:, coor_idx][
polar_res[:, coor_idx] >
max_bound[coor_idx]] = max_bound[coor_idx]
polar_res_clamp[:, coor_idx][
polar_res[:, coor_idx] <
min_bound[coor_idx]] = min_bound[coor_idx]
res_coors = torch.floor(
(polar_res_clamp - min_bound) / polar_res_clamp.new_tensor(
self.voxel_layer.voxel_size)).int()
self.get_voxel_seg(res_coors, data_sample)
res_coors = F.pad(res_coors, (1, 0), mode='constant', value=i)
res_voxels = torch.cat((polar_res, res[:, :2], res[:, 3:]),
dim=-1)
voxels.append(res_voxels)
coors.append(res_coors)
voxels = torch.cat(voxels, dim=0)
coors = torch.cat(coors, dim=0)
elif self.voxel_type == 'minkunet':
voxels, coors = [], []
voxel_size = points[0].new_tensor(self.voxel_layer.voxel_size)
for i, (res, data_sample) in enumerate(zip(points, data_samples)):
res_coors = torch.round(res[:, :3] / voxel_size).int()
res_coors -= res_coors.min(0)[0]
res_coors_numpy = res_coors.cpu().numpy()
inds, point2voxel_map = self.sparse_quantize(
res_coors_numpy, return_index=True, return_inverse=True)
point2voxel_map = torch.from_numpy(point2voxel_map).cuda()
if self.training and self.max_voxels is not None:
if len(inds) > self.max_voxels:
inds = np.random.choice(
inds, self.max_voxels, replace=False)
inds = torch.from_numpy(inds).cuda()
if hasattr(data_sample.gt_pts_seg, 'pts_semantic_mask'):
data_sample.gt_pts_seg.voxel_semantic_mask \
= data_sample.gt_pts_seg.pts_semantic_mask[inds]
res_voxel_coors = res_coors[inds]
res_voxels = res[inds]
if self.batch_first:
res_voxel_coors = F.pad(
res_voxel_coors, (1, 0), mode='constant', value=i)
data_sample.batch_idx = res_voxel_coors[:, 0]
else:
res_voxel_coors = F.pad(
res_voxel_coors, (0, 1), mode='constant', value=i)
data_sample.batch_idx = res_voxel_coors[:, -1]
data_sample.point2voxel_map = point2voxel_map.long()
voxels.append(res_voxels)
coors.append(res_voxel_coors)
voxels = torch.cat(voxels, dim=0)
coors = torch.cat(coors, dim=0)
else:
raise ValueError(f'Invalid voxelization type {self.voxel_type}')
voxel_dict['voxels'] = voxels
voxel_dict['coors'] = coors
return voxel_dict
def get_voxel_seg(self, res_coors: Tensor,
data_sample: SampleList) -> None:
"""Get voxel-wise segmentation label and point2voxel map.
Args:
res_coors (Tensor): The voxel coordinates of points, Nx3.
data_sample: (:obj:`Det3DDataSample`): The annotation data of
every samples. Add voxel-wise annotation forsegmentation.
"""
if self.training:
pts_semantic_mask = data_sample.gt_pts_seg.pts_semantic_mask
voxel_semantic_mask, _, point2voxel_map = dynamic_scatter_3d(
F.one_hot(pts_semantic_mask.long()).float(), res_coors, 'mean',
True)
voxel_semantic_mask = torch.argmax(voxel_semantic_mask, dim=-1)
data_sample.gt_pts_seg.voxel_semantic_mask = voxel_semantic_mask
data_sample.point2voxel_map = point2voxel_map
else:
pseudo_tensor = res_coors.new_ones([res_coors.shape[0], 1]).float()
_, _, point2voxel_map = dynamic_scatter_3d(pseudo_tensor,
res_coors, 'mean', True)
data_sample.point2voxel_map = point2voxel_map
def ravel_hash(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""Get voxel coordinates hash for np.unique.
Args:
x (np.ndarray): The voxel coordinates of points, Nx3.
Returns:
np.ndarray: Voxels coordinates hash.
"""
assert x.ndim == 2, x.shape
x = x - np.min(x, axis=0)
x = x.astype(np.uint64, copy=False)
xmax = np.max(x, axis=0).astype(np.uint64) + 1
h = np.zeros(x.shape[0], dtype=np.uint64)
for k in range(x.shape[1] - 1):
h += x[:, k]
h *= xmax[k + 1]
h += x[:, -1]
return h
def sparse_quantize(self,
coords: np.ndarray,
return_index: bool = False,
return_inverse: bool = False) -> List[np.ndarray]:
"""Sparse Quantization for voxel coordinates used in Minkunet.
Args:
coords (np.ndarray): The voxel coordinates of points, Nx3.
return_index (bool): Whether to return the indices of the unique
coords, shape (M,).
return_inverse (bool): Whether to return the indices of the
original coords, shape (N,).
Returns:
List[np.ndarray]: Return index and inverse map if return_index and
return_inverse is True.
"""
_, indices, inverse_indices = np.unique(
self.ravel_hash(coords), return_index=True, return_inverse=True)
coords = coords[indices]
outputs = []
if return_index:
outputs += [indices]
if return_inverse:
outputs += [inverse_indices]
return outputs
为了方便展示,便直接对代码进行截图后进行解读,这一部分为forward()函数:


这里解释一下每个数据到底是什么,后面提取特征时需要使用:
voxels, 维度是[M,32,4]: 表示生成了 M 个 pillar 数据,其中每个 pillar 中的最大点云数量是 32,
如果一个 pillar 中的点云数量超过 32,那么便会进行随机采样选取 32 个点,
如果一个 pillar 中的点云数量少于 32,那么便会对这个 pillar 使用 0 样本填充,
4 表示点云的 xyzr,其中 xyz 表示点云的坐标,r 表示强度或反射值。
coors, 维度是[M,4]: 表示每个生成的 pillar 所在的 batch 编号和 zyx 轴坐标,
如果 batch_size = 8,那么 coors 的第一个维度的取值范围便是 [0, 7],
而且 coors 的第二个维度 z 恒为0,coors 的第三四个维度表示的是该 pillar 在激光点云坐标系下的 x 和 y 坐标。
num_points, 维度是[M,]: 代表了每个生成的 pillar 中实际有多少个有效的点,,因为 pillar 中点云不满足 32 会被 0 填充;
voxel_centers, 维度是[M,3]: 代表了每个生成的 pillar 的中心点所在的 zxy 坐标;
二、体素化网络
实现代码存放位置:mmdetection/mmdet3d/models/detectors/voxelnet.py
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
from typing import Tuple
from torch import Tensor
from mmdet3d.registry import MODELS
from mmdet3d.utils import ConfigType, OptConfigType, OptMultiConfig
from .single_stage import SingleStage3DDetector
@MODELS.register_module()
class VoxelNet(SingleStage3DDetector):
r"""`VoxelNet <https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.06396>`_ for 3D detection."""
def __init__(self,
voxel_encoder: ConfigType,
middle_encoder: ConfigType,
backbone: ConfigType,
neck: OptConfigType = None,
bbox_head: OptConfigType = None,
train_cfg: OptConfigType = None,
test_cfg: OptConfigType = None,
data_preprocessor: OptConfigType = None,
init_cfg: OptMultiConfig = None) -> None:
super().__init__(
backbone=backbone,
neck=neck,
bbox_head=bbox_head,
train_cfg=train_cfg,
test_cfg=test_cfg,
data_preprocessor=data_preprocessor,
init_cfg=init_cfg)
self.voxel_encoder = MODELS.build(voxel_encoder)
self.middle_encoder = MODELS.build(middle_encoder)
def extract_feat(self, batch_inputs_dict: dict) -> Tuple[Tensor]:
"""Extract features from points."""
voxel_dict = batch_inputs_dict['voxels']
voxel_features = self.voxel_encoder(voxel_dict['voxels'],
voxel_dict['num_points'],
voxel_dict['coors'])
batch_size = voxel_dict['coors'][-1, 0].item() + 1
x = self.middle_encoder(voxel_features, voxel_dict['coors'],
batch_size)
x = self.backbone(x)
if self.with_neck:
x = self.neck(x)
return x
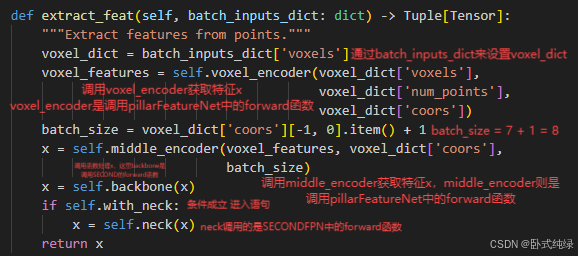
经过上述网络结构后得到的特征x,再送入Anchor3Dhead的检测头获得最终的类别、检测框和方向。【详细见第二章第三节】
三、PillarFeatureNet
实现代码位置:mmdetection/mmdet3d/models/voxel_encoders/pillar_encoder.py
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
from typing import Optional, Tuple
import torch
from mmcv.cnn import build_norm_layer
from mmcv.ops import DynamicScatter
from torch import Tensor, nn
from mmdet3d.registry import MODELS
from .utils import PFNLayer, get_paddings_indicator
@MODELS.register_module()
class PillarFeatureNet(nn.Module):
"""Pillar Feature Net.
The network prepares the pillar features and performs forward pass
through PFNLayers.
Args:
in_channels (int, optional): Number of input features,
either x, y, z or x, y, z, r. Defaults to 4.
feat_channels (tuple, optional): Number of features in each of the
N PFNLayers. Defaults to (64, ).
with_distance (bool, optional): Whether to include Euclidean distance
to points. Defaults to False.
with_cluster_center (bool, optional): [description]. Defaults to True.
with_voxel_center (bool, optional): [description]. Defaults to True.
voxel_size (tuple[float], optional): Size of voxels, only utilize x
and y size. Defaults to (0.2, 0.2, 4).
point_cloud_range (tuple[float], optional): Point cloud range, only
utilizes x and y min. Defaults to (0, -40, -3, 70.4, 40, 1).
norm_cfg ([type], optional): [description].
Defaults to dict(type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01).
mode (str, optional): The mode to gather point features. Options are
'max' or 'avg'. Defaults to 'max'.
legacy (bool, optional): Whether to use the new behavior or
the original behavior. Defaults to True.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels: Optional[int] = 4,
feat_channels: Optional[tuple] = (64, ),
with_distance: Optional[bool] = False,
with_cluster_center: Optional[bool] = True,
with_voxel_center: Optional[bool] = True,
voxel_size: Optional[Tuple[float]] = (0.2, 0.2, 4),
point_cloud_range: Optional[Tuple[float]] = (0, -40, -3, 70.4,
40, 1),
norm_cfg: Optional[dict] = dict(
type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),
mode: Optional[str] = 'max',
legacy: Optional[bool] = True):
super(PillarFeatureNet, self).__init__()
assert len(feat_channels) > 0
self.legacy = legacy
if with_cluster_center:
in_channels += 3
if with_voxel_center:
in_channels += 3
if with_distance:
in_channels += 1
self._with_distance = with_distance
self._with_cluster_center = with_cluster_center
self._with_voxel_center = with_voxel_center
# Create PillarFeatureNet layers
self.in_channels = in_channels
feat_channels = [in_channels] + list(feat_channels)
pfn_layers = []
for i in range(len(feat_channels) - 1):
in_filters = feat_channels[i]
out_filters = feat_channels[i + 1]
if i < len(feat_channels) - 2:
last_layer = False
else:
last_layer = True
pfn_layers.append(
PFNLayer(
in_filters,
out_filters,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
last_layer=last_layer,
mode=mode))
self.pfn_layers = nn.ModuleList(pfn_layers)
# Need pillar (voxel) size and x/y offset in order to calculate offset
self.vx = voxel_size[0]
self.vy = voxel_size[1]
self.vz = voxel_size[2]
self.x_offset = self.vx / 2 + point_cloud_range[0]
self.y_offset = self.vy / 2 + point_cloud_range[1]
self.z_offset = self.vz / 2 + point_cloud_range[2]
self.point_cloud_range = point_cloud_range
def forward(self, features: Tensor, num_points: Tensor, coors: Tensor,
*args, **kwargs) -> Tensor:
"""Forward function.
Args:
features (torch.Tensor): Point features or raw points in shape
(N, M, C).
num_points (torch.Tensor): Number of points in each pillar.
coors (torch.Tensor): Coordinates of each voxel.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Features of pillars.
"""
features_ls = [features]
# Find distance of x, y, and z from cluster center
if self._with_cluster_center:
points_mean = features[:, :, :3].sum(
dim=1, keepdim=True) / num_points.type_as(features).view(
-1, 1, 1)
f_cluster = features[:, :, :3] - points_mean
features_ls.append(f_cluster)
# Find distance of x, y, and z from pillar center
dtype = features.dtype
if self._with_voxel_center:
if not self.legacy:
f_center = torch.zeros_like(features[:, :, :3])
f_center[:, :, 0] = features[:, :, 0] - (
coors[:, 3].to(dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.vx +
self.x_offset)
f_center[:, :, 1] = features[:, :, 1] - (
coors[:, 2].to(dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.vy +
self.y_offset)
f_center[:, :, 2] = features[:, :, 2] - (
coors[:, 1].to(dtype).unsqueeze(1) * self.vz +
self.z_offset)
else:
f_center = features[:, :, :3]
f_center[:, :, 0] = f_center[:, :, 0] - (
coors[:, 3].type_as(features).unsqueeze(1) * self.vx +
self.x_offset)
f_center[:, :, 1] = f_center[:, :, 1] - (
coors[:, 2].type_as(features).unsqueeze(1) * self.vy +
self.y_offset)
f_center[:, :, 2] = f_center[:, :, 2] - (
coors[:, 1].type_as(features).unsqueeze(1) * self.vz +
self.z_offset)
features_ls.append(f_center)
if self._with_distance:
points_dist = torch.norm(features[:, :, :3], 2, 2, keepdim=True)
features_ls.append(points_dist)
# Combine together feature decorations
features = torch.cat(features_ls, dim=-1)
# The feature decorations were calculated without regard to whether
# pillar was empty. Need to ensure that
# empty pillars remain set to zeros.
voxel_count = features.shape[1]
mask = get_paddings_indicator(num_points, voxel_count, axis=0)
mask = torch.unsqueeze(mask, -1).type_as(features)
features *= mask
for pfn in self.pfn_layers:
features = pfn(features, num_points)
return features.squeeze(1)
@MODELS.register_module()
class DynamicPillarFeatureNet(PillarFeatureNet):
"""Pillar Feature Net using dynamic voxelization.
The network prepares the pillar features and performs forward pass
through PFNLayers. The main difference is that it is used for
dynamic voxels, which contains different number of points inside a voxel
without limits.
Args:
in_channels (int, optional): Number of input features,
either x, y, z or x, y, z, r. Defaults to 4.
feat_channels (tuple, optional): Number of features in each of the
N PFNLayers. Defaults to (64, ).
with_distance (bool, optional): Whether to include Euclidean distance
to points. Defaults to False.
with_cluster_center (bool, optional): [description]. Defaults to True.
with_voxel_center (bool, optional): [description]. Defaults to True.
voxel_size (tuple[float], optional): Size of voxels, only utilize x
and y size. Defaults to (0.2, 0.2, 4).
point_cloud_range (tuple[float], optional): Point cloud range, only
utilizes x and y min. Defaults to (0, -40, -3, 70.4, 40, 1).
norm_cfg ([type], optional): [description].
Defaults to dict(type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01).
mode (str, optional): The mode to gather point features. Options are
'max' or 'avg'. Defaults to 'max'.
legacy (bool, optional): Whether to use the new behavior or
the original behavior. Defaults to True.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels: Optional[int] = 4,
feat_channels: Optional[tuple] = (64, ),
with_distance: Optional[bool] = False,
with_cluster_center: Optional[bool] = True,
with_voxel_center: Optional[bool] = True,
voxel_size: Optional[Tuple[float]] = (0.2, 0.2, 4),
point_cloud_range: Optional[Tuple[float]] = (0, -40, -3, 70.4,
40, 1),
norm_cfg: Optional[dict] = dict(
type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),
mode: Optional[str] = 'max',
legacy: Optional[bool] = True):
super(DynamicPillarFeatureNet, self).__init__(
in_channels,
feat_channels,
with_distance,
with_cluster_center=with_cluster_center,
with_voxel_center=with_voxel_center,
voxel_size=voxel_size,
point_cloud_range=point_cloud_range,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
mode=mode,
legacy=legacy)
feat_channels = [self.in_channels] + list(feat_channels)
pfn_layers = []
# TODO: currently only support one PFNLayer
for i in range(len(feat_channels) - 1):
in_filters = feat_channels[i]
out_filters = feat_channels[i + 1]
if i > 0:
in_filters *= 2
norm_name, norm_layer = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, out_filters)
pfn_layers.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_filters, out_filters, bias=False), norm_layer,
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)))
self.num_pfn = len(pfn_layers)
self.pfn_layers = nn.ModuleList(pfn_layers)
self.pfn_scatter = DynamicScatter(voxel_size, point_cloud_range,
(mode != 'max'))
self.cluster_scatter = DynamicScatter(
voxel_size, point_cloud_range, average_points=True)
def map_voxel_center_to_point(self, pts_coors: Tensor, voxel_mean: Tensor,
voxel_coors: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""Map the centers of voxels to its corresponding points.
Args:
pts_coors (torch.Tensor): The coordinates of each points, shape
(M, 3), where M is the number of points.
voxel_mean (torch.Tensor): The mean or aggregated features of a
voxel, shape (N, C), where N is the number of voxels.
voxel_coors (torch.Tensor): The coordinates of each voxel.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Corresponding voxel centers of each points, shape
(M, C), where M is the number of points.
"""
# Step 1: scatter voxel into canvas
# Calculate necessary things for canvas creation
canvas_y = int(
(self.point_cloud_range[4] - self.point_cloud_range[1]) / self.vy)
canvas_x = int(
(self.point_cloud_range[3] - self.point_cloud_range[0]) / self.vx)
canvas_channel = voxel_mean.size(1)
batch_size = pts_coors[-1, 0] + 1
canvas_len = canvas_y * canvas_x * batch_size
# Create the canvas for this sample
canvas = voxel_mean.new_zeros(canvas_channel, canvas_len)
# Only include non-empty pillars
indices = (
voxel_coors[:, 0] * canvas_y * canvas_x +
voxel_coors[:, 2] * canvas_x + voxel_coors[:, 3])
# Scatter the blob back to the canvas
canvas[:, indices.long()] = voxel_mean.t()
# Step 2: get voxel mean for each point
voxel_index = (
pts_coors[:, 0] * canvas_y * canvas_x +
pts_coors[:, 2] * canvas_x + pts_coors[:, 3])
center_per_point = canvas[:, voxel_index.long()].t()
return center_per_point
def forward(self, features: Tensor, coors: Tensor) -> Tensor:
"""Forward function.
Args:
features (torch.Tensor): Point features or raw points in shape
(N, M, C).
coors (torch.Tensor): Coordinates of each voxel
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Features of pillars.
"""
features_ls = [features]
# Find distance of x, y, and z from cluster center
if self._with_cluster_center:
voxel_mean, mean_coors = self.cluster_scatter(features, coors)
points_mean = self.map_voxel_center_to_point(
coors, voxel_mean, mean_coors)
# TODO: maybe also do cluster for reflectivity
f_cluster = features[:, :3] - points_mean[:, :3]
features_ls.append(f_cluster)
# Find distance of x, y, and z from pillar center
if self._with_voxel_center:
f_center = features.new_zeros(size=(features.size(0), 3))
f_center[:, 0] = features[:, 0] - (
coors[:, 3].type_as(features) * self.vx + self.x_offset)
f_center[:, 1] = features[:, 1] - (
coors[:, 2].type_as(features) * self.vy + self.y_offset)
f_center[:, 2] = features[:, 2] - (
coors[:, 1].type_as(features) * self.vz + self.z_offset)
features_ls.append(f_center)
if self._with_distance:
points_dist = torch.norm(features[:, :3], 2, 1, keepdim=True)
features_ls.append(points_dist)
# Combine together feature decorations
features = torch.cat(features_ls, dim=-1)
for i, pfn in enumerate(self.pfn_layers):
point_feats = pfn(features)
voxel_feats, voxel_coors = self.pfn_scatter(point_feats, coors)
if i != len(self.pfn_layers) - 1:
# need to concat voxel feats if it is not the last pfn
feat_per_point = self.map_voxel_center_to_point(
coors, voxel_feats, voxel_coors)
features = torch.cat([point_feats, feat_per_point], dim=1)
return voxel_feats, voxel_coors
文件代码如上。

PFN代码如下所示,将Feature依次经过线性层——>标准化层——>RELU激活函数——>dim=1的维度取最大值的过程,最终获得Feature。
class PFNLayer(nn.Module):
"""Pillar Feature Net Layer.
The Pillar Feature Net is composed of a series of these layers, but the
PointPillars paper results only used a single PFNLayer.
Args:
in_channels (int): Number of input channels.
out_channels (int): Number of output channels.
norm_cfg (dict, optional): Config dict of normalization layers.
Defaults to dict(type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01).
last_layer (bool, optional): If last_layer, there is no
concatenation of features. Defaults to False.
mode (str, optional): Pooling model to gather features inside voxels.
Defaults to 'max'.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN1d', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),
last_layer=False,
mode='max'):
super().__init__()
self.fp16_enabled = False
self.name = 'PFNLayer'
self.last_vfe = last_layer
if not self.last_vfe:
out_channels = out_channels // 2
self.units = out_channels
self.norm = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, self.units)[1]
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_channels, self.units, bias=False)
assert mode in ['max', 'avg']
self.mode = mode
def forward(self, inputs, num_voxels=None, aligned_distance=None):
"""Forward function.
Args:
inputs (torch.Tensor): Pillar/Voxel inputs with shape (N, M, C).
N is the number of voxels, M is the number of points in
voxels, C is the number of channels of point features.
num_voxels (torch.Tensor, optional): Number of points in each
voxel. Defaults to None.
aligned_distance (torch.Tensor, optional): The distance of
each points to the voxel center. Defaults to None.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Features of Pillars.
"""
x = self.linear(inputs)
x = self.norm(x.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()).permute(0, 2,
1).contiguous()
x = F.relu(x)
if self.mode == 'max':
if aligned_distance is not None:
x = x.mul(aligned_distance.unsqueeze(-1))
x_max = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)[0]
elif self.mode == 'avg':
if aligned_distance is not None:
x = x.mul(aligned_distance.unsqueeze(-1))
x_max = x.sum(
dim=1, keepdim=True) / num_voxels.type_as(inputs).view(
-1, 1, 1)
if self.last_vfe:
return x_max
else:
x_repeat = x_max.repeat(1, inputs.shape[1], 1)
x_concatenated = torch.cat([x, x_repeat], dim=2)
return x_concatenated
代码解读如下:

这里只对部分内容进行讲解,欢迎大家在评论区讨论留言!
























 473
473

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








