离线推理参考之前的博客:
VLLM V1 offline推理1 - 基本流程_推理offline server-CSDN博客
VLLM V1 offline推理2 - Model Executor-CSDN博客
VLLM V1 part 3 - Scheduler-CSDN博客
等,可以看到在线和离线推理底层的一些组件是共用的。
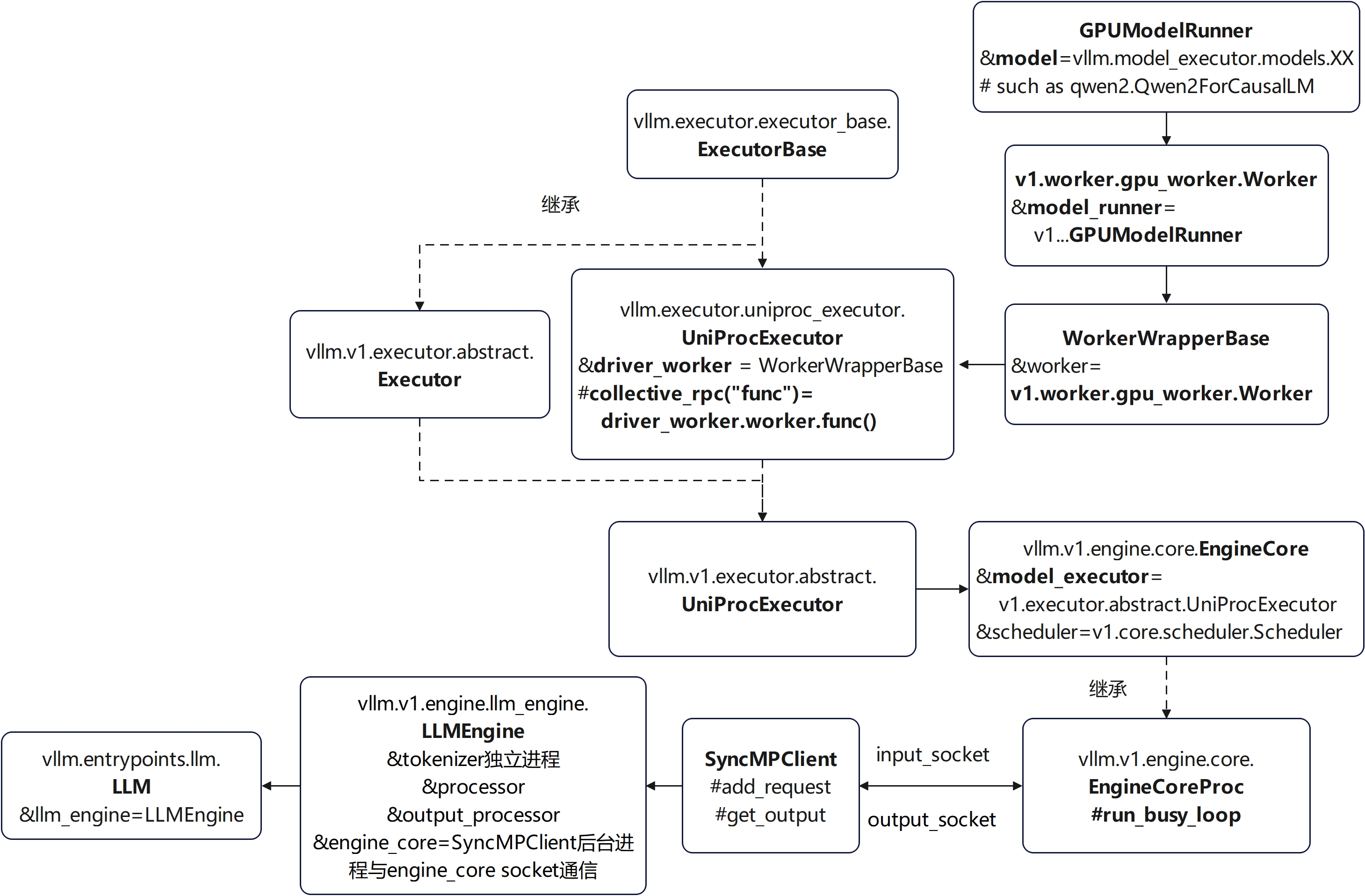
offline执行架构图-单进程
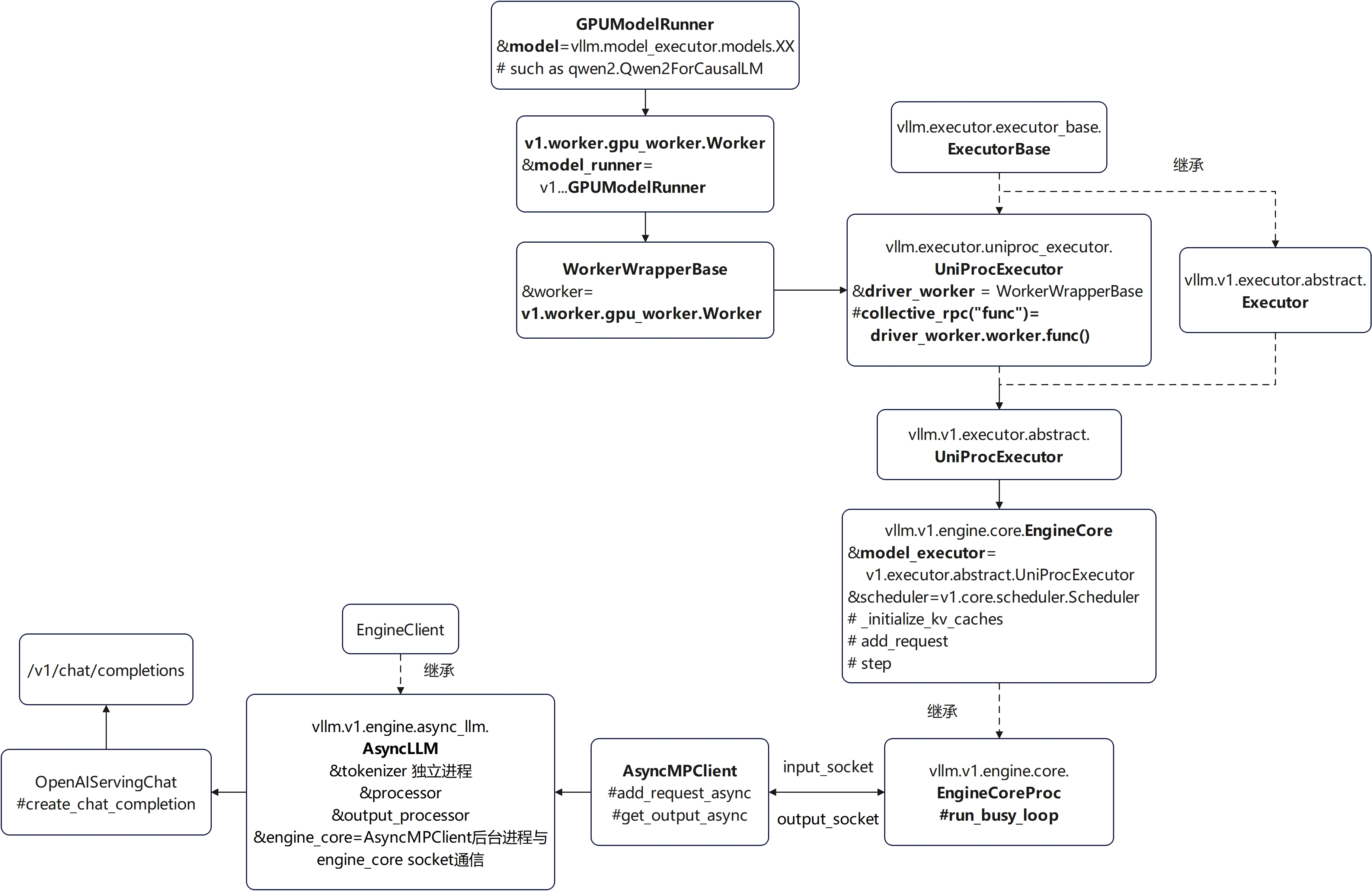
online执行架构图-单进程
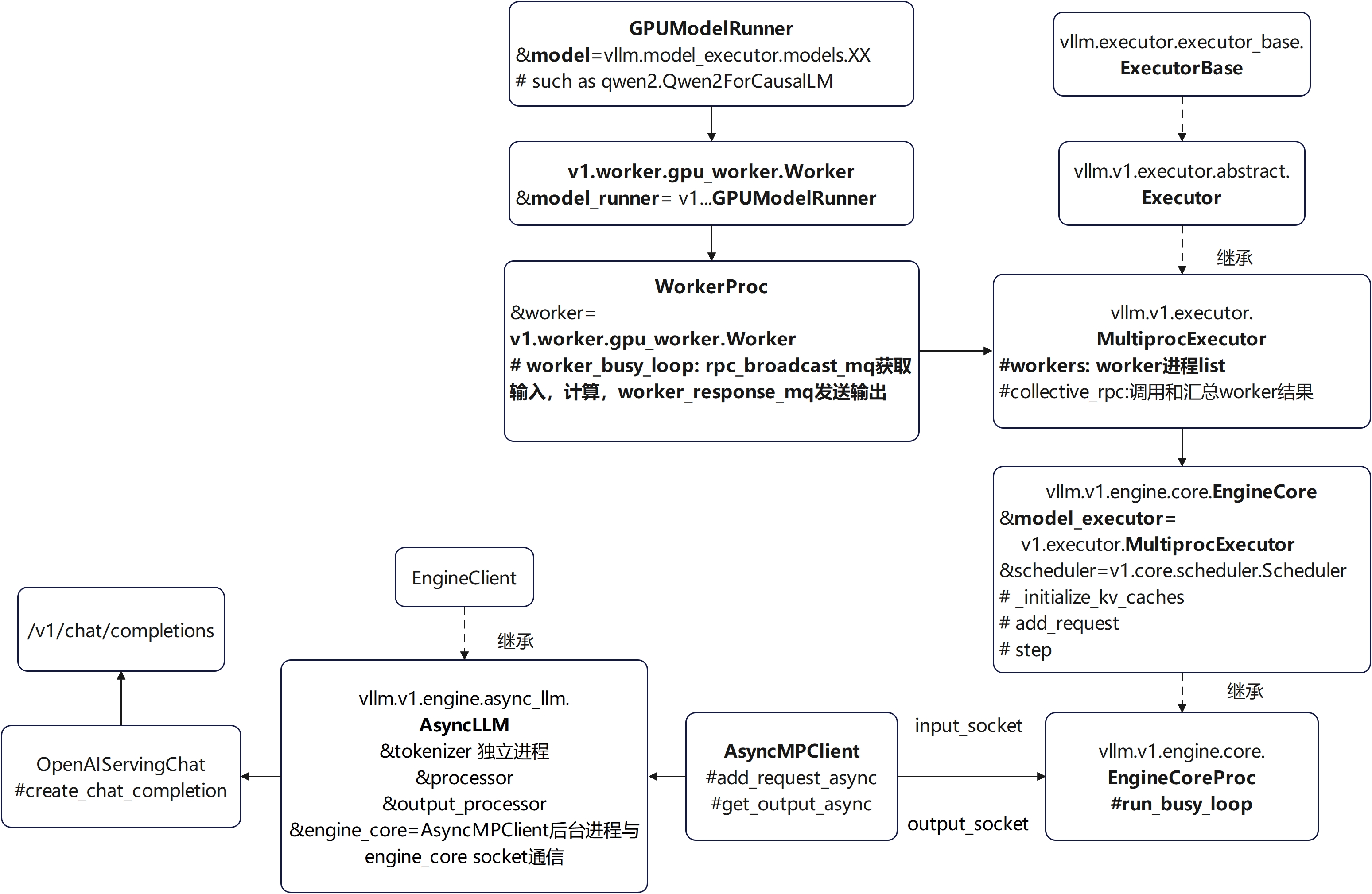
online执行架构图-多卡张量并行
AsyncLLM与LLMEngine看上去接口基本上是类似的,但是一个是async def,一个是常规python def。
V0架构简单对比
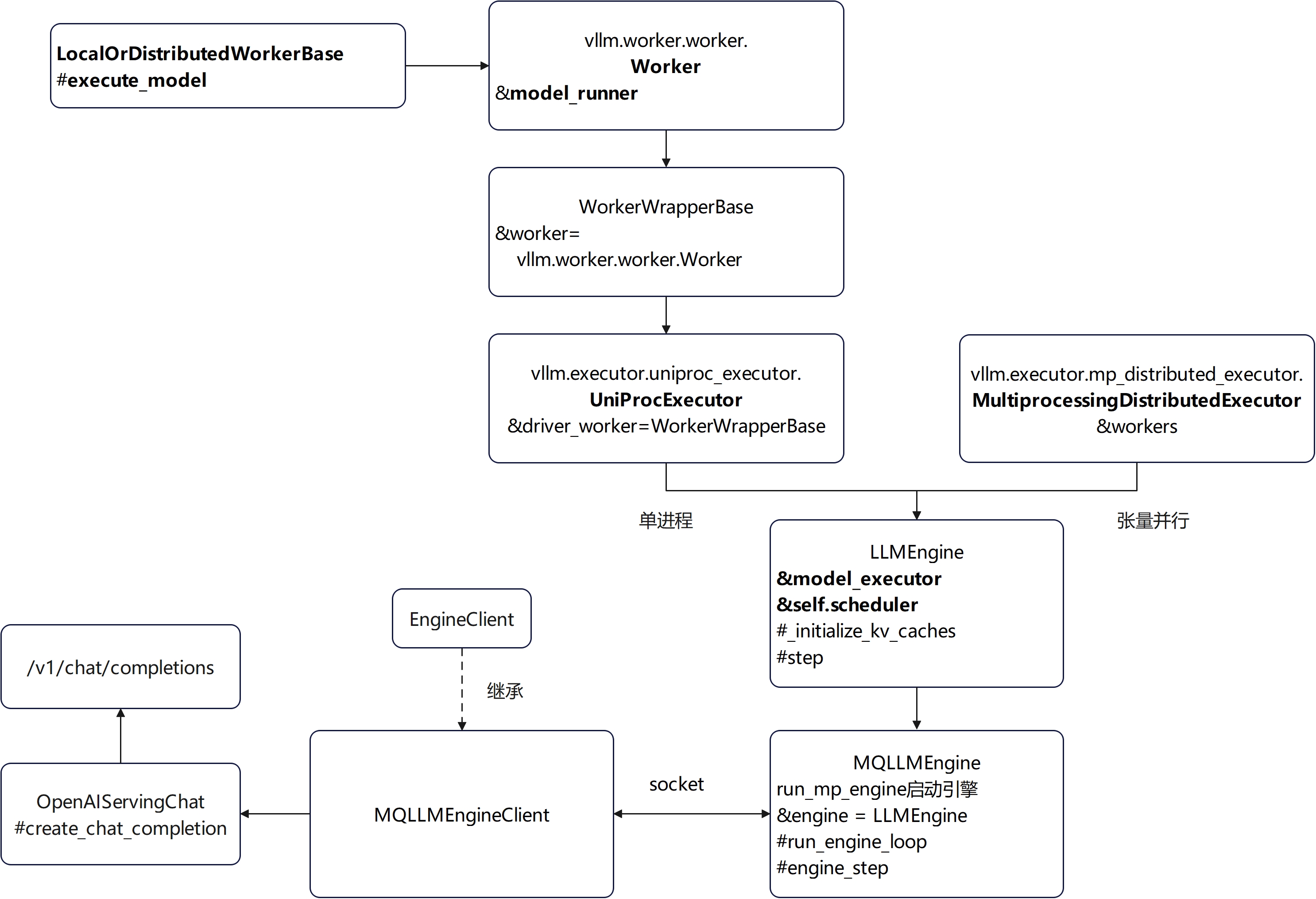
看了V1再看V0真是一团乱麻,V1架构确实更加简洁清晰易于理解。
VLLM V1在线推理example
export VLLM_USE_V1=1
vllm serve models/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct # -tp 4
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "models/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Who won the world series in 2020?"}
]
}'
vllm serve调用入口:vllm.scripts.py调用vllm\entrypoints\openai\api_server.py的run_server
run_server重要工作之一:
async def run_server(args, **uvicorn_kwargs) -> None:
# ...
async with build_async_engine_client(args) as engine_client:
app = build_app(args)
model_config = await engine_client.get_model_config()
await init_app_state(engine_client, model_config, app.state, args)
shutdown_task = await serve_http(
app,
host=args.host,
port=args.port)
@asynccontextmanager
async def build_async_engine_client(args: Namespace) -> AsyncIterator[EngineClient]:
# Context manager to handle engine_client lifecycle
# Ensures everything is shutdown and cleaned up on error/exit
engine_args = AsyncEngineArgs.from_cli_args(args)
async with build_async_engine_client_from_engine_args(engine_args, args.disable_frontend_multiprocessing) as engine:
yield engine
@asynccontextmanager
async def build_async_engine_client_from_engine_args(
engine_args: AsyncEngineArgs, disable_frontend_multiprocessing: bool = False,) -> AsyncIterator[EngineClient]:
# AsyncLLMEngine.
if (MQLLMEngineClient.is_unsupported_config(engine_args) or envs.VLLM_USE_V1 or disable_frontend_multiprocessing):
engine_client: Optional[EngineClient] = None
try:
engine_client = AsyncLLMEngine.from_engine_args(
engine_args=engine_args,
usage_context=UsageContext.OPENAI_API_SERVER)
yield engine_client
async def init_app_state(
engine_client: EngineClient,
model_config: ModelConfig,
state: State,
args: Namespace,
) -> None:
state.openai_serving_models = OpenAIServingModels(
engine_client=engine_client,
model_config=model_config,
)
await state.openai_serving_models.init_static_loras()
state.openai_serving_chat = OpenAIServingChat(
engine_client,
model_config,
state.openai_serving_models,
) if model_config.runner_type == "generate" else None
state.openai_serving_completion = OpenAIServingCompletion(
engine_client,
model_config,
state.openai_serving_models,
)build_async_engine_client_from_engine_args返回的引擎是
engine_client类型: vllm.v1.engine.async_llm.AsyncLLM。
if (MQLLMEngineClient.is_unsupported_config(engine_args) or envs.VLLM_USE_V1 or disable_frontend_multiprocessing)使用AsyncLLMEngine否则MQLLMEngineClient。
MQLLMEngineClient和AsyncLLMEngine的区别?
这里是AsyncLLMEngine.from_engine_args,为何返回的却是engine.async_llm.AsyncLLM对象?
因为vllm\engine\async_llm_engine.py中虽然定义了个单独的AsyncLLMEngine但是V1实际上被覆盖为了vllm.v1.engine.async_llm.AsyncLLM:
# TODO(v1): Remove this class proxy when V1 goes default.
if envs.VLLM_USE_V1:
from vllm.v1.engine.async_llm import AsyncLLM
AsyncLLMEngine = AsyncLLM # type: ignore
chat入口
@router.post("/v1/chat/completions")
@with_cancellation
async def create_chat_completion(request: ChatCompletionRequest,
raw_request: Request):
handler = chat(raw_request)
# handler: OpenAIServingChat
generator = await handler.create_chat_completion(request, raw_request)
if isinstance(generator, ErrorResponse):
return JSONResponse(content=generator.model_dump(), status_code=generator.code)
elif isinstance(generator, ChatCompletionResponse):
return JSONResponse(content=generator.model_dump())
return StreamingResponse(content=generator, media_type="text/event-stream")
def chat(request: Request) -> Optional[OpenAIServingChat]:
return request.app.state.openai_serving_chat
handler实际上是OpenAIServingChat。
generator可能是vllm.entrypoints.openai.protocol.ChatCompletionResponse




























 920
920

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










