对抗神经网络对抗攻击
In my recent post, I covered what type of cyberattacks could be carried out against neural networks. This brings by two other questions along with it; What are some defenses against these attacks to prevent the hassle of dealing with a spoiled model (during training and inferencing)? + What can be done to detect whether there are adversarial perturbations (messed up data) in the current model, during inferencing?
在我最近的帖子中 ,我介绍了可以对神经网络进行哪种类型的网络攻击。 这带来了另外两个问题。 有哪些针对这些攻击的防御措施,以防止处理被破坏的模型(在训练和推理过程中)的麻烦? +在推理过程中,如何检测当前模型中是否存在对抗性扰动 (混乱的数据)?
In this post, I will try to answer the second question based on a bunch of research papers as well as my attempt to interpret the methods proposed in those papers in simpler terms.
在本文中,我将尝试根据大量研究论文来回答第二个问题,并尝试以更简单的方式解释这些论文中提出的方法。
Recent researches have shown that deep learning methods can be vulnerable to maliciously generated adversarial examples. Adversarial inputs/perturbations are usually not visible to the human eye hence requires more work to detect.
最近的研究表明,深度学习方法可能容易受到恶意生成的对抗示例的攻击。 对抗性输入/干扰通常是人眼不可见的,因此需要更多工作来检测。
Therefore, various methods have been proposed attempting to correctly classify adversarial examples. However, most of these methods are not effective enough, which can be successfully attacked by more powerful adversaries.
因此,已经提出了各种方法来尝试正确地将对抗性示例分类。 但是,这些方法大多数都不足够有效,可以被更强大的对手成功攻击。
A few recent studies have focused on detecting adversarial examples. The strategies they explored can be divided into three groups: training a detector (secondary classifier), distributional/statistical detection, and prediction inconsistency.
最近的一些研究集中在检测对抗性例子。 他们探索的策略可以分为三类: 训练检测器(二级分类器),分布/统计检测和预测不一致。
检测对抗示例: (Detecting Adversarial Examples:)
基于二级分类的检测 (Secondary classification based detection)
Building a second classifier that attempts to detect adversarial examples:
构建第二个尝试检测对抗性示例的分类器:
If you haven’t already heard of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) it is now time.
如果您还没有听说过生成对抗网络(GANs),那么现在该了。
Briefly, ‘One neural network, called the generator, generates new data instances, while the other, the discriminator, evaluates them for authenticity; i.e. the discriminator decides whether each instance of data that it reviews belongs to the actual training dataset or not.’
简而言之, “一个神经网络(称为 生成器 )生成新的数据实例,而 另一个神经网络( 鉴别器 )评估它们的真实性; 即,判别器 决定它查看的每个数据实例是否属于实际的训练数据集 。”
Check this out for more information:
请查看此以获取更多信息:
Generative models can be used to defend against adversarial attacks and detect adversarial examples.
生成模型可用于防御对抗攻击并检测对抗示例。
The GAN model architecture involves two sub-models: a generator and a discriminator.
GAN模型架构包含两个子模型:生成器和鉴别器。
Generator: Model used to generate new plausible examples from the problem domain.
生成器:用于从问题域生成新的合理示例的模型。
Discriminator: Model that is used to classify examples as real (from the domain) or fake (generated — adversarial examples).
鉴别器:用于将示例分类为真实( 来自域 )或伪造( 生成的对抗示例 )的模型。
“Generative adversarial networks are based on a game-theoretic scenario in which the generator network must compete against an adversary. The generator network directly produces samples. Its adversary, the discriminator network, attempts to distinguish between samples drawn from the training data and samples drawn from the generator.”
“生成式对抗网络是基于博弈论的场景,其中生成器网络必须与对手竞争。 发生器网络直接产生样品。 它的对手是鉴别器网络,它试图区分从训练数据中提取的样本和从生成器中提取的样本。”
page 699 of Deep Learning by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville.
Ian Goodfellow,Yoshua Bengio和Aaron Courville撰写的《 深度学习》第699页。
Information from:
信息来自:
We augment classification networks by subnetworks, which branch off the main network at some layer and produce an output which is interpreted as the probability of the input being adversarial.
我们通过子网扩展分类网络,这些子网在某个层次上从主网络分支出来,并产生输出,该输出被解释为输入具有对抗性的可能性 。
For this, we first train the classification networks on the regular dataset as usual and subsequently generate adversarial examples for each data point of the train set using one of the methods such as the DeepFool method, Basic iterative methods, etc. We thus obtain a balanced, binary classification dataset of twice the size of the original dataset consisting of the original data and the corresponding adversarial examples. More in section 3.2 of ‘On detecting adversarial perturbations’.
为此,我们首先像往常一样在常规数据集上训练分类网络,然后使用DeepFool方法,Basic迭代方法等方法之一为训练集的每个数据点生成对抗性示例。因此,我们获得了平衡是二进制分类数据集,其大小是原始数据集的两倍,由原始数据和相应的对抗性示例组成。 第3.2节 “检测对抗性扰动”中的更多内容。
The main idea is to allow the normal dataset and the adversarial equivalent data points to ‘compete’ with discriminator model as the referee, calling out whether they tie or not (will the adversarial examples be called out?).
主要思想是允许正常数据集和对抗性等效数据点以区分模型作为裁判“竞争”,指出它们是否并列(会否列出对抗性示例?)。
分布/统计检测 (Distributional/Statistical detection)
The main limitation of statistical tests is that they cannot detect adversarial examples on a per-input basis. Thus, the defender must be able to collect a sufficiently large batch of adversarial inputs before it can detect the presence of adversaries.
统计测试的主要局限性在于,它们无法基于每个输入来检测对抗性示例。 因此,防御者必须能够收集足够多的对抗输入,然后才能检测到敌方的存在。
Statistical Hypothesis Testing: The framework of two-sample statistical hypothesis testing was introduced to determine whether two randomly drawn samples originate from the same distribution. A two-tailed test is carried out with a set null hypothesis and consequently an alternate hypothesis. The p-value returned is matched to a significance level, denoted α. The p-value is the probability that we obtain the observed outcome or a more extreme one. α relates to the confidence of the test (aka. significance level), typically at 0.05 or 0.01. We reject or accept the null hypothesis according to the p-value. Read more in section 2.3 of ‘On the (Statistical) Detection of Adversarial Examples’.
统计假设检验:引入了两样本统计假设检验的框架,以确定两个随机抽取的样本是否源自同一分布。 使用设定为零的假设并因此使用替代假设进行了两尾检验。 返回的p值与表示为α的显着性水平匹配。 p值是我们获得观察到的结果或更为极端的结果的概率。 α与测试的置信度(也就是显着性水平)有关,通常为0.05或0.01。 我们根据p值拒绝或接受零假设。 在“ 关于对抗性示例的(统计)检测 ”的第2.3节中了解更多信息。
Most of these tests are not appropriate when considering data with high dimensionality (check out Extra, scroll down — for PCA). This led to measuring the distance between two probabilities. In practice, this distance is formalized as the biased estimator of the true Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD).
当考虑具有高维度的数据时,这些测试中的大多数都不适合(请查看Extra,向下滚动-用于PCA)。 这导致测量两个概率之间的距离。 实际上,该距离被形式化为真实的最大平均差异(MMD)的有偏估计。
We want to see if we can determine, from a set of samples of data, whether a piece of data is normal or an adversarial perturbation.
我们想看看是否可以从一组数据样本中确定一条数据是正常的还是对抗性的扰动。
To achieve this, they use the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD), a statistical hypothesis test that answers the question “are these two sets drawn from the same underlying distribution?”
为此,他们使用了最大平均差异(MMD),这是一种统计假设检验,回答了以下问题:“这两套是从相同的基础分布中得出的吗?”
To test whether X1 and X2 are drawn from the same distribution, we use Fisher’s permutation test with the MMD test statistic. Read more in section 5.1 of ‘Adversarial Examples Are Not Easily Detected: Bypassing Ten Detection Methods’.
为了检验X1和X2是否来自同一分布,我们使用Fisher置换检验和MMD检验统计量。 在“难以发现专业示例:绕过十种检测方法”的第5.1节中阅读更多内容。
The researchers in the paper above state that they have repeated this experiment, producing targeted adversarial examples with C&W’s attack algorithm. Even when using a set of 100 images, MMD failed to reject the null hypothesis (p > 0.05). Since MMD is one of the most powerful multidimensional statistical tests, and even it is not effective, the researchers have unfortunately argued that without significant modification, statistical tests will not be able to detect adversarial examples.
上述论文的研究人员指出,他们已经重复了该实验,并利用C&W的攻击算法生成了有针对性的对抗示例。 即使使用一组100张图像,MMD也无法拒绝原假设(p> 0.05)。 由于MMD是最强大的多维统计测试之一,即使它没有效果,不幸的是,研究人员认为,如果不进行重大修改,统计测试将无法检测出对抗性示例。
Lastly, the paper presents a defense they call kernel density estimation. They use a Gaussian Mixture Model to model outputs from the final hidden layer of a neural network and argue that adversarial examples belong to a different distribution than that of the original one. I won’t get into it here but you can read more in section 5.2 of the same paper mentioned above for MMD.
最后,本文提出了一种称为核密度估计的防御方法。 他们使用高斯混合模型对神经网络最终隐藏层的输出进行建模,并认为对抗性示例与原始示例的分布不同。 我在这里不做介绍,但是您可以在上面提到的MMD的同一篇文章的5.2节中阅读更多内容。
预测不一致 (Prediction inconsistency)
The basic idea of prediction inconsistency is to measure the disagreement among several models in predicting an unknown input example, since one adversarial example may not fool every DNN model. Briefly, we should be able to compare the accuracies and confidences of detections across different datasets produced by various neural network models to get an idea as to whether prediction inconsistency is real. A detection technique called Bayesian neural network (BNN)uncertainty was proposed.
预测不一致的基本思想是在预测未知输入示例时测量几种模型之间的分歧,因为一个对抗性示例可能不会欺骗每个DNN模型 。 简而言之,我们应该能够比较由各种神经网络模型产生的不同数据集上的检测结果的准确性和可信度,从而获得有关预测不一致是否真实的想法。 提出了一种称为贝叶斯神经网络(BNN)不确定性的检测技术。
In a paper called On the Validity of Bayesian Neural Networks for Uncertainty Estimation, some data is provided on the confidence and consequent accuracy of detections of various DNNs and BNNs, using three separate, image classification, datasets (CIFAR-10, SVHN, and FashionMNIST).
在一篇名为《不确定性估计的贝叶斯神经网络的有效性》的论文中,使用三个单独的图像分类数据集(CIFAR-10,SVHN和FashionMNIST),提供了有关各种DNN和BNN检测的置信度和随之而来的准确性的一些数据。 )。
This paper describes a study that empirically evaluates and compares Bayesian Neural Networks to their equivalent point estimate Deep Neural Networks to quantify the predictive uncertainty induced by their parameters, as well as their performance in view of this uncertainty.
本文介绍了一项根据经验评估和比较贝叶斯神经网络与其等效点估计深度神经网络的研究,以量化由其参数引起的预测不确定性以及鉴于此不确定性而产生的性能。
You can read more on it yourself (section 5 of the paper) but I will briefly present the conclusion here to make a point.
您可以自己阅读更多内容(本文的第5节),但在此我将简要介绍结论以阐明观点。
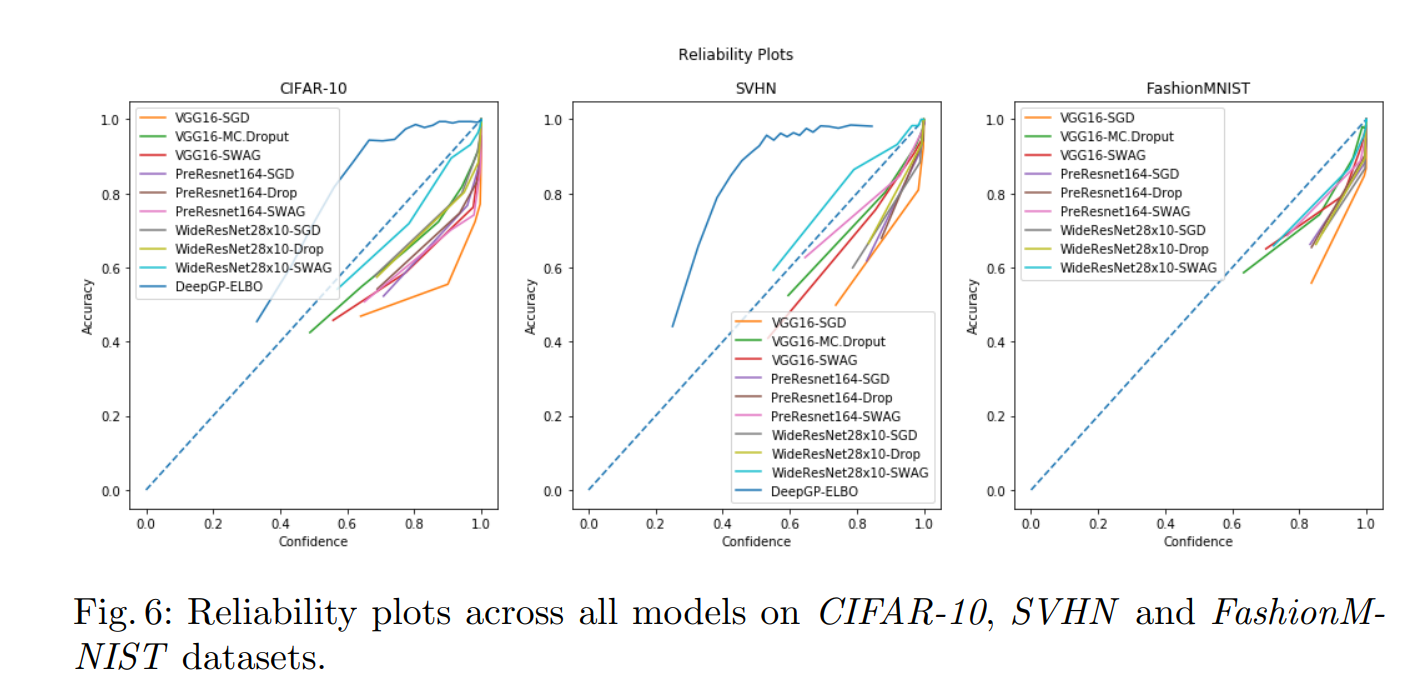
It may be a little hard to see — briefly, the orange one and the other cluster of models nearest to it is the BNNs (high confidences and accuracies) while the dark blue one (relatively lower confidences hence lower accuracies) and some in the cluster nearer to the dark blue one are DNNs. These results suggest that the Bayesian methods are better at identifying out of sample instances.
可能很难看到-简而言之,橙色模型和与其最接近的另一类模型是BNN(高置信度和准确度),而深蓝色模型(相对较低的置信度和较低准确度)以及其中的一些模型接近深蓝色的是DNN。 这些结果表明,贝叶斯方法可以更好地识别出样本实例。
In conclusion, as we have shown that point estimate deep neural networks indeed suffer from high uncertainties. Bayesian deep neural networks provide a principled and viable alternative that allows the models to be informed about the uncertainty in their parameters and at the same time exhibits a lower degree of sensitivity against noisy samples compared to their point estimate DNN. This suggests that this is a promising research direction for improving the performance of deep neural networks.
总而言之,正如我们已经表明的那样,深度神经网络的点估计确实存在很大的不确定性 。 贝叶斯深度神经网络提供了一种原则上可行的替代方法,该方法可让模型了解其参数的不确定性,并且与点估计DNN相比, 对噪声样本的敏感性较低 。 这表明这是改善深度神经网络性能的有前途的研究方向。
额外: (Extra:)
主成分分析防御+检测 (Principal component analysis defense + detection)
I have found a paper recently that proposed dimensionality reduction as a method of defense (yes, not detection) against evasion attacks on ML classifiers (read more on evasion attacks on my post here). Briefly, a method for incorporating dimensionality reduction via Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to enhance the resilience of machine learning has been investigated, targeting both the classification and the training phase.
我发现了一个纸最近,提出降维作为防御的方法(是的,不是检测)对上ML分类逃避攻击(阅读更多的在我的岗位逃避攻击这里 )。 简而言之,针对分类和训练阶段,已经研究了一种通过主成分分析(PCA)合并降维以增强机器学习弹性的方法。
With this method, you could detect the statistical properties of network parameters in use.
使用此方法,您可以检测使用中的网络参数的统计属性。
The main idea of principal component analysis (PCA) is to reduce the dimensionality of a data set consisting of many variables correlated with each other, either heavily or lightly, while retaining the variation present in the dataset, up to the maximum extent. — Principal Component Analysis Tutorial.
主成分分析(PCA)的主要思想是减小包含彼此相关的多个变量的数据集的维数,无论是重度还是轻度,同时最大程度地保留数据集中的变化。 — 主成分分析教程。
Here is a post I found recently on it:
这是我最近在上面找到的帖子:
翻译自: https://medium.com/swlh/how-would-you-detect-an-adversarial-attack-26ca576d0adc
对抗神经网络对抗攻击







 本文探讨了如何检测对抗性攻击,特别是在神经网络领域的应用。随着计算机视觉和深度学习的发展,对抗攻击成为了一个重要的安全问题。通过理解这些攻击的原理,我们可以采取措施来防御和检测针对神经网络的恶意行为。
本文探讨了如何检测对抗性攻击,特别是在神经网络领域的应用。随着计算机视觉和深度学习的发展,对抗攻击成为了一个重要的安全问题。通过理解这些攻击的原理,我们可以采取措施来防御和检测针对神经网络的恶意行为。














 5237
5237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








