该例程演示如何使用距离传感器的数据创建或更新地图,以及如何使用Robotics System Toolbox™中的转换函数(如“quat2eul”和“axang2rotm”)。该例程根据距离传感器的读数和机器人的已知位姿创建地图。出于本例程的目的,距离传感器记录和机器人位姿作为消息存储于rosbag文件,该文件由Gazebo仿真器中的仿真机器人TurtleBot生成。Gazebo仿真器还发布了机器人的位置到“gazebo/model_states”话题上,这在本例程中将作为地面真实机器人位姿的来源。
从rosbag(记录文件)导入传感器记录和机器人位姿
使用“rosbag”函数,根据已有的ROS包文件,创建一个“robotics.ros.BagSelection”对象:
filePath = fullfile(fileparts(which('MapUpdateUsingSensorDataExample')), 'data', 'rosbagWithSensorData.bag');
bag = rosbag(filePath);
从rosbag文件提取机器人的位姿和激光扫描仪的数据,在本例中,使用了一个文件助手“exampleHelperReadPoseAndSensorMsgs”。
[poses, laserRanges] = exampleHelperReadPoseAndSensorMsgs(bag);
定义空地图
定义一个高分辨率的地图以精确地捕捉传感器的读数,此处创建一个大小为,精度为每米20个网格的地图。
map = robotics.BinaryOccupancyGrid(16,16,20)
map =
BinaryOccupancyGrid with properties:
GridSize: [320 320]
Resolution: 20
XWorldLimits: [0 16]
YWorldLimits: [0 16]
GridLocationInWorld: [0 0]
定义原点作为地图的中心,当前,世界的限制是X和Y坐标的0到16米。设置左下角的网格为[-8,-8],以转换世界的原点为网格的中心。新的世界限制将是X和Y坐标的-8米到8米。
map.GridLocationInWorld = [-8 -8]
map =
BinaryOccupancyGrid with properties:
GridSize: [320 320]
Resolution: 20
XWorldLimits: [-8 8]
YWorldLimits: [-8 8]
GridLocationInWorld: [-8 -8]
显示空地图和它的边界:
show(map)
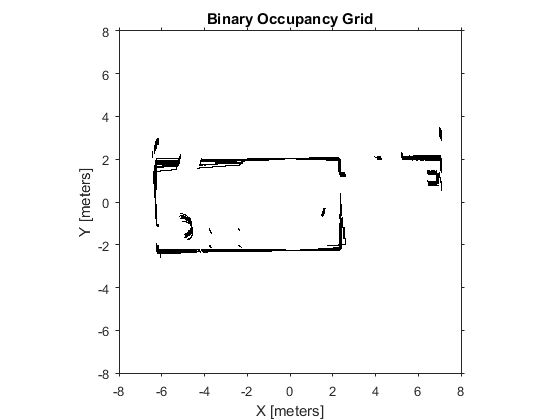
基于传感器记录跟新地图
距离传感器用于探测障碍物,这可用于更新地图。传感器读数在机器人参考坐标系上,用户需要转换该读数到世界坐标系(即地图定义的坐标系)。为了转换机器人坐标系到世界坐标系,用户需要机器人的当前方向和位置,rosbag文件包含机器人位姿的记录。本例应用的rosbag文件,在机器人围绕原点旋转扫描环境过程中获取。因此,本例程中,用户只需要使用机器人的当前方向将传感器的读数从机器人坐标系旋转到世界坐标系中。
% Loop over all the messages
for j=1:length(poses)
% Define the Quaternion in a vector form
q = [poses{j}.Orientation.W poses{j}.Orientation.X poses{j}.Orientation.Y poses{j}.Orientation.Z];
% Convert the Quaternion into Euler angles
orientation = quat2eul(q, 'ZYX');
% The z-direction rotation component is the heading of the
% robot. Use the heading value along with the z-rotation axis to define
% the rotation matrix
rotMatrixAlongZ = axang2rotm([0 0 1 orientation(1)]);
% Convert sensor values (originally in the robot's frame) into the
% world coordinate frame. This is a 2D coordinate transformation, so
% only the first two rows and columns are used from the rotation matrix.
rangesInWorldFrame = rotMatrixAlongZ(1:2,1:2) * laserRanges{j}';
% Update map based on laser scan data in the world coordinate frame.
% Populate the map, using the setOccupancy function, by setting the
% obstacle location on the map as occupied for every sensor reading that
% detects obstacles
setOccupancy(map, rangesInWorldFrame', 1);
end
显示更新的地图,此时包含了所有传感器的读数。
show(map)





















 1352
1352











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








