APB slave设计spec
参考ARM公司的例子得到的,链接如下,
APB3.0例子
APB4.0例子

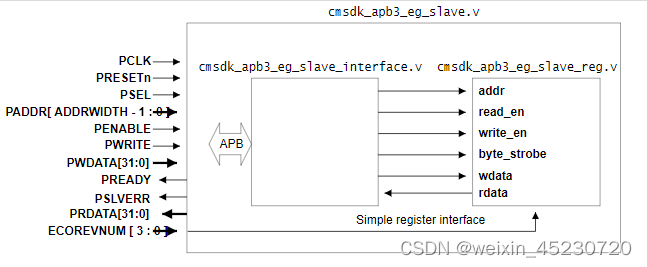
一个简单的APB从接口。
32位数据总线,端独立。对于APB3从机示例,数据处理仅为32位。对于APB4从机示例,使用PSTRB信号对单个字节执行写操作。
数据传输需要两个时钟周期。
4个32位RW寄存器
该模块是一个基于APB协议完成寄存器配置或读取的设计实例,上面APB相关的信号都介绍过,这里不再重复介绍,其中的ECOREVNUM的意思是ECO revision number,如果没有用到ARM的ECO的话,将该信号固定为全0即可。右边这个slave_reg实际上就对应我们自己设计的IP的寄存器配置部分。这一部分的接口是native interface,也就是没有考虑通用性的原生接口。想要通过APB总线对其进行配置,就需要通过slave_interface这个模块进行协议转换,进而完成APB协议的传输.
- 不支持反压
- 不支持错误传输
- 支持4个RW类型的寄存器
- 支持12个RO类型寄存器
- 支持字节选通信号
APB slave设计代码
apb_slave_interface代码
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// The confidential and proprietary information contained in this file may
// only be used by a person authorised under and to the extent permitted
// by a subsisting licensing agreement from ARM Limited.
//
// (C) COPYRIGHT 2010-2015 ARM Limited or its affiliates.
// ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
//
// This entire notice must be reproduced on all copies of this file
// and copies of this file may only be made by a person if such person is
// permitted to do so under the terms of a subsisting license agreement
// from ARM Limited.
//
// Version and Release Control Information:
//
// File Revision : $Revision: 275084 $
// File Date : $Date: 2014-03-27 15:09:11 +0000 (Thu, 27 Mar 2014) $
//
// Release Information : Cortex-M0 DesignStart-r1p0-00rel0
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Verilog-2001 (IEEE Std 1364-2001)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Abstract : AMBA APB4 example slave interface module. Transfer APB BUS protocol to
// simple register read write protocol
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module cmsdk_apb4_eg_slave_interface #(
// parameter for address width
parameter ADDRWIDTH = 12)
(
// IO declaration
input wire pclk, // pclk
input wire presetn, // reset
// apb interface inputs
input wire psel,
input wire [ADDRWIDTH-1:0] paddr,
input wire penable,
input wire pwrite,
input wire [31:0] pwdata,
input wire [3:0] pstrb,
// apb interface outputs
output wire [31:0] prdata,
output wire pready,
output wire pslverr,
//Register interface
output wire [ADDRWIDTH-1:0] addr,
output wire read_en,
output wire write_en,
output wire [3:0] byte_strobe,
output wire [31:0] wdata,
input wire [31:0] rdata);
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic start
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// APB interface
assign pready = 1'b1; //always ready. Can be customized to support waitstate if required.
assign pslverr = 1'b0; //always OKAY. Can be customized to support error response if required.
// register read and write signal
assign addr = paddr;
assign read_en = psel & (~pwrite); // assert for whole apb read transfer
assign write_en = psel & (~penable) & pwrite; // assert for 1st cycle of write transfer
// It is also possible to change the design to perform the write in the 2nd
// APB cycle. E.g.
// assign write_en = psel & penable & pwrite;
// However, if the design generate waitstate, this expression will result
// in write_en being asserted for multiple cycles.
assign byte_strobe = pstrb;
assign wdata = pwdata;
assign prdata = rdata;
`ifdef ARM_APB_ASSERT_ON
`include "std_ovl_defines.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------
// Assertions
// ------------------------------------------------------------
// Check error response should not be generated if not selected
assert_never
#(`OVL_ERROR,
`OVL_ASSERT,
"Error! Should not generate error response if not selected")
u_ovl_apb4_eg_slave_response_illegal
(.clk (pclk),
.reset_n (presetn),
.test_expr (pslverr & pready & (~psel))
);
`endif
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic end
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
endmodule
我们对其进行分析:
- 首先由于不支持反压和错误传输,因此将pready固定为1,pslverr固定为0。
- APB传输进来的paddr可以直接赋给addr,作为读写的地址。
- read_en需要在psel为1且pwrite为0的时候拉高。这实际上是希望在整个读传输过程中都让read_en信号有效。读者可能就想问了,读应该对应着两个阶段吗?不需要判断吗?实际上读的话,master那边自己控制好就行了,对于slave而言完全可以在第一拍和第二拍都把rdata提供好,这个是没有关系的
- write_en则对应着setup phase,实际上在这个场景中修改write_en的逻辑让该信号对应着access phase也是可以的
- 其它的信号直接赋值就可以,应该很好理解.
apb_slave_reg代码
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// The confidential and proprietary information contained in this file may
// only be used by a person authorised under and to the extent permitted
// by a subsisting licensing agreement from ARM Limited.
//
// (C) COPYRIGHT 2010-2015 ARM Limited or its affiliates.
// ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
//
// This entire notice must be reproduced on all copies of this file
// and copies of this file may only be made by a person if such person is
// permitted to do so under the terms of a subsisting license agreement
// from ARM Limited.
//
// Version and Release Control Information:
//
// File Revision : $Revision: 275084 $
// File Date : $Date: 2014-03-27 15:09:11 +0000 (Thu, 27 Mar 2014) $
//
// Release Information : Cortex-M0 DesignStart-r1p0-00rel0
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Verilog-2001 (IEEE Std 1364-2001)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Abstract : APB example slave register module.
// Support AMBA APB4
// This is an example slave with four 32-bit registers, provides write
// and read operation. The Data and address valid at the same clock
// cycle. Byte strobe signal is supported.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module cmsdk_apb4_eg_slave_reg #(
// parameter for address width
parameter ADDRWIDTH = 12)
(
input wire pclk, // clock
input wire presetn, // reset
// Register interface
input wire [ADDRWIDTH-1:0] addr,
input wire read_en,
input wire write_en,
input wire [3:0] byte_strobe,
input wire [31:0] wdata,
input wire [3:0] ecorevnum,
output reg [31:0] rdata);
// Local ID parameters, APB4 example slave has part number of 819
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID4 = 32'h00000004; // 0xFD0 : PID 4
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID5 = 32'h00000000; // 0xFD4 : PID 5
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID6 = 32'h00000000; // 0xFD8 : PID 6
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID7 = 32'h00000000; // 0xFDC : PID 7
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID0 = 32'h00000019; // 0xFE0 : PID 0 APB4 Example slave part number[7:0]
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID1 = 32'h000000B8; // 0xFE4 : PID 1 [7:4] jep106_id_3_0. [3:0] part number [11:8]
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID2 = 32'h0000001B; // 0xFE8 : PID 2 [7:4] revision, [3] jedec_used. [2:0] jep106_id_6_4
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID3 = 32'h00000000; // 0xFEC : PID 3
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID0 = 32'h0000000D; // 0xFF0 : CID 0
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID1 = 32'h000000F0; // 0xFF4 : CID 1 PrimeCell class
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID2 = 32'h00000005; // 0xFF8 : CID 2
localparam ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID3 = 32'h000000B1; // 0xFFC : CID 3
// Note : Customer changing the design should modify
// - jep106 value (www.jedec.org)
// - part number (customer define)
// - Optional revision and modification number (e.g. rXpY)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// internal signals
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
reg [31:0] data0;
reg [31:0] data1;
reg [31:0] data2;
reg [31:0] data3;
wire [3:0] wr_sel;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic start
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Address decoding for write operations
assign wr_sel[0] = ((addr[(ADDRWIDTH-1):2]==10'b0000000000)&(write_en)) ? 1'b1: 1'b0;
assign wr_sel[1] = ((addr[(ADDRWIDTH-1):2]==10'b0000000001)&(write_en)) ? 1'b1: 1'b0;
assign wr_sel[2] = ((addr[(ADDRWIDTH-1):2]==10'b0000000010)&(write_en)) ? 1'b1: 1'b0;
assign wr_sel[3] = ((addr[(ADDRWIDTH-1):2]==10'b0000000011)&(write_en)) ? 1'b1: 1'b0;
// register write, byte enable
// Data register: data0
always @(posedge pclk or negedge presetn)
begin
if (~presetn)
begin
data0 <= {32{1'b0}}; // Reset data 0 to 0x00000000
end
else if (wr_sel[0])
begin
if (byte_strobe[0])
data0[ 7: 0] <= wdata[ 7: 0];
if (byte_strobe[1])
data0[15: 8] <= wdata[15: 8];
if (byte_strobe[2])
data0[23:16] <= wdata[23:16];
if (byte_strobe[3])
data0[31:24] <= wdata[31:24];
end
end
// Data register: data1
always @(posedge pclk or negedge presetn)
begin
if (~presetn)
begin
data1 <= {32{1'b0}}; // Reset data 1 to 0x00000000
end
else if (wr_sel[1])
begin
if (byte_strobe[0])
data1[ 7: 0] <= wdata[7:0];
if (byte_strobe[1])
data1[15: 8] <= wdata[15:8];
if (byte_strobe[2])
data1[23:16] <= wdata[23:16];
if (byte_strobe[3])
data1[31:24] <= wdata[31:24];
end
end
// Data register: data2
always @(posedge pclk or negedge presetn)
begin
if (~presetn)
begin
data2 <= {32{1'b0}}; // Reset data 2 to 0x00000000
end
else if (wr_sel[2])
begin
if (byte_strobe[0])
data2[ 7: 0] <= wdata[ 7: 0];
if (byte_strobe[1])
data2[15: 8] <= wdata[15: 8];
if (byte_strobe[2])
data2[23:16] <= wdata[23:16];
if (byte_strobe[3])
data2[31:24] <= wdata[31:24];
end
end
// Data register: data3
always @(posedge pclk or negedge presetn)
begin
if (~presetn)
begin
data3 <= {32{1'b0}}; // Reset data 3 to 0x00000000
end
else if (wr_sel[3])
begin
if (byte_strobe[0])
data3[ 7: 0] <= wdata[ 7: 0];
if (byte_strobe[1])
data3[15: 8] <= wdata[15: 8];
if (byte_strobe[2])
data3[23:16] <= wdata[23:16];
if (byte_strobe[3])
data3[31:24] <= wdata[31:24];
end
end
// register read
always @ (read_en or addr or data0 or data1 or data2 or data3 or ecorevnum)
begin
case (read_en)
1'b1:
begin
if (addr[11:4] == 8'h00) begin
case(addr[3:2])
2'b00: rdata = data0;
2'b01: rdata = data1;
2'b10: rdata = data2;
2'b11: rdata = data3;
default: rdata = {32{1'bx}};
endcase
end
else if (addr[11:6] == 6'h3F) begin
case(addr[5:2])
// Peripheral IDs and Component IDs.
// AHB example slave has part number of 818
4'b0100: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID4; // 0xFD0 : PID 4
4'b0101: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID5; // 0xFD4 : PID 5
4'b0110: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID6; // 0xFD8 : PID 6
4'b0111: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID7; // 0xFDC : PID 7
4'b1000: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID0; // 0xFE0 : PID 0 APB Example slave part number[7:0]
4'b1001: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID1; // 0xFE4 : PID 1 [7:4] jep106_id_3_0. [3:0] part number [11:8]
4'b1010: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID2; // 0xFE8 : PID 2 [7:4] revision, [3] jedec_used. [2:0] jep106_id_6_4
4'b1011: rdata ={ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_PID3[31:8], ecorevnum[3:0], 4'h0};
// 0xFEC : PID 3 [7:4] ECO rev number, [3:0] modification number
4'b1100: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID0; // 0xFF0 : CID 0
4'b1101: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID1; // 0xFF4 : CID 1 PrimeCell class
4'b1110: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID2; // 0xFF8 : CID 2
4'b1111: rdata = ARM_CMSDK_APB4_EG_SLAVE_CID3; // 0xFFC : CID 3
// Note : Customer changing the design should modify
// - jep106 value (www.jedec.org)
// - part number (customer define)
// - Optional revision and modification number (e.g. rXpY)
4'b0000, 4'b0001,4'b0010,4'b0011: rdata = {32'h00000000}; // default
default: rdata = {32{1'bx}}; // x propagation
endcase
end
else begin
rdata = {32'h00000000}; // default
end
end
1'b0:
begin
rdata = {32{1'b0}};
end
default:
begin
rdata = {32{1'bx}};
end
endcase
end
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic end
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
endmodule我们对其进行分析:
- 首先由于分为RW寄存器和RO寄存器。这里确定写地址是否在规定区间,同时写使能是否有效,以及byte_strobe信号,来决定要不要写,写哪个字节。
- 读的话就比较简单了,当读使能有效,根据地址信号决定rdata。实际上这就是个MUX选择逻辑。根据read_en加地址从多个寄存器的Q端选出某一个来。
顶层apb4_eg_slave设计代码
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// The confidential and proprietary information contained in this file may
// only be used by a person authorised under and to the extent permitted
// by a subsisting licensing agreement from ARM Limited.
//
// (C) COPYRIGHT 2010-2015 ARM Limited or its affiliates.
// ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
//
// This entire notice must be reproduced on all copies of this file
// and copies of this file may only be made by a person if such person is
// permitted to do so under the terms of a subsisting license agreement
// from ARM Limited.
//
// Version and Release Control Information:
//
// File Revision : $Revision: 275084 $
// File Date : $Date: 2014-03-27 15:09:11 +0000 (Thu, 27 Mar 2014) $
//
// Release Information : Cortex-M0 DesignStart-r1p0-00rel0
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Verilog-2001 (IEEE Std 1364-2001)
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Abstract : APB example slave, support AMBA APB4.
// slave is always ready and response is always OKAY.
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
module cmsdk_apb4_eg_slave #(
// parameter for address width
parameter ADDRWIDTH = 12)
(
// IO declaration
input wire PCLK, // pclk
input wire PRESETn, // reset
// apb interface inputs
input wire PSEL,
input wire [ADDRWIDTH-1:0] PADDR,
input wire PENABLE,
input wire PWRITE,
input wire [31:0] PWDATA,
input wire [3:0] PSTRB,
input wire [3:0] ECOREVNUM, // Engineering-change-order revision bits
// apb interface outputs
output wire [31:0] PRDATA,
output wire PREADY,
output wire PSLVERR);
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// internal wires
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Register module interface signals
wire [ADDRWIDTH-1:0] reg_addr;
wire reg_read_en;
wire reg_write_en;
wire [3:0] reg_byte_strobe;
wire [31:0] reg_wdata;
wire [31:0] reg_rdata;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic start
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Interface to convert APB signals to simple read and write controls
cmsdk_apb4_eg_slave_interface
#(.ADDRWIDTH (ADDRWIDTH))
u_apb_eg_slave_interface(
.pclk (PCLK), // pclk
.presetn (PRESETn), // reset
.psel (PSEL), // apb interface inputs
.paddr (PADDR),
.penable (PENABLE),
.pwrite (PWRITE),
.pwdata (PWDATA),
.pstrb (PSTRB),
.prdata (PRDATA), // apb interface outputs
.pready (PREADY),
.pslverr (PSLVERR),
// Register interface
.addr (reg_addr),
.read_en (reg_read_en),
.write_en (reg_write_en),
.byte_strobe (reg_byte_strobe),
.wdata (reg_wdata),
.rdata (reg_rdata)
);
// Example hardware register block
cmsdk_apb4_eg_slave_reg
#(.ADDRWIDTH (ADDRWIDTH))
u_apb_eg_slave_reg (
.pclk (PCLK),
.presetn (PRESETn),
// Register interface
.addr (reg_addr),
.read_en (reg_read_en),
.write_en (reg_write_en),
.byte_strobe (reg_byte_strobe),
.wdata (reg_wdata),
.ecorevnum (ECOREVNUM),
.rdata (reg_rdata)
);
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// module logic end
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
`ifdef ARM_APB_ASSERT_ON
`include "std_ovl_defines.h"
// ------------------------------------------------------------
// Assertions
// ------------------------------------------------------------
// Check the reg_write_en signal generated
assert_implication
#(`OVL_ERROR,
`OVL_ASSERT,
"Error! register write signal was not generated! "
)
u_ovl_apb4_eg_slave_reg_write
(.clk (PCLK),
.reset_n (PRESETn),
.antecedent_expr ( (PSEL & (~PENABLE) & PWRITE) ),
.consequent_expr ( reg_write_en == 1'b1)
);
// Check the reg_read_en signal generated
assert_implication
#(`OVL_ERROR,
`OVL_ASSERT,
"Error! register read signal was not generated! "
)
u_ovl_apb4_eg_slave_reg_read
(.clk (PCLK),
.reset_n (PRESETn),
.antecedent_expr ( (PSEL & (~PENABLE) & (~PWRITE)) ),
.consequent_expr ( reg_read_en == 1'b1)
);
// Check register read and write operation won't assert at the same cycle
assert_never
#(`OVL_ERROR,
`OVL_ASSERT,
"Error! register read and write active at the same cycle!")
u_ovl_apb4_eg_slave_rd_wr_illegal
(.clk (PCLK),
.reset_n (PRESETn),
.test_expr ((reg_write_en & reg_read_en))
);
`endif
endmodule参考代码
参考文章








 本文围绕APB slave设计展开,介绍了基于APB协议完成寄存器配置或读取的设计实例,包括其数据总线、寄存器类型等规格。还对apb_slave_interface、apb_slave_reg等代码进行分析,给出顶层apb4_eg_slave设计代码的参考链接。
本文围绕APB slave设计展开,介绍了基于APB协议完成寄存器配置或读取的设计实例,包括其数据总线、寄存器类型等规格。还对apb_slave_interface、apb_slave_reg等代码进行分析,给出顶层apb4_eg_slave设计代码的参考链接。
















 271
271

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








