💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
传递路径分析(TPA)是一种用于齿轮系统的振动分析和故障诊断的技术。该方法旨在通过跟踪振动信号的传递路径,确定齿轮系统中各个部件之间的振动传递路径,以识别潜在的故障源。通过TPA,可以及时发现齿轮系统中的故障,并采取适当的维护措施,以避免因故障造成的损失和停机时间。齿轮系统的故障跟踪:一种基于原位测量的传递路径分析方法采用虚拟解耦方法实现基于原位测量的TPA。基于Tikhonov正则化理论对轴承力进行识别。
📚2 运行结果

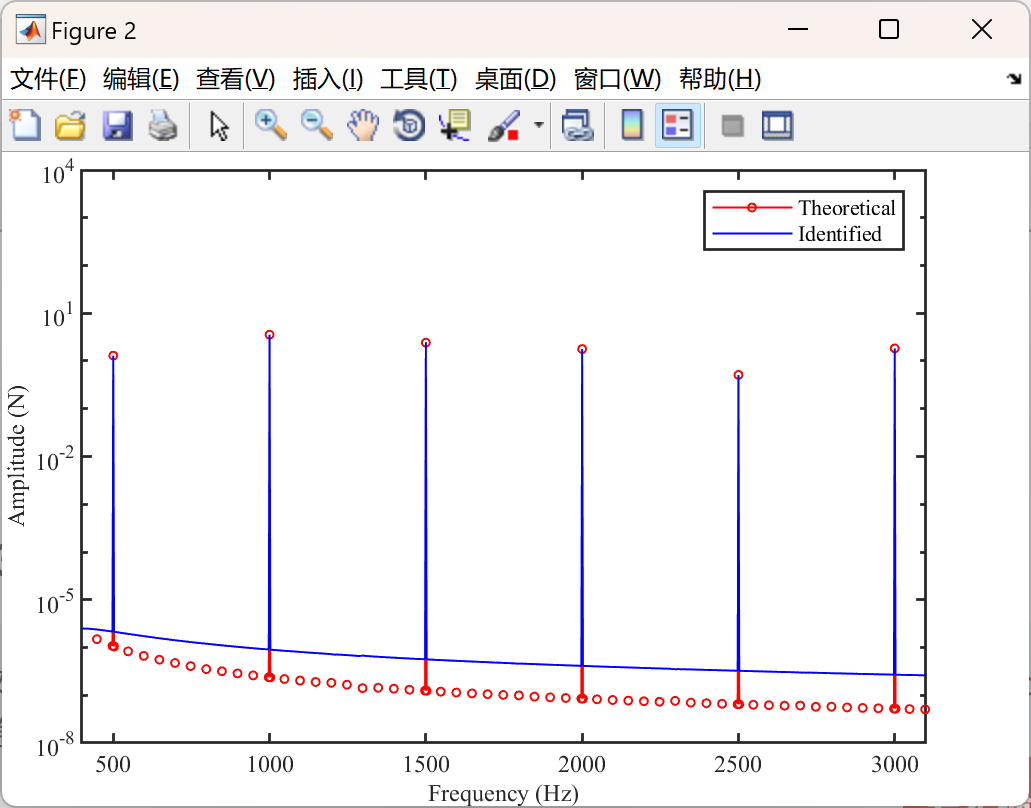


部分代码:
clc
clearvars
close all
%% Gear parameter
rho=7850; %density
m=2.5/1000; %modulus
z1=25; z2=58; %teeth number
B1=16/1000; B2=16/1000; %face width
rint1=12.5/1000; rint2=12.5/1000; %radius of the shaft (hub radius)
alpha0=20*pi/180; %pressure angle
Torque=60; %input torque
r1=m*z1/2; %radius of the reference circle
r2=m*z2/2;
rb1=r1*cos(alpha0); %radius of the base circle
rb2=r2*cos(alpha0);
Rot_period=12; %number of the rotational period
Tm_num=100; %data points in a meshing period
zhouqi_shu=z1*Rot_period; %number of the meshing period
step_num=zhouqi_shu*(Tm_num); %total data points of the simulation
%% Parameter of the lumped mass
m1=pi*(r1^2-rint1^2)*B1*rho;
J1=1/2*m1*(rint1^2+r1^2);
m2=pi*(r2^2-rint2^2)*B2*rho;
J2=1/2*m2*(rint2^2+r2^2);
m5=1; m6=2; m7=23.5;
M=diag([m1,J1,m2,J2,m5,m6,m7]);
%% Time varying meshing stiffness and Time varying meshing damping
K_health=load('K_health.txt');
K_ext=interp1(linspace(0,1,length(K_health)),K_health(1:60),linspace(0,1,Tm_num));
KM=repmat(K_ext,1,zhouqi_shu);
CM=2*0.02*sqrt(KM/(r1^2/J1+r2^2/J2));
%% Project vector of the meshing element
V=[1,rb1,-1,rb2];
unit_VV=zeros(length(M));
unit_VV(1:4,1:4)=V'*V;
%% Stiffness and damping parameter of the spring-damping element
k15=1e7; k36=1e7; k57=1e8; k67=1e8; k07=1e8;
c15=1e4; c36=1e4; c57=1e3; c67=1e3; c07=1e3;
%% Matirx assembling of the whole system
K=zeros(length(M));
K([1,5],[1,5])=K([1,5],[1,5])+[k15,-k15;-k15,k15];
K([3,6],[3,6])=K([3,6],[3,6])+[k36,-k36;-k36,k36];
K([5,7],[5,7])=K([5,7],[5,7])+[k57,-k57;-k57,k57];
K([6,7],[6,7])=K([6,7],[6,7])+[k67,-k67;-k67,k67];
K(7,7)=K(7,7)+k07;
C=zeros(length(M));
C([1,5],[1,5])=C([1,5],[1,5])+[c15,-c15;-c15,c15];
C([3,6],[3,6])=C([3,6],[3,6])+[c36,-c36;-c36,c36];
C([5,7],[5,7])=C([5,7],[5,7])+[c57,-c57;-c57,c57];
C([6,7],[6,7])=C([6,7],[6,7])+[c67,-c67;-c67,c67];
C(7,7)=C(7,7)+c07;
%% Natural frequency of the whole system (coupled system)
K_mean=K+mean(K_health)*unit_VV;
D=eig(K_mean/M);
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]周子强,孙勇,姬姗姗.DFC2型光电日照计典型故障分析与日常维护[J].现代化农业,2024(03):88-90.







 本文介绍了齿轮系统中的传递路径分析(TPA)技术,结合Matlab代码详细展示了如何通过追踪振动信号来检测和诊断潜在故障。使用虚拟解耦方法和Tikhonov正则化处理轴承力,以提高故障识别的准确性。
本文介绍了齿轮系统中的传递路径分析(TPA)技术,结合Matlab代码详细展示了如何通过追踪振动信号来检测和诊断潜在故障。使用虚拟解耦方法和Tikhonov正则化处理轴承力,以提高故障识别的准确性。


















 1962
1962

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










