概述
噪声对图像处理的影响很大,它影响图像处理的输入、采集和处理等各个环节以及输出结果。因此,在进行其它的图像处理前,需要对图像进行去噪处理。
从统计学的观点来看,凡是统计特征不随时间变化的噪声称为平稳噪声,而统计特征随时间变化的噪声称为非平稳噪声。幅值基本相同,但是噪声出现的位置是随机的,称为椒盐噪声;如果噪声的幅值是随机的,根据幅值大小的分布,有高斯型和瑞利型两种,分别称为高斯噪声和瑞利噪声。常见的去噪处理有均值滤波,中值滤波,灰度最小方差均值滤波,K近邻平滑滤波,对称近邻均值滤波,西戈玛平滑滤波等。
均值滤波
定义
均值滤波方法是,对待处理的当前像素,选择一个模板,该模板为其邻近的若干个像素组成,用模板的均值来替代原像素的值的方法。

如下图,1~8为(x,y)的邻近像素。

权系数矩阵模板

g = (f(x-1,y-1) + f(x,y-1)+ f(x+1,y-1) + f(x-1,y) + f(x,y) + f(x+1,y) + f(x-1,y+1) + f(x,y+1) + f(x+1,y+1))/9
方法优缺点
优点:算法简单,计算速度快;
缺点:降低噪声的同时使图像产生模糊,特别是景物的边缘和细节部分。
中值滤波
定义
中值滤波方法是,对待处理的当前像素,选择一个模板,该模板为其邻近的若干个像素组成,对模板的像素由小到大进行排序,再用模板的中值来替代原像素的值的方法。
权系数矩阵模板

g = median[(x-1,y-1) + f(x,y-1)+ f(x+1,y-1) + f(x-1,y) + f(x,y) + f(x+1,y) + f(x-1,y+1) + f(x,y+1) + f(x+1,y+1)]
优缺点
优点:抑制效果很好,画面的清析度基本保持;
缺点:对高斯噪声的抑制效果不是很好。
对称近邻均值滤波
定义
对称近邻(SNN:Symmetric Nearest Neighbor)均值滤波的核心思想是,在一个局部范围内,通过几对对称点像素的比较,获得相对区域及不同区域的差别,然后将均值计算在所判定的同一个区域内进行,这样可以使边界的保持更加灵活的同时又降低计算。
设一个(2N+1)*(2N+1)的模板,则有2N*(2N+1)个对称点,2N*(2N+1)个选择点的像素均值代替原像素值,如下:

优缺点
使边界的保持更加灵活的同时又降低计算。
图像滤波----低通滤波,中值滤波,高通滤波,方向滤波(Sobel),拉普拉斯变换
①观察灰度分布来描述一幅图像成为空间域,观察图像变化的频率被成为频域。
②频域分析:低频对应区域的图像强度变化缓慢,高频对应的变化快。低通滤波器去除了图像的高频部分,高通滤波器去除了图像的低频部分。
(1)低通滤波
①栗子:
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
int main()
{
// Read input image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("boldt.jpg",0);
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Original Image");
cv::imshow("Original Image",image);
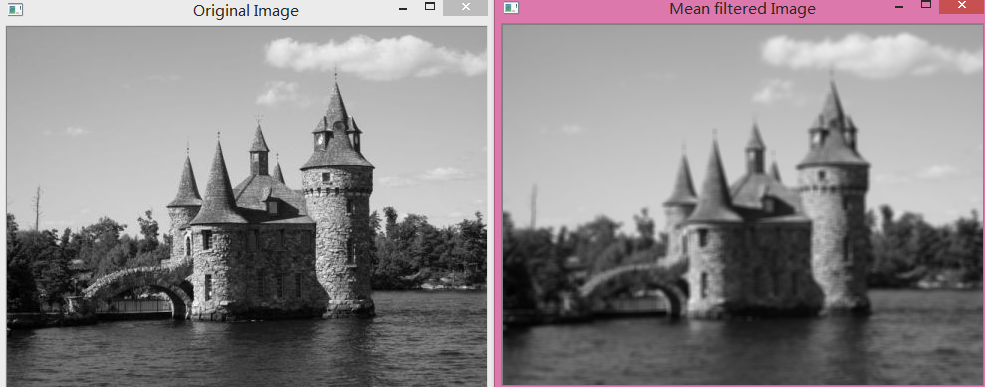
// Blur the image with a mean filter
cv::Mat result;
cv::blur(image,result,cv::Size(5,5));
// Display the blurred image
cv::namedWindow("Mean filtered Image");
cv::imshow("Mean filtered Image",result);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
结果:每个像素变为相邻像素的平均值, 快速的强度变化转化为平缓的过度
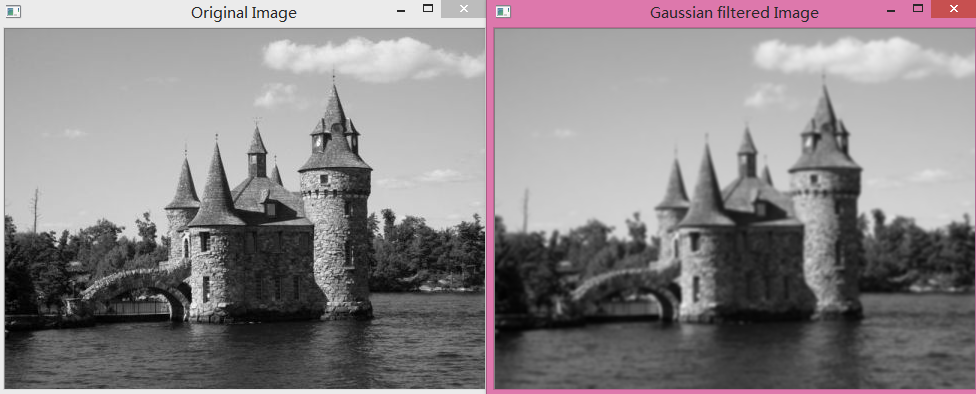
②栗子:近的像素添加更多的权重。:高斯滤波器
cv::GaussianBlur(image,result,cv::Size(5,5),1.5);- 1
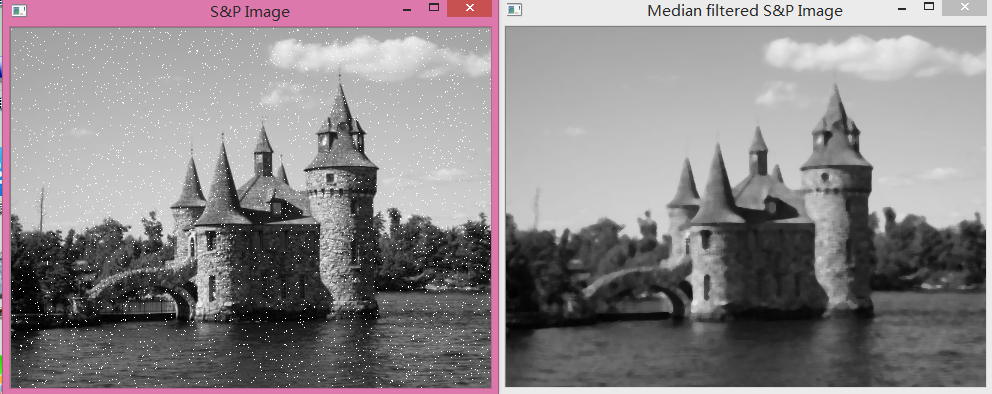
(2)中值滤波 :非线性滤波
有效去除椒盐噪点
cv::medianBlur(image,result,5);- 1
(3)方向滤波(Sobel)
强调图像中的高频分量,使用高通滤波器进行边缘检测。
Sobel算子是一种经典的边缘检测线性滤波器,可被认为是图像在垂直和水平方向变化的测量。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include "laplacianZC.h"
int main()
{
//Read input image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("boldt.jpg",0);
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Original Image");
cv::imshow("Original Image",image);
// Compute Sobel X derivative
cv::Mat sobelX;
cv::Sobel(image,sobelX,CV_8U,1,0,3,0.4,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel X Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel X Image",sobelX);
// Compute Sobel Y derivative
cv::Mat sobelY;
cv::Sobel(image,sobelY,CV_8U,0,1,3,0.4,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel Y Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel Y Image",sobelY);
// Compute norm of Sobel 得到sobel的摸
cv::Sobel(image,sobelX,CV_16S,1,0);
cv::Sobel(image,sobelY,CV_16S,0,1);
cv::Mat sobel;
//compute the L1 norm
sobel= abs(sobelX)+abs(sobelY);
double sobmin, sobmax;
cv::minMaxLoc(sobel,&sobmin,&sobmax);
std::cout << "sobel value range: " << sobmin << " " << sobmax << std::endl;
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(sobel.at<short>(i+135,j+362)) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
// Conversion to 8-bit image
// sobelImage = -alpha*sobel + 255
cv::Mat sobelImage;
sobel.convertTo(sobelImage,CV_8U,-255./sobmax,255);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel Image",sobelImage);
// Apply threshold to Sobel norm (low threshold value)
cv::Mat sobelThresholded;
cv::threshold(sobelImage, sobelThresholded, 225, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Binary Sobel Image (low)");
cv::imshow("Binary Sobel Image (low)",sobelThresholded);
// Apply threshold to Sobel norm (high threshold value)
cv::threshold(sobelImage, sobelThresholded, 190, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Binary Sobel Image (high)");
cv::imshow("Binary Sobel Image (high)",sobelThresholded);- 结果:
(4)图像的拉普拉斯变换
是一种基于图像导数的高通线性滤波器,计算二阶倒数已衡量图像的弯曲度。
// Compute Laplacian 3x3
cv::Mat image = cv::imread("boldt.jpg", 0);
cv::Mat laplace;
cv::Laplacian(image,laplace,CV_8U,1,1,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image",laplace);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(laplace.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362))-128 << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
// Compute Laplacian 7x7
cv::Laplacian(image,laplace,CV_8U,7,0.01,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image",laplace);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(laplace.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362))-128 << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Extract small window
cv::Mat window(image,cv::Rect(362,135,12,12));
cv::namedWindow("Image window");
cv::imshow("Image window",window);
cv::imwrite("window.bmp",window);
// Compute Laplacian using LaplacianZC class
LaplacianZC laplacian;
laplacian.setAperture(7);
cv::Mat flap= laplacian.computeLaplacian(image);
double lapmin, lapmax;
cv::minMaxLoc(flap,&lapmin,&lapmax);
std::cout << "Laplacian value range=[" << lapmin << "," << lapmax << "]\n";
laplace= laplacian.getLaplacianImage();
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image (7x7)");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image (7x7)",laplace);
// Print Laplacian values
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(flap.at<float>(i+135,j+362)/100) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// Compute and display the zero-crossing points
cv::Mat zeros;
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossings(lapmax);
cv::namedWindow("Zero-crossings");
cv::imshow("Zero-crossings",zeros);
// Compute and display the zero-crossing points (Sobel version)
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossings();
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossingsWithSobel(50);
cv::namedWindow("Zero-crossings (2)");
cv::imshow("Zero-crossings (2)",zeros);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(2) << static_cast<int>(zeros.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362)) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Display the image with window
cv::rectangle(image,cv::Point(362,135),cv::Point(374,147),cv::Scalar(255,255,255));
cv::namedWindow("Original Image with window");
cv::imshow("Original Image with window",image);
cv::waitKey();
return 0;
}


























 8049
8049











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








