今天做一下元胞状态机的题吧。
More Circuits
116 Rule90 Exams/ece241_2013_q12
Cellular automaton:元胞自动机。
Rule 90 is a one-dimensional cellular automaton with interesting properties.The rules are simple. There is a one-dimensional array of cells (on or off). At each time step, the next state of each cell is the XOR of the cell's two current neighbours. A more verbose way of expressing this rule is the following table, where a cell's next state is a function of itself and its two neighbours:(The name "Rule 90" comes from reading the "next state" column: 01011010 is decimal 90.)
有一个一维的细胞阵列(打开或关闭)。在每个time step,每个细胞的下一个状态是该细胞两个当前邻居的异或。下表更详细地描述了这一规则,其中细胞的下一个状态是它本身及其两个邻居的函数。
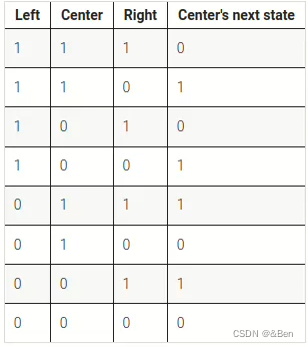
题目要求构建一个具有512个细胞的元胞自动机,假设边界(q[-1] q[512])均为0.这个题定义一下边界情况,然后写个循环就好了。
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [511:0] data,
output [511:0] q );
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(load)
q<=data;
else begin
q[0]<=0^q[1];
q[511]<=0^q[510];
for(int i=1;i<511;i++)
q[i]<=q[i-1]^q[i+1];
end
end
endmodule
117 Rule 110
Rule 110 is a one-dimensional cellular automaton with interesting properties (such as being Turing-complete).
There is a one-dimensional array of cells (on or off). At each time step, the state of each cell changes. In Rule 110, the next state of each cell depends only on itself and its two neighbours, according to the following table:(The name "Rule 110" comes from reading the "next state" column: 01101110 is decimal 110.)
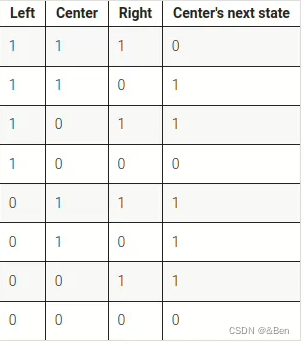
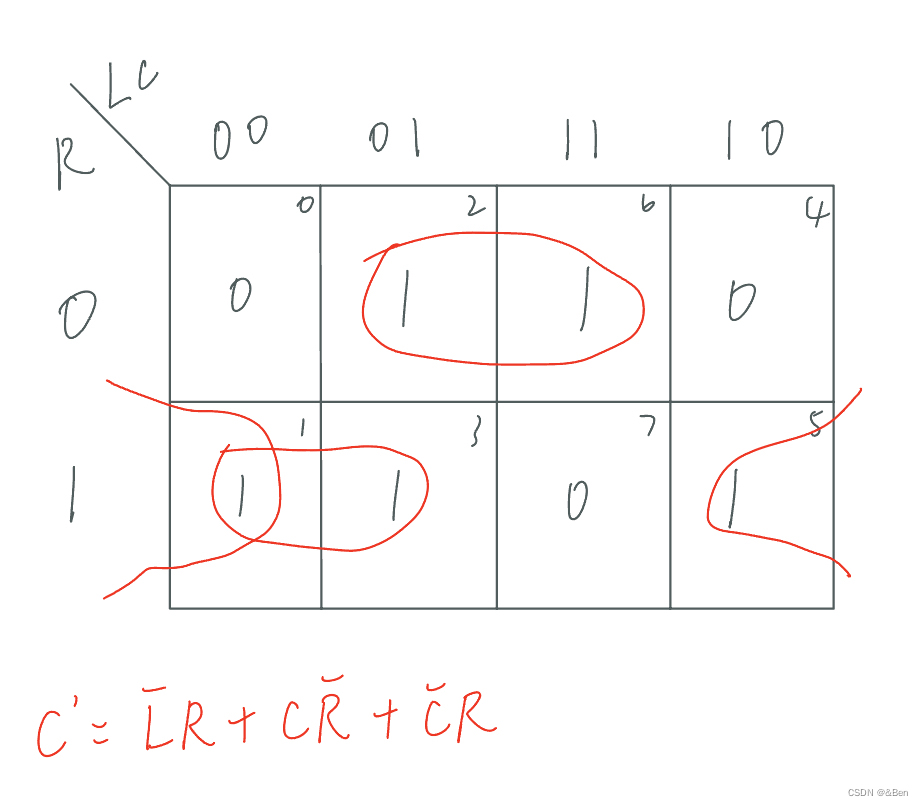
本题没给具体的逻辑关系,需要自己推导。
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [511:0] data,
output [511:0] q
);
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(load)
q<=data;
else begin
q[0]<=(~q[1]&&0)||(q[0]&&1)||(~q[0]&&0);
q[511]<=(1&&q[510])||(q[511]&&~q[510])||(~q[511]&&q[510]);
for(int i=1;i<511;i++)
q[i]<=(~q[i+1]&&q[i-1])||(q[i]&&~q[i-1])||(~q[i]&&q[i-1]);
end
end
endmodule
118 Conway's Game of Life 16x16
Conway's Game of Life is a two-dimensional cellular automaton.
The "game" is played on a two-dimensional grid of cells, where each cell is either 1 (alive) or 0 (dead). At each time step, each cell changes state depending on how many neighbours it has:
- 0-1 neighbour: Cell becomes 0.
- 2 neighbours: Cell state does not change.
- 3 neighbours: Cell becomes 1.
- 4+ neighbours: Cell becomes 0.
The game is formulated for an infinite grid. In this circuit, we will use a 16x16 grid. To make things more interesting, we will use a 16x16 toroid, where the sides wrap around to the other side of the grid. For example, the corner cell (0,0) has 8 neighbours: (15,1), (15,0), (15,15), (0,1), (0,15), (1,1), (1,0), and (1,15). The 16x16 grid is represented by a length 256 vector, where each row of 16 cells is represented by a sub-vector: q[15:0] is row 0, q[31:16] is row 1, etc. (This tool accepts SystemVerilog, so you may use 2D vectors if you wish.)
- load: Loads data into q at the next clock edge, for loading initial state.
- q: The 16x16 current state of the game, updated every clock cycle.
The game state should advance by one timestep every clock cycle.
John Conway, mathematician and creator of the Game of Life cellular automaton, passed away from COVID-19 on April 11, 2020.
这个题目属于二维元胞自动机,细胞更新的规则根据存活的邻居个数,0-1个存活,细胞死亡;2个邻居存活,细胞状态不变;3个邻居存活,细胞复活;4个及以上邻居存活,细胞死亡。
那么这个题目的关键点就在于:
1.统计上一状态邻居存活个数;
2.根据上一状态邻居个数更新自己的下一状态。
考虑使用case语句和for循环。
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [255:0] data,
output [255:0] q );
reg [3:0] count;
integer i;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if(load)begin
q <= data;
end
else begin
for(i=0;i<256;i++)begin
if(i == 0)begin
count = q[255] + q[240] + q[241] + q[15] + q[1] + q[31] + q[16] + q[17];
end
else if(i == 15)begin
count = q[254] + q[255] + q[240] + q[14] + q[0] + q[30] + q[31] + q[16];
end
else if(i == 240)begin
count = q[239] + q[224] + q[225] + q[255] + q[241] + q[15] + q[0] + q[1];
end
else if(i == 255)begin
count = q[238] + q[239] + q[224] + q[254] + q[240] + q[15] + q[0] + q[14];
end
else if( i>0 && i<15)begin
count = q[239+i]+q[240+i]+q[241+i]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
else if(i>240 && i<255)begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i-239]+q[i-240]+q[i-241];
end
else if( i%16 == 0)begin
count = q[i-1]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i+15]+q[i+1]+q[i+31]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
else if(i % 16 == 15)begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-31]+q[i-1]+q[i-15]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+1];
end
else begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
case(count)
4'd2:q[i] <= q[i];
4'd3:q[i] <= 1'b1;
default:q[i] <= 1'b0;
endcase
end
end
end
endmodule




















 3320
3320











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








