简介
所谓CGAN,就是conditional Gan,针对GAN本身不可控的缺点,加入监督信息,指导GAN网络进行生成。关于GAN,可以参考这篇博客,GAN算法讲解。
不同之处
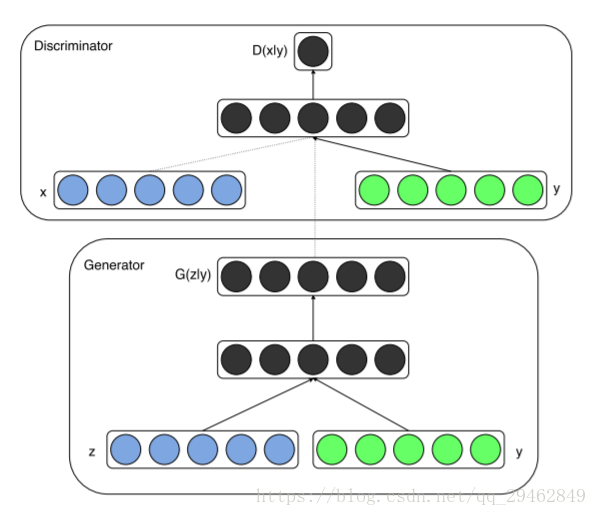
CGAN和GAN唯一不同处就是,CGAN是在条件下的概率,y就是加入的监督信息,比如说MNIST数据集可以提供数字label信息,人脸生成可以提供性别、是否微笑、年龄等信息。从下面的公式可以看出,CGAN和GAN几乎相同。
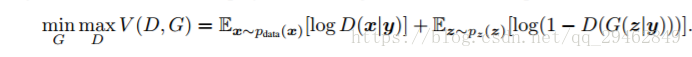
实验
在这里通过图像翻译的例子,来具体说明CGAN是怎么工作的。如下图所示,通过CGAN网络来把右边图像转换成左边真实图像。(数据集包含在源代码中)

源代码
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import argparse
import os
import json
import glob
import random
import collections
import math
import time
#所有的参数在这里设置修改
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--input_dir", default="C:/Users/new/Desktop/chapter_9/tools/facades/val")
parser.add_argument("--mode", default="test")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", default="facades_test")
parser.add_argument("--seed", type=int)
parser.add_argument("--checkpoint", default="facades_train")
parser.add_argument("--max_steps", type=int, help="number of training steps (0 to disable)")
parser.add_argument("--max_epochs", type=int,default=10)
parser.add_argument("--summary_freq", type=int, default=100, help="update summaries every summary_freq steps")
parser.add_argument("--progress_freq", type=int, default=50, help="display progress every progress_freq steps")
parser.add_argument("--trace_freq", type=int, default=0, help="trace execution every trace_freq steps")
parser.add_argument("--display_freq", type=int, default=0, help="write current training images every display_freq steps")
parser.add_argument("--save_freq", type=int, default=5000, help="save model every save_freq steps, 0 to disable")
parser.add_argument("--aspect_ratio", type=float, default=1.0, help="aspect ratio of output images (width/height)")
parser.add_argument("--lab_colorization", action="store_true", help="split input image into brightness (A) and color (B)")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=1, help="number of images in batch")
parser.add_argument("--which_direction", type=str, default="BtoA", choices=["AtoB", "BtoA"])
parser.add_argument("--ngf", type=int, default=64, help="number of generator filters in first conv layer")
parser.add_argument("--ndf", type=int, default=64, help="number of discriminator filters in first conv layer")
parser.add_argument("--scale_size", type=int, default=286, help="scale images to this size before cropping to 256x256")
parser.add_argument("--flip", dest="flip", action="store_true", help="flip images horizontally")
parser.add_argument("--no_flip", dest="flip", action="store_false", help="don't flip images horizontally")
parser.set_defaults(flip=True)
parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=0.0002, help="initial learning rate for adam")
parser.add_argument("--beta1", type=float, default=0.5, help="momentum term of adam")
parser.add_argument("--l1_weight", type=float, default=100.0, help="weight on L1 term for generator gradient")
parser.add_argument("--gan_weight", type=float, default=1.0, help="weight on GAN term for generator gradient")
# export options
parser.add_argument("--output_filetype", default="png", choices=["png", "jpeg"])
a = parser.parse_args()
EPS = 1e-12
CROP_SIZE = 256
Examples = collections.namedtuple("Examples", "paths, inputs, targets, count, steps_per_epoch")
Model = collections.namedtuple("Model", "outputs, predict_real, predict_fake, discrim_loss, discrim_grads_and_vars, gen_loss_GAN, gen_loss_L1, gen_grads_and_vars, train")
def preprocess(image):
with tf.name_scope("preprocess"):
# [0, 1] => [-1, 1]
return image * 2 - 1
def deprocess(image):
with tf.name_scope("deprocess"):
# [-1, 1] => [0, 1]
return (image + 1) / 2
def preprocess_lab(lab):
with tf.name_scope("preprocess_lab"):
L_chan, a_chan, b_chan = tf.unstack(lab, axis=2)
# L_chan: black and white with input range [0, 100]
# a_chan/b_chan: color channels with input range ~[-110, 110], not exact
# [0, 100] => [-1, 1], ~[-110, 110] => [-1, 1]
return [L_chan / 50 - 1, a_chan / 110, b_chan / 110]
def deprocess_lab(L_chan, a_chan, b_chan):
with tf.name_scope("deprocess_lab"):
# this is axis=3 instead of axis=2 because we process individual images but deprocess batches
return tf.stack([(L_chan + 1) / 2 * 100, a_chan * 110, b_chan * 110], axis=3)
def augment(image, brightness):
# (a, b) color channels, combine with L channel and convert to rgb
a_chan, b_chan = tf.unstack(image, axis=3)
L_chan = tf.squeeze(brightness, axis=3)
lab = deprocess_lab(L_chan, a_chan, b_chan)
rgb = lab_to_rgb(lab)
return rgb
def conv(batch_input, out_channels, stride):
with tf.variable_scope("conv"):
in_channels = batch_input.get_shape()[3]
filter = tf.get_variable("filter", [4, 4, in_channels, out_channels], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0, 0.02))
# [batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels], [filter_width, filter_height, in_channels, out_channels]
# => [batch, out_height, out_width, out_channels]
padded_input = tf.pad(batch_input, [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]], mode="CONSTANT")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(padded_input, filter, [1, stride, stride, 1], padding="VALID")
return conv
def lrelu(x, a):
with tf.name_scope("lrelu"):
# adding these together creates the leak part and linear part
# then cancels them out by subtracting/adding an absolute value term
# leak: a*x/2 - a*abs(x)/2
# linear: x/2 + abs(x)/2
# this block looks like it has 2 inputs on the graph unless we do this
x = tf.identity(x)
return (0.5 * (1 + a)) * x + (0.5 * (1 - a)) * tf.abs(x)
def batchnorm(input):
with tf.variable_scope("batchnorm"):
# this block looks like it has 3 inputs on the graph unless we do this
input = tf.identity(input)
channels = input.get_shape()[3]
offset = tf.get_variable("offset", [channels], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.zeros_initializer())
scale = tf.get_variable("scale", [channels], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(1.0, 0.02))
mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(input, axes=[0, 1, 2], keep_dims=False)
variance_epsilon = 1e-5
normalized = tf.nn.batch_normalization(input, mean, variance, offset, scale, variance_epsilon=variance_epsilon)
return normalized
def deconv(batch_input, out_channels):
with tf.variable_scope("deconv"):
batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels = [int(d) for d in batch_input.get_shape()]
filter = tf.get_variable("filter", [4, 4, out_channels, in_channels], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(0, 0.02))
# [batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels], [filter_width, filter_height, out_channels, in_channels]
# => [batch, out_height, out_width, out_channels]
conv = tf







 CGAN(条件生成式对抗网络)通过引入监督信息改进了GAN的可控性,适用于如图像翻译等任务。本文介绍了CGAN的基本概念,与GAN的区别,并提供了源代码及实验结果展示。在实验中,CGAN尝试将图像从输入状态转换为真实图像,尽管在仅迭代10轮的情况下,效果仍有提升空间。
CGAN(条件生成式对抗网络)通过引入监督信息改进了GAN的可控性,适用于如图像翻译等任务。本文介绍了CGAN的基本概念,与GAN的区别,并提供了源代码及实验结果展示。在实验中,CGAN尝试将图像从输入状态转换为真实图像,尽管在仅迭代10轮的情况下,效果仍有提升空间。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 494
494

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








