ceres库
参考大佬链接:链接: 视觉SLAM十四讲学习6 Ceres Solver (1) 入门
最简单的最小二乘构建
ceres.cpp
#include "ceres/ceres.h"
//此项目的优化函数为1/2||10-x||^2
//esidual是最小二乘中的残差,x是迭代变量
// //以下代码是两个代价函数
// struct CostFunctor
// {
// template <typename T>//这是一个模板函数,使得成本函数能够适用于不同的数值类型
// //这是一个函数调用运算符的重载,它接受一个指向参数数组 x 的指针和一个指向残差数组 residual 的指针,并返回一个布尔值
// bool operator()(const T* const x, T* residual) const {
// residual[0] = 10.0 - x[0];
// //residual[0]=x[0]*x[0]-2*x[0]+4;
// return true;
// }
// };
struct NumericCostFunctor{
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = 10.0 - x[0];
//residual[0]=x[0]*x[0]-2*x[0]+4;
return true;
}
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);//初始化Google日志系统,用于在终端输出日志信息
double x_init = 1.;//初始化变量x的初始值为5.0
double x = x_init;
ceres::Problem problem;//创建一个Ceres Solver的问题对象,用于定义优化问题
// ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<CostFunctor, 1, 1>(new CostFunctor);
//创建一个成本函数对象,使用数值微分方法计算成本函数的梯度
ceres::CostFunction* cost_function = new ceres::NumericDiffCostFunction<NumericCostFunctor, ceres::CENTRAL, 1, 1>(new NumericCostFunctor);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, nullptr, &x);//向问题中添加一个残差块,将成本函数和变量x关联起来。这样,在优化过程中,Ceres Solver将根据残差来调整变量x的值
ceres::Solver::Options options;//创建一个优化器的选项对象,用于配置求解器的参数
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;//指定线性求解器类型为Dense QR,用于求解优化问题的线性方程组
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;//设置为true时,在终端输出优化过程的详细信息
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;//创建一个求解器的汇总对象,用于存储求解器的执行结果和统计信息
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);//调用Ceres Solver的求解函数,传入选项、问题和汇总对象,开始求解优化问题
std::cout<<summary.BriefReport()<<"\n";
std::cout<<"x: "<< x_init << " -> " << x << " \n";//输出最终的x
std::cout<<"the last result:"<<summary.final_cost<<std::endl;//输出最终的y
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
# 声明要求的 cmake 最低版本
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
# 声明一个 cmake 工程
project(ceres)
# 添加一个可执行程序
# 语法:add_executable( 程序名 源代码文件 )
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
add_executable(ceres1 ceres.cpp)
target_link_libraries(ceres1 ${CERES_LIBRARIES})
运行结果
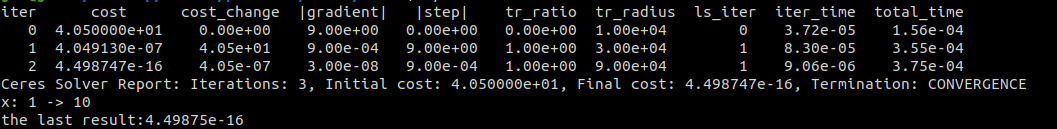
多函数多变量最小二乘
#include<ceres/ceres.h>
//以下内容为多个函数
struct F1
{
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x1, const T* const x2, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = x1[0] + x2[0] * 10.;
return true;
}
};
struct F2
{
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x3, const T* const x4, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = sqrt(5) * (x3[0] - x4[0]);
return true;
}
};
struct F3{
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x2, const T* const x3, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = pow(x2[0] - x3[0] * 2., 2);
return true;
}
};
struct F4{
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T* const x1, const T* const x4, T* residual) const {
residual[0] = sqrt(10) * pow(x1[0] - x4[0], 2);
return true;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
google::InitGoogleLogging(argv[0]);
double x1 = 3.0, x2 = -1.0, x3 = 0.0, x4 = 1.0;
ceres::Problem problem;
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<F1, 1, 1, 1>(new F1), nullptr, &x1, &x2);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<F2, 1, 1, 1>(new F2), nullptr, &x3, &x4);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<F3, 1, 1, 1>(new F3), nullptr, &x2, &x3);
problem.AddResidualBlock(new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<F4, 1, 1, 1>(new F4), nullptr, &x1, &x4);
ceres::Solver::Options options;
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_QR;
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true;
ceres::Solver::Summary summary;
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary);
std::cout<< summary.BriefReport()<<std::endl;
std::cout<< "[3.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0] -> [" <<x1<<", "<<x2<<", "<<x3<<", "<<x4<<", "<<std::endl;
return 0;
}
cmakelisits文件同上
运行结果
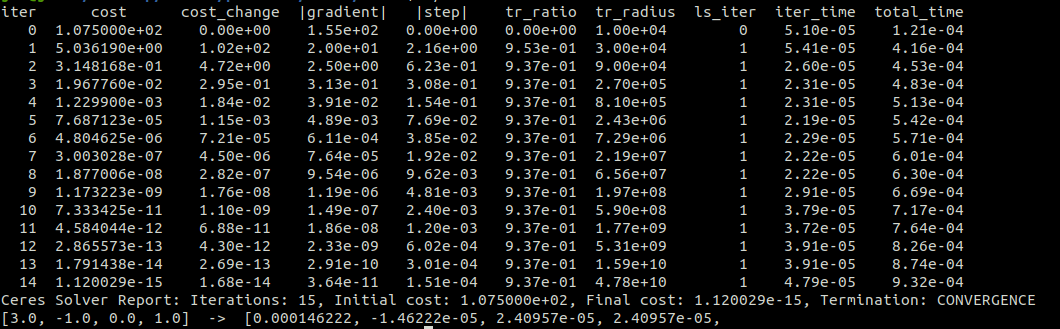
视觉slam14讲中的ceres优化
源文件
//
// Created by xiang on 18-11-19.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
// 代价函数的计算模型
struct CURVE_FITTING_COST
{
//结构体
CURVE_FITTING_COST(double x, double y) : _x(x), _y(y) {}
// 残差的计算
template<typename T>
//这是一个重载的函数调用运算符,它定义了仿函数的行为。
//这个函数接受两个参数:abc 是优化问题的参数,residual 是用于存储计算得到的残差的数组。
bool operator()(const T *const abc, T *residual)const
{
residual[0] = T(_y) - ceres::exp(abc[0] * T(_x) * T(_x) + abc[1] * T(_x) + abc[2]); // y-exp(ax^2+bx+c)
return true;
}
const double _x, _y; // x,y数据
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
double ar = 1.0, br = 2.0, cr = 1.0; // 真实参数值
double ae = 2.0, be = -1.0, ce = 5.0; // 估计参数值
int N = 100; // 数据点
double w_sigma = 1.0; // 噪声Sigma值
double inv_sigma = 1.0 / w_sigma;
cv::RNG rng; // OpenCV随机数产生器
vector<double> x_data, y_data; // 数据
//随机产生100个x,y点
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
double x = i / 100.0;
x_data.push_back(x);
y_data.push_back(exp(ar * x * x + br * x + cr) + rng.gaussian(w_sigma * w_sigma));
}
//数组abc,对应三个参数
double abc[3] = {ae, be, ce};
// 构建最小二乘问题
ceres::Problem problem;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
problem.AddResidualBlock( // 向问题中添加误差项
// 使用自动求导,模板参数:误差类型,输出维度,输入维度,维数要与前面struct中一致
new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<CURVE_FITTING_COST, 1, 3>(
//把数据传入结构体
new CURVE_FITTING_COST(x_data[i], y_data[i])
),
nullptr, // 核函数,这里不使用,为空
abc // 待估计参数
);
}
// 配置求解器
ceres::Solver::Options options; // 这里有很多配置项可以填
options.linear_solver_type = ceres::DENSE_NORMAL_CHOLESKY; // 增量方程如何求解
options.minimizer_progress_to_stdout = true; // 输出到cout
//存储优化信息
ceres::Solver::Summary summary; // 优化信息
//计时
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
ceres::Solve(options, &problem, &summary); // 开始优化
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration<double> time_used = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::duration<double>>(t2 - t1);
cout << "solve time cost = " << time_used.count() << " seconds. " << endl;
// 输出结果
cout << summary.BriefReport() << endl;
cout << "estimated a,b,c = ";
for (auto a:abc) cout << a << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
cmakelists
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(ch6)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++14 -O3")
list(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
# OpenCV
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Ceres
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED)
include_directories(${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS})
# Eigen
include_directories("/usr/include/eigen3")
add_executable(ceresCurveFitting ceresCurveFitting.cpp)
target_link_libraries(ceresCurveFitting ${OpenCV_LIBS} ${CERES_LIBRARIES})






















 880
880











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








