原文链接:什么是ORB
关于Orb特征的获取:参考 最新版的OpenCV中新增加的ORB特征的使用
ORB是是ORiented Brief 的简称,对Brief的特定性质进行了改进。
ORB的描述在下面文章中:
Ethan Rublee and Vincent Rabaud and Kurt Konolige and Gary Bradski,ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF, ICCV 2011
没有加上链接是因为作者确实还没有放出论文,不过OpenCV2.3RC中已经有了实现,WillowGarage有一个talk也提到了这个算法,因此我不揣浅陋,在这里总结一下。
Brief是Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features的缩写。这个特征描述子是由EPFL的Calonder在ECCV2010上提出的。主要思路就是在特征点附近随机选取若干点对,将这些点对的灰度值的大小,组合成一个二进制串,并将这个二进制串作为该特征点的特征描述子。详细算法描述参考如下论文:
注意在BRIEF eccv2010的文章中,BRIEF描述子中的每一位是由随机选取的两个像素点做二进制比较得来的。文章同样提到,在此之前,需要选取合适的gaussian kernel对图像做平滑处理。(为什么要强调这一点,因为下述的ORB对此作了改进。)
BRIEF的优点在于速度,缺点也相当明显:
1:不具备旋转不变性。
2:对噪声敏感
3:不具备尺度不变性。
ORB就是试图解决上述缺点中的1和2.
如何解决旋转不变性:
在ORB的方案中,是采用了FAST作为特征点检测算子。FAST应用的很多了,是出名的快,以防有人不知道,请看这里:
FastCornerDetecting
在Sift的方案中,特征点的主方向是由梯度直方图的最大值和次大值所在的bin对应的方向决定的。略嫌耗时。
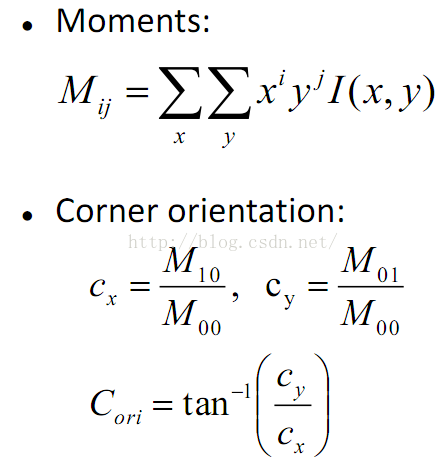
在ORB的方案中,特征点的主方向是通过矩(moment)计算而来,公式如下:
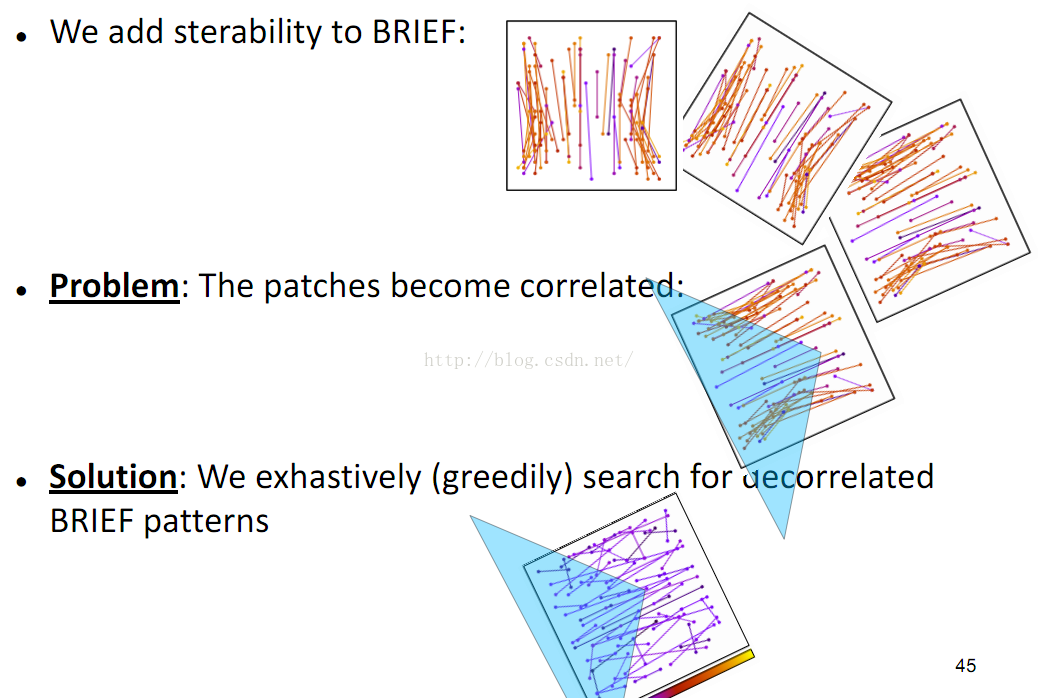
有了主方向之后,就可以依据该主方向提取BRIEF描述子。但是由此带来的问题是,由于主方向会发生变化,随机点对的相关性会比较大,从而降低描述子的判别性。解决方案也很直接,采取贪婪的,穷举的方法,暴力找到相关性较低的随机点对。
如何解决对噪声敏感的问题:
在前面提到过,在最早的eccv2010的文章中,BRIEF使用的是pixel跟pixel的大小来构造描述子的每一个bit。这样的后果就是对噪声敏感。因此,在ORB的方案中,做了这样的改进,不再使用pixel-pair,而是使用9×9的patch-pair,也就是说,对比patch的像素值之和。(可以通过积分图快速计算)。
关于尺度不变性:
ORB没有试图解决尺度不变性,(因为FAST本身就不具有尺度不变性。)但是这样只求速度的特征描述子,一般都是应用在实时的视频处理中的,这样的话就可以通过跟踪还有一些启发式的策略来解决尺度不变性的问题。
关于计算速度:
ORB是sift的100倍,是surf的10倍。
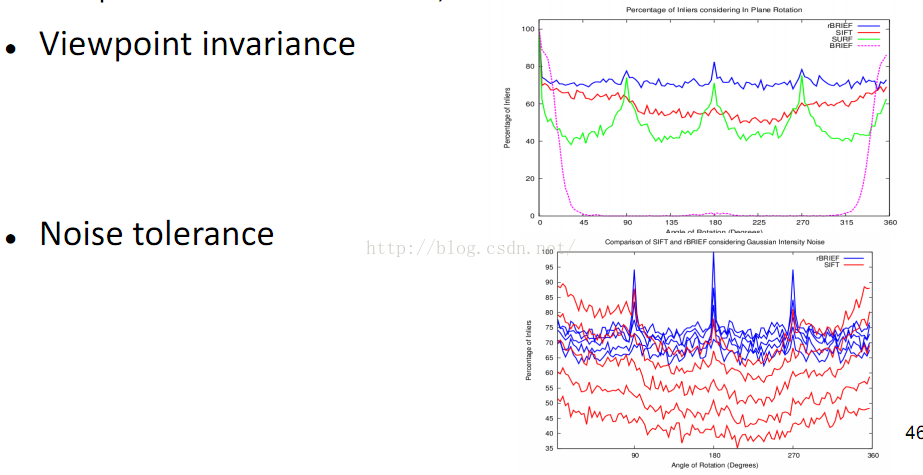
关于性能:
下面是一个性能对比,ORB还是很给力。点击看大图。
结果评测...............................
OpenCV的参数描述:
C++:
ORB::ORB( int nfeatures=500, float scaleFactor=1.2f, int nlevels=8, int edgeThreshold=31, int firstLevel=0,
int WTA_K=2, int scoreType=ORB::HARRIS_SCORE, int patchSize=31)Parameters:
nfeatures – The maximum number of features to retain. 最多保留特征的个数
scaleFactor – Pyramid decimation ratio, greater than 1. scaleFactor==2 means the classical pyramid, where each next level has 4x less pixels than the previous, but such a big scale factor will degrade feature matching scores dramatically. On the other hand, too close to 1 scale factor will mean that to cover certain scale range you will need more pyramid levels and so the speed will suffer.
缩放因子:金字塔抽取比率,大于1的浮点数。2表示1/4像素抽取。接近于1需要多次抽取扩增实现浮点级别的金字塔效果。
nlevels – The number of pyramid levels. The smallest level will have linear size equal to input_image_linear_size/pow(scaleFactor, nlevels).
edgeThreshold – This is size of the border where the features are not detected. It should roughly match the patchSize parameter.
边缘阈值:大致等同于块大小参数。
firstLevel – It should be 0 in the current implementation.
WTA_K – The number of points that produce each element of the oriented BRIEF descriptor. The default value 2 means the BRIEF where we take a random point pair and compare their brightnesses, so we get 0/1 response. Other possible values are 3 and 4. For example, 3 means that we take 3 random points (of course, those point coordinates are random, but they are generated from the pre-defined seed, so each element of BRIEF descriptor is computed deterministically from the pixel rectangle), find point of maximum brightness and output index of the winner (0, 1 or 2). Such output will occupy 2 bits, and therefore it will need a special variant of Hamming distance, denoted as NORM_HAMMING2 (2 bits per bin). When WTA_K=4, we take 4 random points to compute each bin (that will also occupy 2 bits with possible values 0, 1, 2 or 3).
生成ORB描述子的选取데随机匹配种子点데个数。
scoreType – The default HARRIS_SCORE means that Harris algorithm is used to rank features ( the score is written to KeyPoint::score and is used to retain best nfeatures features ); 默认使用了HARRIS角点检测的算法。
FAST_SCORE is alternative value of the parameter that produces slightly less stable keypoints, but it is a little faster to compute.
patchSize – size of the patch used by the oriented BRIEF descriptor. Of course, on smaller pyramid layers the perceived image area covered by a feature will be larger. 检测特征데局部块데大小。
使用OpenCV的代码段
cv::Mat mDescriptors;//每一列关联到一个ORB特征
cv::ORB m_Orb;//提取器
m_Orb.detect( im, mvKeys );
m_Orb.compute( im, mvKeys, mDescriptors);
























 294
294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








