参考网址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhiyishou/p/4430017.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/soroman/archive/2007/05/17/750430.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/172749e6116a
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1700073
https://www.doc88.com/p-694154354521.html?r=1 论文下载
http://www.geom.uiuc.edu/~samuelp/del_project.html 分治算法参考,本文的参考网址
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~quake/triangle.html 三角剖分网址
https://github.com/Geri-Borbas/Triangle.NET 分治算法源码参考网址
https://blog.csdn.net/hunter_wwq/article/details/39053891
三角形剖分的算法:
1.随机增量法(incremental)
2.分治法(divide and conquer) http://www.geom.uiuc.edu/~samuelp/del_project.html
3.扫描线法(sweepline)
4.Bowyer逐点插入法
delaunay 三角剖分,由俄罗斯数学家 boris delaunay提出来的。
术语:
1.circumscribed circle 外接圆
2.constrained edge 约束边,其实就是给定一些点云,这也是个术语(就是点的集合)。连接其中的两个顶点,构成一条边,这条边不能去除,就是约束边。在三角化的过程中,此边将一直存在,不能删除。
3.delaunay 三角剖分并不是一种算法,它只是给出了一个好的三角剖分的定义。
4.voronoi图,也叫thiessen泰森多边形,即泰森多边形。
三角剖分的重要特性:
特性1:三角形的任何一个点,不能在其他三个点的外接圆的内部。
比如,下图:

左图点C,在ABE三个点的外接圆的内部,则不满足此特性。
右图点B和点C,在ADE三个点的外接圆的内部,则也不满足此特性。
特性二:最小角最大化特性
避免狭长三角形的产生。
分治法(divide and conquer):
将给定的点集,安装x递增的顺序的排序,如果x相同,则安装y的递增进行排序。
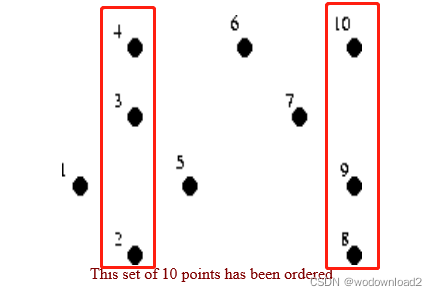
比如上图,点2、3、4的x轴相同,那么则按照其y轴的递增顺序排列。
又比如上图,点8、9、10的x轴相同,那么则按照其y轴的递增顺序排列。
我们将这些点,分成两个部分,直到,每个部分的点数都不超过3个为止。当然不会剩余一个点的情况。
那么在两个点的情况下,则构成线段。三个点的情况下,则构成一个三角形。如下图所示:

这里的1,2,3构成三角形‘;
4,5构成线段;
6,7,8构成三角形;
9,10构成线段。
LL边——线段的两个端点都在左边
LR边——线段的两个端点一个在左边,一个在右边
RR边——线段的两个端点都在右边
base LR边——从左边选取y轴最下面的点,然后从右边选取y轴最下面的点,这样保证此条LR边,不会与LL边和RR边相交。
两个部分的合并过程中,选取候选点的规则:
规则1:
从base LR边,顺时针转动到候选点与R点的边其角度要小于180度。比如这里的6为候选点,而R点是8,那么线段(2,8)顺时针旋转到(6,8)这条边,角度小于180度。
规则2:
base LR边的两个端点和候选点,构成的三角形的外接圆,不能包含下一个候选点。
举例:
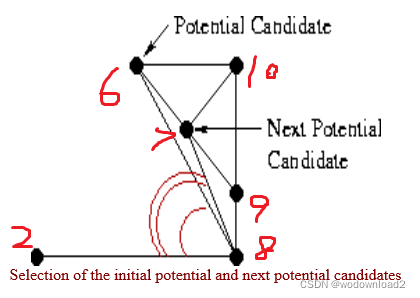
线段(2,8)为base LR边。
第一个候选点为6,因为线段(2,8)和线段(6,8)夹角最小,所以先考虑此候选点。
而此时三角形(2,8,6)的外接圆如下:

此时下一个候选点7,此时落在了三角形(2,8,6)外接圆的内部。所以不满足规则2。那么6则不是合理的候选点。
那么此时删除边(6,8)

第二个候选点7,此时由点(2,8,7)构成的三角形的外接圆如下:

此时9这个候选点在三角形(2,8,7)外接圆的外部。此时7为合法的候选点。
然后呢?7为合法的点之后呢?
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
// <copyright file="Dwyer.cs">
// Original Triangle code by Jonathan Richard Shewchuk, http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~quake/triangle.html
// Triangle.NET code by Christian Woltering, http://triangle.codeplex.com/
// </copyright>
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace TriangleNet.Algorithm
{
using System;
using TriangleNet.Data;
using TriangleNet.Log;
/// <summary>
/// Builds a delaunay triangulation using the divide-and-conquer algorithm.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// The divide-and-conquer bounding box
///
/// I originally implemented the divide-and-conquer and incremental Delaunay
/// triangulations using the edge-based data structure presented by Guibas
/// and Stolfi. Switching to a triangle-based data structure doubled the
/// speed. However, I had to think of a few extra tricks to maintain the
/// elegance of the original algorithms.
///
/// The "bounding box" used by my variant of the divide-and-conquer
/// algorithm uses one triangle for each edge of the convex hull of the
/// triangulation. These bounding triangles all share a common apical
/// vertex, which is represented by NULL and which represents nothing.
/// The bounding triangles are linked in a circular fan about this NULL
/// vertex, and the edges on the convex hull of the triangulation appear
/// opposite the NULL vertex. You might find it easiest to imagine that
/// the NULL vertex is a point in 3D space behind the center of the
/// triangulation, and that the bounding triangles form a sort of cone.
///
/// This bounding box makes it easy to represent degenerate cases. For
/// instance, the triangulation of two vertices is a single edge. This edge
/// is represented by two bounding box triangles, one on each "side" of the
/// edge. These triangles are also linked together in a fan about the NULL
/// vertex.
///
/// The bounding box also makes it easy to traverse the convex hull, as the
/// divide-and-conquer algorithm needs to do.
/// </remarks>
class Dwyer
{
static Random rand = new Random(DateTime.Now.Millisecond);
bool useDwyer = true;
Vertex[] sortarray;
Mesh mesh;
/// <summary>
/// Sort an array of vertices by x-coordinate, using the y-coordinate as a secondary key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left"></param>
/// <param name="right"></param>
/// <remarks>
/// Uses quicksort. Randomized O(n log n) time. No, I did not make any of
/// the usual quicksort mistakes.
/// </remarks>
void VertexSort(int left, int right)
{
int oleft = left;
int oright = right;
int arraysize = right - left + 1;
int pivot;
double pivotx, pivoty;
Vertex temp;
if (arraysize < 32)
{
// Insertion sort
for (int i = left + 1; i <= right; i++)
{
var a = sortarray[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= left && (sortarray[j].x > a.x || (sortarray[j].x == a.x && sortarray[j].y > a.y)))
{
sortarray[j + 1] = sortarray[j];
j--;
}
sortarray[j + 1] = a;
}
return;
}
// Choose a random pivot to split the array.
pivot = rand.Next(left, right);
pivotx = sortarray[pivot].x;
pivoty = sortarray[pivot].y;
// Split the array.
left--;
right++;
while (left < right)
{
// Search for a vertex whose x-coordinate is too large for the left.
do
{
left++;
}
while ((left <= right) && ((sortarray[left].x < pivotx) ||
((sortarray[left].x == pivotx) &&
(sortarray[left].y < pivoty))));
// Search for a vertex whose x-coordinate is too small for the right.
do
{
right--;
}
while ((left <= right) && ((sortarray[right].x > pivotx) ||
((sortarray[right].x == pivotx) &&
(sortarray[right].y > pivoty))));
if (left < right)
{
// Swap the left and right vertices.
temp = sortarray[left];
sortarray[left] = sortarray[right];
sortarray[right] = temp;
}
}
if (left > oleft)
{
// Recursively sort the left subset.
VertexSort(oleft, left);
}
if (oright > right + 1)
{
// Recursively sort the right subset.
VertexSort(right + 1, oright);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// An order statistic algorithm, almost. Shuffles an array of vertices so that
/// the first 'median' vertices occur lexicographically before the remaining vertices.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left"></param>
/// <param name="right"></param>
/// <param name="median"></param>
/// <param name="axis"></param>
/// <remarks>
/// Uses the x-coordinate as the primary key if axis == 0; the y-coordinate
/// if axis == 1. Very similar to the vertexsort() procedure, but runs in
/// randomized linear time.
/// </remarks>
void VertexMedian(int left, int right, int median, int axis)
{
int arraysize = right - left + 1;
int oleft = left, oright = right;
int pivot;
double pivot1, pivot2;
Vertex temp;
if (arraysize == 2)
{
// Recursive base case.
if ((sortarray[left][axis] > sortarray[right][axis]) ||
((sortarray[left][axis] == sortarray[right][axis]) &&
(sortarray[left][1 - axis] > sortarray[right][1 - axis])))
{
temp = sortarray[right];
sortarray[right] = sortarray[left];
sortarray[left] = temp;
}
return;
}
// Choose a random pivot to split the array.
pivot = rand.Next(left, right); //left + arraysize / 2;
pivot1 = sortarray[pivot][axis];
pivot2 = sortarray[pivot][1 - axis];
left--;
right++;
while (left < right)
{
// Search for a vertex whose x-coordinate is too large for the left.
do
{
left++;
}
while ((left <= right) && ((sortarray[left][axis] < pivot1) ||
((sortarray[left][axis] == pivot1) &&
(sortarray[left][1 - axis] < pivot2))));
// Search for a vertex whose x-coordinate is too small for the right.
do
{
right--;
}
while ((left <= right) && ((sortarray[right][axis] > pivot1) ||
((sortarray[right][axis] == pivot1) &&
(sortarray[right][1 - axis] > pivot2))));
if (left < right)
{
// Swap the left and right vertices.
temp = sortarray[left];
sortarray[left] = sortarray[right];
sortarray[right] = temp;
}
}
// Unlike in vertexsort(), at most one of the following conditionals is true.
if (left > median)
{
// Recursively shuffle the left subset.
VertexMedian(oleft, left - 1, median, axis);
}
if (right < median - 1)
{
// Recursively shuffle the right subset.
VertexMedian(right + 1, oright, median, axis);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Sorts the vertices as appropriate for the divide-and-conquer algorithm with
/// alternating cuts.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left"></param>
/// <param name="right"></param>
/// <param name="axis"></param>
/// <remarks>
/// Partitions by x-coordinate if axis == 0; by y-coordinate if axis == 1.
/// For the base case, subsets containing only two or three vertices are
/// always sorted by x-coordinate.
/// </remarks>
void AlternateAxes(int left, int right, int axis)
{
int arraysize = right - left + 1;
int divider;
divider = arraysize >> 1;
//divider += left; // TODO: check
if (arraysize <= 3)
{
// Recursive base case: subsets of two or three vertices will be
// handled specially, and should always be sorted by x-coordinate.
axis = 0;
}
// Partition with a horizontal or vertical cut.
VertexMedian(left, right, left + divider, axis);
// Recursively partition the subsets with a cross cut.
if (arraysize - divider >= 2)
{
if (divider >= 2)
{
AlternateAxes(left, left + divider - 1, 1 - axis);
}
AlternateAxes(left + divider, right, 1 - axis);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Merge two adjacent Delaunay triangulations into a single Delaunay triangulation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="farleft">Bounding triangles of the left triangulation.</param>
/// <param name="innerleft">Bounding triangles of the left triangulation.</param>
/// <param name="innerright">Bounding triangles of the right triangulation.</param>
/// <param name="farright">Bounding triangles of the right triangulation.</param>
/// <param name="axis"></param>
/// <remarks>
/// This is similar to the algorithm given by Guibas and Stolfi, but uses
/// a triangle-based, rather than edge-based, data structure.
///
/// The algorithm walks up the gap between the two triangulations, knitting
/// them together. As they are merged, some of their bounding triangles
/// are converted into real triangles of the triangulation. The procedure
/// pulls each hull's bounding triangles apart, then knits them together
/// like the teeth of two gears. The Delaunay property determines, at each
/// step, whether the next "tooth" is a bounding triangle of the left hull
/// or the right. When a bounding triangle becomes real, its apex is
/// changed from NULL to a real vertex.
///
/// Only two new triangles need to be allocated. These become new bounding
/// triangles at the top and bottom of the seam. They are used to connect
/// the remaining bounding triangles (those that have not been converted
/// into real triangles) into a single fan.
///
/// On entry, 'farleft' and 'innerleft' are bounding triangles of the left
/// triangulation. The origin of 'farleft' is the leftmost vertex, and
/// the destination of 'innerleft' is the rightmost vertex of the
/// triangulation. Similarly, 'innerright' and 'farright' are bounding
/// triangles of the right triangulation. The origin of 'innerright' and
/// destination of 'farright' are the leftmost and rightmost vertices.
///
/// On completion, the origin of 'farleft' is the leftmost vertex of the
/// merged triangulation, and the destination of 'farright' is the rightmost
/// vertex.
/// </remarks>
void MergeHulls(ref Otri farleft, ref Otri innerleft, ref Otri innerright,
ref Otri farright, int axis)
{
Otri leftcand = default(Otri), rightcand = default(Otri);
Otri nextedge = default(Otri);
Otri sidecasing = default(Otri), topcasing = default(Otri), outercasing = default(Otri);
Otri checkedge = default(Otri);
Otri baseedge = default(Otri);
Vertex innerleftdest;
Vertex innerrightorg;
Vertex innerleftapex, innerrightapex;
Vertex farleftpt, farrightpt;
Vertex farleftapex, farrightapex;
Vertex lowerleft, lowerright;
Vertex upperleft, upperright;
Vertex nextapex;
Vertex checkvertex;
bool changemade;
bool badedge;
bool leftfinished, rightfinished;
innerleftdest = innerleft.Dest();
innerleftapex = innerleft.Apex();
innerrightorg = innerright.Org();
innerrightapex = innerright.Apex();
// Special treatment for horizontal cuts.
if (useDwyer && (axis == 1))
{
farleftpt = farleft.Org();
farleftapex = farleft.Apex();
farrightpt = farright.Dest();
farrightapex = farright.Apex();
// The pointers to the extremal vertices are shifted to point to the
// topmost and bottommost vertex of each hull, rather than the
// leftmost and rightmost vertices.
while (farleftapex.y < farleftpt.y)
{
farleft.LnextSelf();
farleft.SymSelf();
farleftpt = farleftapex;
farleftapex = farleft.Apex();
}
innerleft.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
while (checkvertex.y > innerleftdest.y)
{
checkedge.Lnext(ref innerleft);
innerleftapex = innerleftdest;
innerleftdest = checkvertex;
innerleft.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
}
while (innerrightapex.y < innerrightorg.y)
{
innerright.LnextSelf();
innerright.SymSelf();
innerrightorg = innerrightapex;
innerrightapex = innerright.Apex();
}
farright.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
while (checkvertex.y > farrightpt.y)
{
checkedge.Lnext(ref farright);
farrightapex = farrightpt;
farrightpt = checkvertex;
farright.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
}
}
// Find a line tangent to and below both hulls.
do
{
changemade = false;
// Make innerleftdest the "bottommost" vertex of the left hull.
if (Primitives.CounterClockwise(innerleftdest, innerleftapex, innerrightorg) > 0.0)
{
innerleft.LprevSelf();
innerleft.SymSelf();
innerleftdest = innerleftapex;
innerleftapex = innerleft.Apex();
changemade = true;
}
// Make innerrightorg the "bottommost" vertex of the right hull.
if (Primitives.CounterClockwise(innerrightapex, innerrightorg, innerleftdest) > 0.0)
{
innerright.LnextSelf();
innerright.SymSelf();
innerrightorg = innerrightapex;
innerrightapex = innerright.Apex();
changemade = true;
}
} while (changemade);
// Find the two candidates to be the next "gear tooth."
innerleft.Sym(ref leftcand);
innerright.Sym(ref rightcand);
// Create the bottom new bounding triangle.
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref baseedge);
// Connect it to the bounding boxes of the left and right triangulations.
baseedge.Bond(ref innerleft);
baseedge.LnextSelf();
baseedge.Bond(ref innerright);
baseedge.LnextSelf();
baseedge.SetOrg(innerrightorg);
baseedge.SetDest(innerleftdest);
// Apex is intentionally left NULL.
// Fix the extreme triangles if necessary.
farleftpt = farleft.Org();
if (innerleftdest == farleftpt)
{
baseedge.Lnext(ref farleft);
}
farrightpt = farright.Dest();
if (innerrightorg == farrightpt)
{
baseedge.Lprev(ref farright);
}
// The vertices of the current knitting edge.
lowerleft = innerleftdest;
lowerright = innerrightorg;
// The candidate vertices for knitting.
upperleft = leftcand.Apex();
upperright = rightcand.Apex();
// Walk up the gap between the two triangulations, knitting them together.
while (true)
{
// Have we reached the top? (This isn't quite the right question,
// because even though the left triangulation might seem finished now,
// moving up on the right triangulation might reveal a new vertex of
// the left triangulation. And vice-versa.)
leftfinished = Primitives.CounterClockwise(upperleft, lowerleft, lowerright) <= 0.0;
rightfinished = Primitives.CounterClockwise(upperright, lowerleft, lowerright) <= 0.0;
if (leftfinished && rightfinished)
{
// Create the top new bounding triangle.
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref nextedge);
nextedge.SetOrg(lowerleft);
nextedge.SetDest(lowerright);
// Apex is intentionally left NULL.
// Connect it to the bounding boxes of the two triangulations.
nextedge.Bond(ref baseedge);
nextedge.LnextSelf();
nextedge.Bond(ref rightcand);
nextedge.LnextSelf();
nextedge.Bond(ref leftcand);
// Special treatment for horizontal cuts.
if (useDwyer && (axis == 1))
{
farleftpt = farleft.Org();
farleftapex = farleft.Apex();
farrightpt = farright.Dest();
farrightapex = farright.Apex();
farleft.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
// The pointers to the extremal vertices are restored to the
// leftmost and rightmost vertices (rather than topmost and
// bottommost).
while (checkvertex.x < farleftpt.x)
{
checkedge.Lprev(ref farleft);
farleftapex = farleftpt;
farleftpt = checkvertex;
farleft.Sym(ref checkedge);
checkvertex = checkedge.Apex();
}
while (farrightapex.x > farrightpt.x)
{
farright.LprevSelf();
farright.SymSelf();
farrightpt = farrightapex;
farrightapex = farright.Apex();
}
}
return;
}
// Consider eliminating edges from the left triangulation.
if (!leftfinished)
{
// What vertex would be exposed if an edge were deleted?
leftcand.Lprev(ref nextedge);
nextedge.SymSelf();
nextapex = nextedge.Apex();
// If nextapex is NULL, then no vertex would be exposed; the
// triangulation would have been eaten right through.
if (nextapex != null)
{
// Check whether the edge is Delaunay.
badedge = Primitives.InCircle(lowerleft, lowerright, upperleft, nextapex) > 0.0;
while (badedge)
{
// Eliminate the edge with an edge flip. As a result, the
// left triangulation will have one more boundary triangle.
nextedge.LnextSelf();
nextedge.Sym(ref topcasing);
nextedge.LnextSelf();
nextedge.Sym(ref sidecasing);
nextedge.Bond(ref topcasing);
leftcand.Bond(ref sidecasing);
leftcand.LnextSelf();
leftcand.Sym(ref outercasing);
nextedge.LprevSelf();
nextedge.Bond(ref outercasing);
// Correct the vertices to reflect the edge flip.
leftcand.SetOrg(lowerleft);
leftcand.SetDest(null);
leftcand.SetApex(nextapex);
nextedge.SetOrg(null);
nextedge.SetDest(upperleft);
nextedge.SetApex(nextapex);
// Consider the newly exposed vertex.
upperleft = nextapex;
// What vertex would be exposed if another edge were deleted?
sidecasing.Copy(ref nextedge);
nextapex = nextedge.Apex();
if (nextapex != null)
{
// Check whether the edge is Delaunay.
badedge = Primitives.InCircle(lowerleft, lowerright, upperleft, nextapex) > 0.0;
}
else
{
// Avoid eating right through the triangulation.
badedge = false;
}
}
}
}
// Consider eliminating edges from the right triangulation.
if (!rightfinished)
{
// What vertex would be exposed if an edge were deleted?
rightcand.Lnext(ref nextedge);
nextedge.SymSelf();
nextapex = nextedge.Apex();
// If nextapex is NULL, then no vertex would be exposed; the
// triangulation would have been eaten right through.
if (nextapex != null)
{
// Check whether the edge is Delaunay.
badedge = Primitives.InCircle(lowerleft, lowerright, upperright, nextapex) > 0.0;
while (badedge)
{
// Eliminate the edge with an edge flip. As a result, the
// right triangulation will have one more boundary triangle.
nextedge.LprevSelf();
nextedge.Sym(ref topcasing);
nextedge.LprevSelf();
nextedge.Sym(ref sidecasing);
nextedge.Bond(ref topcasing);
rightcand.Bond(ref sidecasing);
rightcand.LprevSelf();
rightcand.Sym(ref outercasing);
nextedge.LnextSelf();
nextedge.Bond(ref outercasing);
// Correct the vertices to reflect the edge flip.
rightcand.SetOrg(null);
rightcand.SetDest(lowerright);
rightcand.SetApex(nextapex);
nextedge.SetOrg(upperright);
nextedge.SetDest(null);
nextedge.SetApex(nextapex);
// Consider the newly exposed vertex.
upperright = nextapex;
// What vertex would be exposed if another edge were deleted?
sidecasing.Copy(ref nextedge);
nextapex = nextedge.Apex();
if (nextapex != null)
{
// Check whether the edge is Delaunay.
badedge = Primitives.InCircle(lowerleft, lowerright, upperright, nextapex) > 0.0;
}
else
{
// Avoid eating right through the triangulation.
badedge = false;
}
}
}
}
if (leftfinished || (!rightfinished &&
(Primitives.InCircle(upperleft, lowerleft, lowerright, upperright) > 0.0)))
{
// Knit the triangulations, adding an edge from 'lowerleft'
// to 'upperright'.
baseedge.Bond(ref rightcand);
rightcand.Lprev(ref baseedge);
baseedge.SetDest(lowerleft);
lowerright = upperright;
baseedge.Sym(ref rightcand);
upperright = rightcand.Apex();
}
else
{
// Knit the triangulations, adding an edge from 'upperleft'
// to 'lowerright'.
baseedge.Bond(ref leftcand);
leftcand.Lnext(ref baseedge);
baseedge.SetOrg(lowerright);
lowerleft = upperleft;
baseedge.Sym(ref leftcand);
upperleft = leftcand.Apex();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Recursively form a Delaunay triangulation by the divide-and-conquer method.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="left"></param>
/// <param name="right"></param>
/// <param name="axis"></param>
/// <param name="farleft"></param>
/// <param name="farright"></param>
/// <remarks>
/// Recursively breaks down the problem into smaller pieces, which are
/// knitted together by mergehulls(). The base cases (problems of two or
/// three vertices) are handled specially here.
///
/// On completion, 'farleft' and 'farright' are bounding triangles such that
/// the origin of 'farleft' is the leftmost vertex (breaking ties by
/// choosing the highest leftmost vertex), and the destination of
/// 'farright' is the rightmost vertex (breaking ties by choosing the
/// lowest rightmost vertex).
/// </remarks>
void DivconqRecurse(int left, int right, int axis,
ref Otri farleft, ref Otri farright)
{
Otri midtri = default(Otri);
Otri tri1 = default(Otri);
Otri tri2 = default(Otri);
Otri tri3 = default(Otri);
Otri innerleft = default(Otri), innerright = default(Otri);
double area;
int vertices = right - left + 1;
int divider;
if (vertices == 2)
{
// The triangulation of two vertices is an edge. An edge is
// represented by two bounding triangles.
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref farleft);
farleft.SetOrg(sortarray[left]);
farleft.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
// The apex is intentionally left NULL.
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref farright);
farright.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 1]);
farright.SetDest(sortarray[left]);
// The apex is intentionally left NULL.
farleft.Bond(ref farright);
farleft.LprevSelf();
farright.LnextSelf();
farleft.Bond(ref farright);
farleft.LprevSelf();
farright.LnextSelf();
farleft.Bond(ref farright);
// Ensure that the origin of 'farleft' is sortarray[0].
farright.Lprev(ref farleft);
return;
}
else if (vertices == 3)
{
// The triangulation of three vertices is either a triangle (with
// three bounding triangles) or two edges (with four bounding
// triangles). In either case, four triangles are created.
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref midtri);
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref tri1);
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref tri2);
mesh.MakeTriangle(ref tri3);
area = Primitives.CounterClockwise(sortarray[left], sortarray[left + 1], sortarray[left + 2]);
if (area == 0.0)
{
// Three collinear vertices; the triangulation is two edges.
midtri.SetOrg(sortarray[left]);
midtri.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri1.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri1.SetDest(sortarray[left]);
tri2.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 2]);
tri2.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri3.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri3.SetDest(sortarray[left + 2]);
// All apices are intentionally left NULL.
midtri.Bond(ref tri1);
tri2.Bond(ref tri3);
midtri.LnextSelf();
tri1.LprevSelf();
tri2.LnextSelf();
tri3.LprevSelf();
midtri.Bond(ref tri3);
tri1.Bond(ref tri2);
midtri.LnextSelf();
tri1.LprevSelf();
tri2.LnextSelf();
tri3.LprevSelf();
midtri.Bond(ref tri1);
tri2.Bond(ref tri3);
// Ensure that the origin of 'farleft' is sortarray[0].
tri1.Copy(ref farleft);
// Ensure that the destination of 'farright' is sortarray[2].
tri2.Copy(ref farright);
}
else
{
// The three vertices are not collinear; the triangulation is one
// triangle, namely 'midtri'.
midtri.SetOrg(sortarray[left]);
tri1.SetDest(sortarray[left]);
tri3.SetOrg(sortarray[left]);
// Apices of tri1, tri2, and tri3 are left NULL.
if (area > 0.0)
{
// The vertices are in counterclockwise order.
midtri.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri1.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri2.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
midtri.SetApex(sortarray[left + 2]);
tri2.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 2]);
tri3.SetDest(sortarray[left + 2]);
}
else
{
// The vertices are in clockwise order.
midtri.SetDest(sortarray[left + 2]);
tri1.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 2]);
tri2.SetDest(sortarray[left + 2]);
midtri.SetApex(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri2.SetOrg(sortarray[left + 1]);
tri3.SetDest(sortarray[left + 1]);
}
// The topology does not depend on how the vertices are ordered.
midtri.Bond(ref tri1);
midtri.LnextSelf();
midtri.Bond(ref tri2);
midtri.LnextSelf();
midtri.Bond(ref tri3);
tri1.LprevSelf();
tri2.LnextSelf();
tri1.Bond(ref tri2);
tri1.LprevSelf();
tri3.LprevSelf();
tri1.Bond(ref tri3);
tri2.LnextSelf();
tri3.LprevSelf();
tri2.Bond(ref tri3);
// Ensure that the origin of 'farleft' is sortarray[0].
tri1.Copy(ref farleft);
// Ensure that the destination of 'farright' is sortarray[2].
if (area > 0.0)
{
tri2.Copy(ref farright);
}
else
{
farleft.Lnext(ref farright);
}
}
return;
}
else
{
// Split the vertices in half.
divider = vertices >> 1;
// Recursively triangulate each half.
DivconqRecurse(left, left + divider - 1, 1 - axis, ref farleft, ref innerleft);
//DebugWriter.Session.Write(mesh, true);
DivconqRecurse(left + divider, right, 1 - axis, ref innerright, ref farright);
//DebugWriter.Session.Write(mesh, true);
// Merge the two triangulations into one.
MergeHulls(ref farleft, ref innerleft, ref innerright, ref farright, axis);
//DebugWriter.Session.Write(mesh, true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Removes ghost triangles.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="startghost"></param>
/// <returns>Number of vertices on the hull.</returns>
int RemoveGhosts(ref Otri startghost)
{
Otri searchedge = default(Otri);
Otri dissolveedge = default(Otri);
Otri deadtriangle = default(Otri);
Vertex markorg;
int hullsize;
bool noPoly = !mesh.behavior.Poly;
// Find an edge on the convex hull to start point location from.
startghost.Lprev(ref searchedge);
searchedge.SymSelf();
Mesh.dummytri.neighbors[0] = searchedge;
// Remove the bounding box and count the convex hull edges.
startghost.Copy(ref dissolveedge);
hullsize = 0;
do
{
hullsize++;
dissolveedge.Lnext(ref deadtriangle);
dissolveedge.LprevSelf();
dissolveedge.SymSelf();
// If no PSLG is involved, set the boundary markers of all the vertices
// on the convex hull. If a PSLG is used, this step is done later.
if (noPoly)
{
// Watch out for the case where all the input vertices are collinear.
if (dissolveedge.triangle != Mesh.dummytri)
{
markorg = dissolveedge.Org();
if (markorg.mark == 0)
{
markorg.mark = 1;
}
}
}
// Remove a bounding triangle from a convex hull triangle.
dissolveedge.Dissolve();
// Find the next bounding triangle.
deadtriangle.Sym(ref dissolveedge);
// Delete the bounding triangle.
mesh.TriangleDealloc(deadtriangle.triangle);
} while (!dissolveedge.Equal(startghost));
return hullsize;
}
/// <summary>
/// Form a Delaunay triangulation by the divide-and-conquer method.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
/// <remarks>
/// Sorts the vertices, calls a recursive procedure to triangulate them, and
/// removes the bounding box, setting boundary markers as appropriate.
/// </remarks>
public int Triangulate(Mesh m)
{
Otri hullleft = default(Otri), hullright = default(Otri);
int divider;
int i, j;
this.mesh = m;
//DebugWriter.Session.Start("test-dbg");
// Allocate an array of pointers to vertices for sorting.
// TODO: use ToArray
this.sortarray = new Vertex[m.invertices];
i = 0;
foreach (var v in m.vertices.Values)
{
sortarray[i++] = v;
}
// Sort the vertices.
//Array.Sort(sortarray);
VertexSort(0, m.invertices - 1);
// Discard duplicate vertices, which can really mess up the algorithm.
i = 0;
for (j = 1; j < m.invertices; j++)
{
if ((sortarray[i].x == sortarray[j].x)
&& (sortarray[i].y == sortarray[j].y))
{
if (Behavior.Verbose)
{
SimpleLog.Instance.Warning(
String.Format("A duplicate vertex appeared and was ignored (ID {0}).", sortarray[j].hash),
"DivConquer.DivconqDelaunay()");
}
sortarray[j].type = VertexType.UndeadVertex;
m.undeads++;
}
else
{
i++;
sortarray[i] = sortarray[j];
}
}
i++;
if (useDwyer)
{
// Re-sort the array of vertices to accommodate alternating cuts.
divider = i >> 1;
if (i - divider >= 2)
{
if (divider >= 2)
{
AlternateAxes(0, divider - 1, 1);
}
AlternateAxes(divider, i - 1, 1);
}
}
// Form the Delaunay triangulation.
DivconqRecurse(0, i-1, 0, ref hullleft, ref hullright);
//DebugWriter.Session.Write(mesh);
//DebugWriter.Session.Finish();
return RemoveGhosts(ref hullleft);
}
}
}
























 1844
1844

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








