A*算法介绍
A*算法是一种常用的寻路算法,被广泛应用于人工智能和游戏开发中。该算法通过评估每个节点的代价和启发式函数来找到最佳路径。在这篇博文中,我们将深入探讨A*算法的原理。
A*算法的核心思想是在搜索过程中综合考虑两个因素:已经花费的代价和还需要花费的代价。具体而言,A*算法通过计算每个节点的综合评估函数f(n)来确定下一个最优的节点进行探索。其中,f(n)的计算方式为:
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
其中,g(n)表示从起始节点到当前节点的实际代价,h(n)表示从当前节点到目标节点的估计代价。通过计算f(n),A*算法可以选择具有最小f(n)值的节点作为下一个探索的节点。
A*算法的启发式函数h(n)在很大程度上决定了算法的搜索效率。一般来说,h(n)应该是一种乐观估计,即不会高估实际代价。如果h(n)准确地估计了到目标节点的代价,那么A*算法将以最短路径找到目标节点。
总的来说,A*算法是一种高效且可靠的寻路算法,适用于许多领域的问题解决。通过深入理解A*算法的原理,我们可以更好地应用该算法,提高问题解决的效率和准确性。希望这篇博文能帮助您更好地理解A*算法的工作原理和应用场景。感谢阅读!
代码原理
这段代码实现了A*搜索算法,用于在二维网格中找到从起点到终点的最短路径。以下是对代码每个部分的详细解释:
function [dis, road] = Axing_fun(startx, starty, endx, endy, Estart_x, Estart_y, Weight, High, C, show_flag)
-
输入参数:
startx, starty:起点坐标。endx, endy:终点坐标。Estart_x, Estart_y:网格的起始坐标。Weight, High:网格的宽度和高度。C:成本矩阵,表示每个格子的代价。show_flag:显示标志,用于控制是否绘制路径。
-
输出参数:
dis:从起点到终点的总距离。road:从起点到终点的路径。
初始化
f = 0 + abs(startx - endx) + abs(starty - endy); % 初始估计总代价(曼哈顿距离)
already_frontier = {f, startx, starty, 0, [startx, starty]}; % 已探索节点列表
f:起始节点的估计总代价,使用曼哈顿距离。already_frontier:已探索节点列表,包含起始节点信息。
寻找邻居点
frontier = cell(0, 5);
N = find_frontier(startx, starty, Estart_x, Estart_x + Weight, Estart_y, Estart_y + High, C, already_frontier);
frontier:待探索节点列表。N:起始节点的邻居点,通过find_frontier函数找到。
处理邻居点
for i = 1:size(N, 2)
g = norm([startx, starty] - [N(1, i), N(2, i)]); % 计算当前代价
f = g + abs(N(1, i) - endx) + abs(N(2, i) - endy);
frontier{i, 1} = f;
frontier{i, 2} = N(1, i);
frontier{i, 3} = N(2, i);
frontier{i, 4} = g;
frontier{i, 5} = [[startx, starty]; [N(1, i), N(2, i)]]; % 记录路径
end
frontier = sortrows(frontier, 1); % 按总代价排序
计算邻居点的代价g和估计总代价f,并将它们添加到frontier中。
主循环:探索节点
while isempty(frontier) == 0
current = frontier(1, :); % 取出当前节点
already_frontier(end + 1, :) = frontier(1, :); % 将当前节点移入已探索列表
frontier(1, :) = []; % 从待探索列表中移除当前节点
mx = current{1, 2}; % 当前节点的坐标
my = current{1, 3};
if show_flag == 2
plot(current{1, 2}, current{1, 3}, 'g*'); % 用绿色*号标记当前节点
end
% 查找当前节点的邻居
N = find_frontier(mx, my, Estart_x, Estart_x + Weight, Estart_y, Estart_y + High, C, already_frontier);
for i = 1:size(N, 2)
b = find([frontier{:, 2}] == N(1, i));
a = b([frontier{b, 3}] == N(2, i));
g = current{1, 4} + norm([mx, my] - [N(1, i), N(2, i)]);
f = g + abs(N(1, i) - endx) + abs(N(2, i) - endy);
if a > 0 % 如果节点已经在frontier中,检查是否有更小的代价
if frontier{a, 4} > g
frontier{a, 5} = [current{1, 5}; [N(1, i), N(2, i)]];
frontier{a, 4} = g;
frontier{a, 1} = f;
end
else % 如果节点不在frontier中,加入frontier
temp{1, 1} = f;
temp{1, 2} = N(1, i);
temp{1, 3} = N(2, i);
temp{1, 4} = g;
temp{1, 5} = [current{1, 5}; [N(1, i), N(2, i)]];
temp_frontier = [temp; temp_frontier];
if show_flag == 2
plot(N(1, i), N(2, i), 'bs'); % 用蓝色正方形标记待检测节点
end
end
end
% 如果终点在already_frontier中,跳出循环
if already_frontier{end, 2} == endx && already_frontier{end, 3} == endy
plot(already_frontier{end, 5}(:, 1), already_frontier{end, 5}(:, 2), 'b', 'LineWidth', 2);
drawnow;
break;
end
% 插入排序,将新节点按代价插入frontier中
for i = 1:size(temp_frontier, 1)
j = 0;
while j <= size(frontier, 1) + 1
j = j + 1;
if j == size(frontier, 1) + 1
frontier = [frontier; temp_frontier(i, :)];
break;
end
if temp_frontier{i, 1} < frontier{j, 1}
if j == 1
frontier = [temp_frontier(i, :); frontier];
else
frontier = [frontier(1:j-1, :); temp_frontier(i, :); frontier(j:end, :)];
end
break;
end
end
end
temp_frontier = cell(0, 5); % 清空临时列表
if show_flag == 1 || show_flag == 2
p = plot(already_frontier{end, 5}(:, 1), already_frontier{end, 5}(:, 2), 'b', 'LineWidth', 2);
drawnow;
delete(p);
end
end
dis = already_frontier{end, 1}; % 返回总路程
road = already_frontier{end, 5}; % 返回最短路径
- 步骤1:取出当前代价最小的节点,将其移到
already_frontier。 - 步骤2:找到当前节点的邻居点,计算邻居点的代价。
- 步骤3:如果邻居点已在
frontier中,检查并更新代价;如果不在,加入frontier。 - 步骤4:检查是否找到终点,如果找到则绘制路径并跳出循环。
- 步骤5:按代价将新节点插入
frontier中。 - 步骤6:更新显示路径。
最后返回最短路径的总路程和路径坐标。
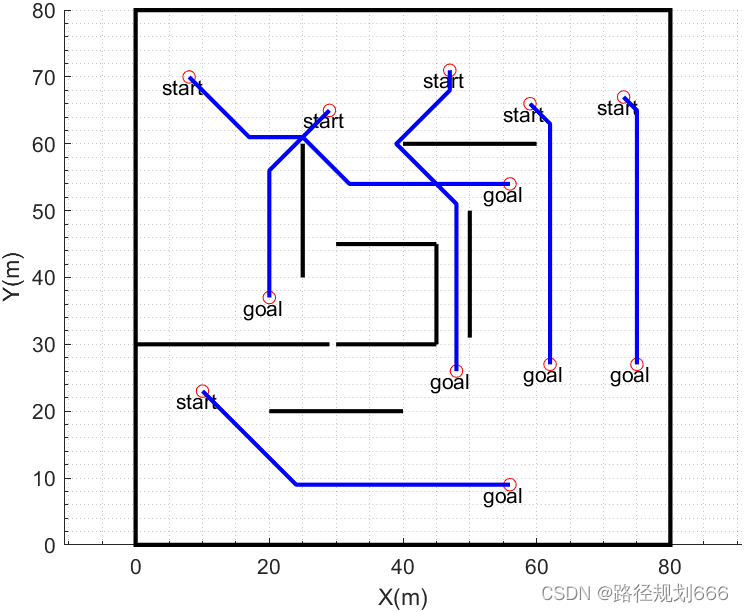
代码运行效果图
代码获取链接
哔哩哔哩工房 (bilibili.com)![]() https://gf.bilibili.com/item/detail/1106192108
https://gf.bilibili.com/item/detail/1106192108






















 7344
7344

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








