
1.背景
2020年,Li等人受到自然界黏菌觅食行为启发,提出了黏菌算法(Slime Mould Algorithm,SMA)。
2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
算法模拟了黏菌在觅食过程中的行为和形态变化,并没有对其完整的生命周期进行建模。同时,算法通过权重来模拟粘菌在觅食过程中产生的正反馈,从而形成三种不同的形态类型。当各种食物源的质量不同时,粘菌可以选择浓度最高的食物源。当粘菌遇到高质量食物时,离开该区域的概率会降低。当食物源的质量很高时,粘菌将采用局部搜索方法,从而将搜索集中在已发现的食物源上。
2.2算法过程
群体位置初始化:
x
=
l
b
+
r
a
n
d
∗
(
u
b
−
l
b
)
x=lb+rand*(ub-lb)
x=lb+rand∗(ub−lb)
其中,
u
b
,
l
b
ub,lb
ub,lb分别代表黏菌上下位置边界。
靠近食物:
X
(
t
+
1
)
→
=
{
X
b
(
t
)
→
+
v
b
→
⋅
(
W
→
⋅
X
A
(
t
)
→
−
X
B
(
t
)
→
)
,
r
<
p
v
c
→
⋅
X
(
t
)
→
,
r
≥
p
\overrightarrow{X\left(t+1\right)}=\begin{cases}\overrightarrow{X_{b}\left(t\right)}+\overrightarrow{vb}\cdot\left(\overrightarrow{W}\cdot\overrightarrow{X_{A}\left(t\right)}-\overrightarrow{X_{B}\left(t\right)}\right),r<p\\\overrightarrow{v\text{c}}\cdot\overrightarrow{X\left(t\right)},r\geq p\end{cases}
X(t+1)=⎩
⎨
⎧Xb(t)+vb⋅(W⋅XA(t)−XB(t)),r<pvc⋅X(t),r≥p
其中,
X
A
→
,
,
X
B
→
\overrightarrow{X_{A}},, \overrightarrow{X_{B}}
XA,,XB代表分别选择两个随机位置。为了理解这个数学公式,首先来看
p
p
p的表达式:
p
=
tanh
∣
S
(
i
)
−
D
F
∣
p=\tanh|S\left(i\right)-DF|
p=tanh∣S(i)−DF∣

这里,
S
(
i
)
,
D
F
S(i),DF
S(i),DF分别代表个体
i
i
i适应度值和当前最优个体适应度。也就是说,当个体
i
i
i适应度值和当前最优个体适应度距离相差较大时,
p
p
p趋近于1。
因此,当
r
<
p
r<p
r<p时,全局搜索;当
r
≥
p
r \ge p
r≥p时,局部搜索。
v
b
⃗
=
[
−
a
,
a
]
a
=
arctanh
(
−
(
t
max
_
t
)
+
1
)
\vec{vb}=[-a,a] \\ a=\operatorname{arctanh}(-\left(\frac{t}{\max\_t}\right)+1)
vb=[−a,a]a=arctanh(−(max_tt)+1)
这里,规定了局部搜索方向,并且随着迭代次数增强,逐渐减小(以达到收敛)。
W
(
S
m
e
l
l
l
n
d
e
x
(
i
)
)
→
=
{
1
+
r
⋅
log
(
b
F
−
S
(
i
)
b
F
−
w
F
+
1
)
,
condition
1
−
r
⋅
log
(
b
F
−
S
(
i
)
b
F
−
w
F
+
1
)
,
others
\overrightarrow{W(Smelllndex(i))}=\begin{cases}1+r\cdot\log\left(\frac{bF-S\left(i\right)}{bF-wF}+1\right),\text{condition}\\1-r\cdot\log\left(\frac{bF-S\left(i\right)}{bF-wF}+1\right),\quad\text{others}\end{cases}
W(Smelllndex(i))=⎩
⎨
⎧1+r⋅log(bF−wFbF−S(i)+1),condition1−r⋅log(bF−wFbF−S(i)+1),others
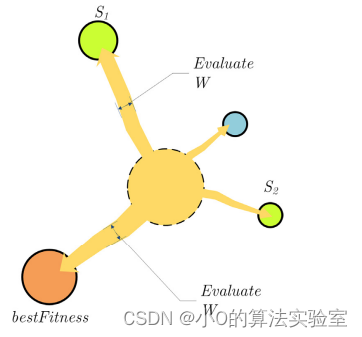
**包裹食物 **:
黏菌根据食物质量调整其搜索模式:当食物浓度足够时,靠近该区域的权重更大;当食物浓度较低时,该区域的权重将减少,从而转而探索其他区域。
X
∗
→
=
{
r
a
n
d
⋅
(
U
B
−
L
B
)
+
L
B
,
r
a
n
d
<
z
X
b
(
t
)
→
+
v
b
→
⋅
(
W
⋅
X
A
(
t
)
→
−
X
B
(
t
)
→
)
,
r
<
p
v
c
→
⋅
X
(
t
)
→
,
r
≥
p
\overrightarrow{X^*}=\begin{cases}rand\cdot(UB-LB)+LB,rand<z\\\overrightarrow{X_b\left(t\right)}+\overrightarrow{vb}\cdot\left(W\cdot\overrightarrow{X_A\left(t\right)}-\overrightarrow{X_B\left(t\right)}\right),r<p\\\overrightarrow{vc}\cdot\overrightarrow{X\left(t\right)},r\geq p\end{cases}
X∗=⎩
⎨
⎧rand⋅(UB−LB)+LB,rand<zXb(t)+vb⋅(W⋅XA(t)−XB(t)),r<pvc⋅X(t),r≥p
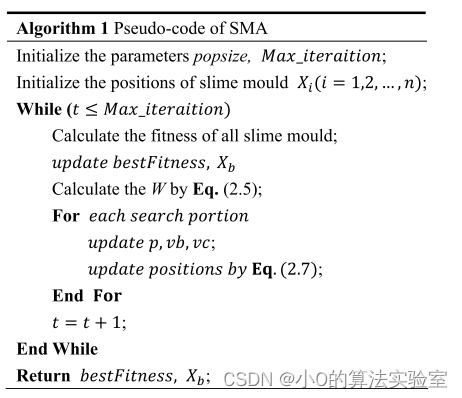
伪代码:
3.代码实现
% 黏菌算法
function [Best_pos, Best_fitness, Iter_curve, History_pos, History_best] = SMA(pop, maxIter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%input
%pop 种群数量
%dim 问题维数
%ub 变量上边界
%lb 变量下边界
%fobj 适应度函数
%maxIter 最大迭代次数
%output
%Best_pos 最优位置
%Best_fitness 最优适应度值
%Iter_curve 每代最优适应度值
%History_pos 每代种群位置
%History_best 每代最优个体位置
%% 控制参数
z=0.03; % parameter
weight = ones(pop,dim); % fitness weight of each slime mold
%% 初始化种群
X = zeros(pop, dim);
for i = 1:dim
X(:,i) = lb(i) + (ub(i) - lb(i)) * rand(pop, 1);
end
%% 计算适应度
AllFitness = zeros(1, pop);
for i=1:pop
AllFitness(i)=fobj(X(i,:));
end
%% 记录
[MinFitness, MinIdx] = sort(AllFitness);
Best_pos = X(MinIdx(1),:);
Best_fitness = MinFitness(1);
%% 迭代
it = 1;
while it <= maxIter
for i=1:pop
% 边界检查
Flag4ub=X(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=X(i,:)<lb;
X(i,:)=(X(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
AllFitness(i) = fobj(X(i,:));
end
[SmellOrder,SmellIndex] = sort(AllFitness); %Eq.(2.6)
worstFitness = SmellOrder(pop);
bestFitness = SmellOrder(1);
S=bestFitness-worstFitness+eps; %避免除0
for i=1:pop
for j=1:dim
if i<=(pop/2) %Eq.(2.5)
weight(SmellIndex(i),j) = 1+rand()*log10((bestFitness-SmellOrder(i))/(S)+1);
else
weight(SmellIndex(i),j) = 1-rand()*log10((bestFitness-SmellOrder(i))/(S)+1);
end
end
end
if bestFitness < Best_fitness
Best_pos=X(SmellIndex(1),:);
Best_fitness = bestFitness;
end
a = atanh(-(it/maxIter)+1); %Eq.(2.4)
b = 1-it/maxIter;
for i=1:pop
if rand<z %Eq.(2.7)
X(i,:) = (ub-lb)*rand+lb;
else
p =tanh(abs(AllFitness(i)-Best_fitness)); %Eq.(2.2)
vb = unifrnd(-a,a,1,dim); %Eq.(2.3)
vc = unifrnd(-b,b,1,dim);
for j=1:dim
r = rand();
A = randi([1,pop]);
B = randi([1,pop]);
if r<p %Eq.(2.1)
X(i,j) = Best_pos(j)+ vb(j)*(weight(i,j)*X(A,j)-X(B,j));
else
X(i,j) = vc(j)*X(i,j);
end
end
end
end
Iter_curve(it)=Best_fitness;
History_best{it} = Best_pos;
History_pos{it} = X;
it=it+1;
end
end
4.参考文献
[1] Li S, Chen H, Wang M, et al. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization[J]. Future generation computer systems, 2020, 111: 300-323.























 975
975











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










