
1.背景
2020年,Xue等人受麻雀觅食行为和逃避觅食者自然行为启发,提出了麻雀搜索算法(Sparrow Search Algorithm, SSA)。
2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
自然界中麻雀主要有觅食和反觅食两种行为:
- 觅食:麻雀中分为探索者和追随者,能够寻找较好食物的麻雀(适应度函数较高)为探索者,其余麻雀为追随者受到探索者方向影响
- 反觅食:麻雀群体中一定比例的麻雀会进行侦察,当发现觅食者来临时会做出相应的行为
2.2算法过程
群体位置初始化:
X
=
l
b
+
r
a
n
d
∗
(
u
b
−
l
b
)
X=lb+rand*(ub-lb)
X=lb+rand∗(ub−lb)
其中,
u
b
,
l
b
ub,lb
ub,lb分别代表种群上下位置边界。
探索者位置更新:
x
i
t
+
1
=
{
x
i
t
∗
exp
(
−
i
α
∗
i
t
e
r
max
)
,
R
2
<
S
T
x
i
t
+
Q
,
R
2
≥
S
T
x_{i}^{t+1}=\begin{cases}x_{i}^{t}*\exp{(\frac{-i}{\alpha *iter_{\max}})},R_{2}<ST\\x_{i}^{t}+Q,R_{2}\geq ST\end{cases}
xit+1={xit∗exp(α∗itermax−i),R2<STxit+Q,R2≥ST
其中,
R
2
,
S
T
R_2,ST
R2,ST分别为安全值和预警值。当
R
2
<
S
T
R_2<ST
R2<ST时,麻雀进行全局搜索觅食;当
R
2
≥
S
T
R_2\geq ST
R2≥ST时,麻雀以正态分布进行随机游走。
追随者位置更新:
x
i
t
+
1
=
{
Q
⋅
exp
(
x
worst
t
−
x
i
t
i
2
)
,
i
>
n
/
2
x
p
t
+
1
+
∣
x
i
t
−
x
p
t
+
1
∣
∗
A
+
,
otherwise
x_{i}^{t+1}=\begin{cases}Q\cdot\exp\left(\frac{x_{\text{worst}}^t-x_{i}^t}{i^2}\right),i>n/2\\x_{p}^{t+1}+|x_{i}^t-x_{p}^{t+1}|*A^+,\text{otherwise}\end{cases}
xit+1={Q⋅exp(i2xworstt−xit),i>n/2xpt+1+∣xit−xpt+1∣∗A+,otherwise
当
i
>
n
/
2
i>n/2
i>n/2时,适应度较低的麻雀没有获取到食物,因此需要获得更多食物;其他情况说明,麻雀在当前最优位置附近随机寻找一个位置。
侦察预警:
x
i
t
+
1
=
{
x
b
i
t
+
β
∗
(
x
i
t
−
x
b
i
t
)
,
f
i
≠
f
g
x
i
t
+
K
(
x
i
t
−
x
w
i
t
∣
f
i
−
f
w
∣
+
ε
)
,
f
i
=
f
g
x_{i}^{t+1}=\begin{cases}xb_{i}^{t}+\beta *(x_{i}^{t}-xb_{i}^{t}),f_{i}\neq f_{g}\\ x_{i}^{t}+K\Bigg(\frac{x_{i}^t-xw_{i}^t}{\mid f_i-f_w\mid+\varepsilon}\Bigg),f_{i}=f_{g}\end{cases}
xit+1=⎩
⎨
⎧xbit+β∗(xit−xbit),fi=fgxit+K(∣fi−fw∣+εxit−xwit),fi=fg
当
f
i
≠
f
g
f_i \neq f_g
fi=fg,麻雀正处于种群的边缘,容易受到觅食者攻击,此时朝着最优麻雀飞行;当
f
i
=
f
g
f_i=f_g
fi=fg时,此时麻雀处于危险位置,远离最差麻雀位置。
伪代码

3.代码实现
% 麻雀优化算法
function [Best_pos,Best_fitness ,Iter_curve,History_pos, History_best] = SSA(pop, M,c,d,dim,fobj )
%input
%pop 种群数量
%dim 问题维数
%c 变量上边界最大值
%d 变量下边界最小值
%fobj 适应度函数
%M 最大迭代次数
%output
%Best_pos 最优位置
%Best_fitness 最优适应度值
%Iter_curve 每代最优适应度值
%History_pos 每代种群位置
%History_best 每代最优麻雀位置
%% 参数
P_percent = 0.2; %探索者比例
pNum = round(pop * P_percent);
lb= c.*ones( 1,dim ); %约束上限
ub= d.*ones( 1,dim ); %约束下限
%% 位置初始化
for i = 1 : pop
x(i, :) = lb + (ub - lb) .* rand( 1, dim );
fit(i) = fobj(x(i, :)) ;
end
% 以下找到最小值对应的麻雀群
pFit = fit;
pX = x;
[ Best_fitness, bestI ] = min( fit );
Best_pos = x( bestI, : );
%% 迭代
for t = 1 : M
[ ans, sortIndex ] = sort(pFit);
[fmax,B]=max( pFit );
worse= x(B,:); %找到最差的个体
r2=rand(1);
if(r2<0.8)
for i = 1 : pNum % Equation (3)
r1=rand(1);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )*exp(-(i)/(r1*M)); %将种群按适应度排序后更新
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub ); %将种群限制在约束范围内
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
else
for i = 1 : pNum
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )+randn(1)*ones(1,dim);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
end
[ fMMin, bestII ] = min( fit );
bestXX = x( bestII, : );
for i = ( pNum + 1 ) : pop % Equation (4)
A=floor(rand(1,dim)*2)*2-1; %产生1和-1的随机数
if( i>(pop/2))
x( sortIndex(i ), : )=randn(1)*exp((worse-pX( sortIndex( i ), : ))/(i)^2);
else
x( sortIndex( i ), : )=bestXX+(abs(( pX( sortIndex( i ), : )-bestXX)))*(A'*(A*A')^(-1))*ones(1,dim);
end
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub ); %更新后种群的限制在变量范围
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) ); %更新过后重新计算适应度
end
c=randperm(numel(sortIndex));
b=sortIndex(c(1:20));
for j = 1 : length(b) % Equation (5)
if( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )>(Best_fitness) )
%如果适应度比最开始最小适应度差的话,就在原来的最好种群上增长一部分值
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )=Best_pos+(randn(1,dim)).*(abs(( pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) -Best_pos)));
else
%如果适应度达到开始最小的适应度值,就在原来的最好种群上随机增长或减小一部分
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) =pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )+(2*rand(1)-1)*(abs(pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )-worse))/ ( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )-fmax+1e-50);
end
x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( b(j) ) ) = fobj( x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) );
end
for i = 1 : pop
if ( fit( i ) < pFit( i ) )
pFit( i ) = fit( i );
pX( i, : ) = x( i, : );
end
if( pFit( i ) < Best_fitness )
Best_fitness= pFit( i );
Best_pos = pX( i, : );
end
end
Iter_curve(t)=Best_fitness;
History_pos{t} = x;
History_best{t} = Best_pos;
end
function s = Bounds( s, Lb, Ub)
% Apply the lower bound vector
temp = s;
I = temp < Lb;
temp(I) = Lb(I);
% Apply the upper bound vector
J = temp > Ub;
temp(J) = Ub(J);
% Update this new move
s = temp;
优化问题
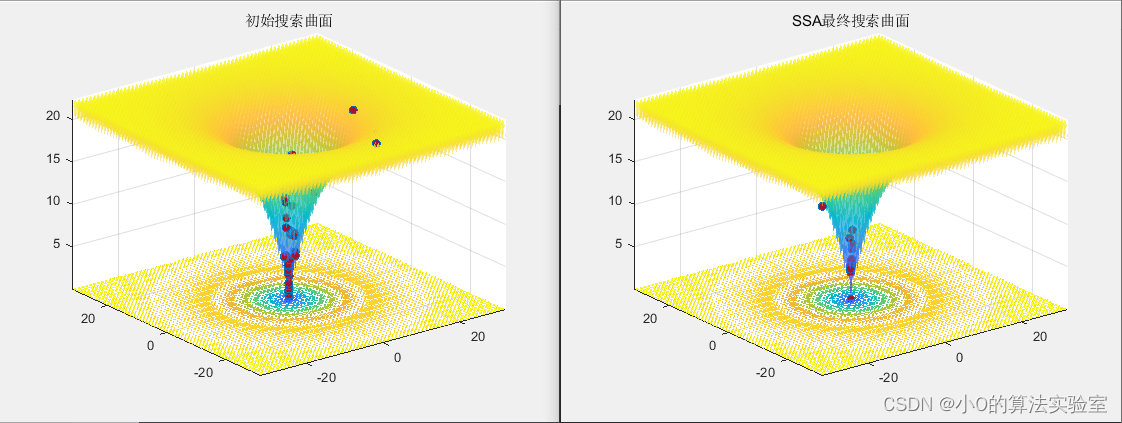
以CEC2005测试函数为例
clear,clc,close all
x = -32:0.1:32;
y = x;
L = length(x);
for i = 1:L
for j = 1:L
f(i,j) = fun([x(i) y(j)]);
end
end
surfc(x, y, f, 'LineStyle', 'none', 'FaceAlpha',0.5);
% 设定麻雀参数
pop = 50;
dim = 2;
ub = 32;
lb = -32;
maxIter = 100;
fobj = @(x) fun(x);
% 求解
[Best_pos, Best_fitness, Iter_curve, History_pos, History_best] = SSA(pop, maxIter, lb, ub, dim,fobj);

4.参考文献
[1] Xue J, Shen B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: sparrow search algorithm[J]. Systems science & control engineering, 2020, 8(1): 22-34.

























 1007
1007

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










