四、Sequential Logic
Finite State Machines
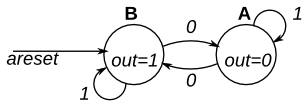
1、Simple FSM 1(asynchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
This is a Moore state machine with two states, one input, and one output. Implement this state machine. Notice that the reset state is B.
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset,
input in,
output out
);
parameter A=0, B=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk or posedge areset) begin
if(areset)
state <= B;
else
state <= next_state;
end
always @(*) begin
if(areset)
next_state <= B;
else
case(state)
A :
if(in)
next_state <= A;
else
next_state <= B;
B :
if(in)
next_state <= B;
else
next_state <= A;
default : ;
endcase
end
assign out = (state) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule2、Simple FSM 1(synchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
This is a Moore state machine with two states, one input, and one output. Implement this state machine. Notice that the reset state is B.
module top_module(clk, reset, in, out);
input clk;
input reset;
input in;
output out;
reg out;
parameter A=0,B=1;
reg present_state, next_state;
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
present_state <= B;
else
present_state <= next_state;
end
always @(*) begin
if (reset) begin
next_state = B;
end
else begin
case (present_state)
A :
if(in)
next_state <= A;
else
next_state <= B;
B :
if(in)
next_state <= B;
else
next_state <= A;
default: ;
endcase
end
end
assign out = (present_state) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule3、Simple FSM 2(asynchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
This is a Moore state machine with two states, two inputs, and one output. Implement this state machine.
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset,
input j,
input k,
output out);
parameter OFF=0, ON=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(*) begin
if(areset)
state <= 0;
else
state <= next_state;
end
always @(posedge clk or posedge areset) begin
if(areset)
next_state <= 0;
else begin
case(state)
1'b0 :
case(j)
1'b0 : next_state <= 1'b0;
1'b1 : next_state <= 1'b1;
default : ;
endcase
1'b1 :
case(k)
1'b0 : next_state <= 1'b1;
1'b1 : next_state <= 1'b0;
default : ;
endcase
endcase
end
end
assign out = (state) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule4、Simple FSM 2(synchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
This is a Moore state machine with two states, two inputs, and one output. Implement this state machine.
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset,
input j,
input k,
output out);
parameter OFF=0, ON=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if(reset)
state <= 1'b0;
else
state <= next_state;
end
always @(*) begin
if(reset)
next_state <= 1'b0;
else begin
case(state)
1'b0 :
case(j)
1'b0 : next_state <= 1'b0;
1'b1 : next_state <= 1'b1;
default : ;
endcase
1'b1 :
case(k)
1'b0 : next_state <= 1'b1;
1'b1 : next_state <= 1'b0;
default : ;
endcase
endcase
end
end
assign out = (state) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule5、Simple state transition 3
Problem Statement:
The following is the state transition table for a Moore state machine with one input, one output, and four states. Use the following state encoding: A=2'b00, B=2'b01, C=2'b10, D=2'b11.
Implement only the state transition logic and output logic (the combinational logic portion) for this state machine. Given the current state (
state), compute thenext_stateand output (out) based on the state transition table.
State Next state Output in=0 in=1 A A B 0 B C B 0 C A D 0 D C B 1
module top_module(
input in,
input [1:0] state,
output [1:0] next_state,
output out);
parameter A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3;
always@(*)begin
case(state)
2'b00 :
case(in)
1'b0 : next_state <= 2'b00;
1'b1 : next_state <= 2'b01;
default : ;
endcase
2'b01 :
case(in)
1'b0 : next_state <= 2'b10;
1'b1 : next_state <= 2'b01;
default : ;
endcase
2'b10 :
case(in)
1'b0 : next_state <= 2'b00;
1'b1 : next_state <= 2'b11;
default : ;
endcase
2'b11 :
case(in)
1'b0 : next_state <= 2'b10;
1'b1 : next_state <= 2'b01;
default : ;
endcase
endcase
end
assign out = (state == 2'b11) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule6、Simple one-hot state transition 3
Problem Statement:
The following is the state transition table for a Moore state machine with one input, one output, and four states. Use the following one-hot state encoding: A=4'b0001, B=4'b0010, C=4'b0100, D=4'b1000.
State Next state Output in=0 in=1 A A B 0 B C B 0 C A D 0 D C B 1
module top_module(
input in,
input [3:0] state,
output [3:0] next_state,
output out);
parameter A=0, B=1, C=2, D=3;
assign next_state[A] = ~in & (state[A] | state[C]);
assign next_state[B] = in & (state[A] | state[B] | state[D]);
assign next_state[C] = ~in & (state[B] | state[D]);
assign next_state[D] = in & state[C];
assign out = (state[D]) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule7、Simple FSM 3(asynchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
The following is the state transition table for a Moore state machine with one input, one output, and four states. Implement this state machine. Include an asynchronous reset that resets the FSM to state A.
State Next state Output in=0 in=1 A A B 0 B C B 0 C A D 0 D C B 1
module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input areset,
output out);
parameter A = 2'b00;
parameter B = 2'b01;
parameter C = 2'b10;
parameter D = 2'b11;
reg [1:0]current_state;
reg [1:0]next_state;
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset)begin
if(areset)
current_state <= 2'b00;
else
current_state <= next_state;
end
always@(*)begin
if(areset)
next_state <= 2'b00;
else begin
case(in)
1'b0 :
case(current_state)
2'b00 : next_state <= 2'b00;
2'b01 : next_state <= 2'b10;
2'b10 : next_state <= 2'b00;
2'b11 : next_state <= 2'b10;
default : ;
endcase
1'b1 :
case(current_state)
2'b00 : next_state <= 2'b01;
2'b01 : next_state <= 2'b01;
2'b10 : next_state <= 2'b11;
2'b11 : next_state <= 2'b01;
default : ;
endcase
endcase
end
end
assign out = (current_state == 2'b11) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule
8、Simple FSM 3(synchronous reset)
Problem Statement:
The following is the state transition table for a Moore state machine with one input, one output, and four states. Implement this state machine. Include a synchronous reset that resets the FSM to state A. (This is the same problem as Fsm3 but with a synchronous reset.)
State Next state Output in=0 in=1 A A B 0 B C B 0 C A D 0 D C B 1
module top_module(
input clk,
input in,
input reset,
output out);
parameter A = 2'b00;
parameter B = 2'b01;
parameter C = 2'b10;
parameter D = 2'b11;
reg[1:0]current_state;
reg[1:0]next_state;
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
current_state <= 2'b00;
else
current_state <= next_state;
end
always@(*)begin
if(reset)
next_state <= 2'b00;
else begin
case(in)
1'b0 :
case(current_state)
2'b00 : next_state <= 2'b00;
2'b01 : next_state <= 2'b10;
2'b10 : next_state <= 2'b00;
2'b11 : next_state <= 2'b10;
default : ;
endcase
1'b1 :
case(current_state)
2'b00 : next_state <= 2'b01;
2'b01 : next_state <= 2'b01;
2'b10 : next_state <= 2'b11;
2'b11 : next_state <= 2'b01;
default : ;
endcase
endcase
end
end
assign out = (current_state == 2'b11) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
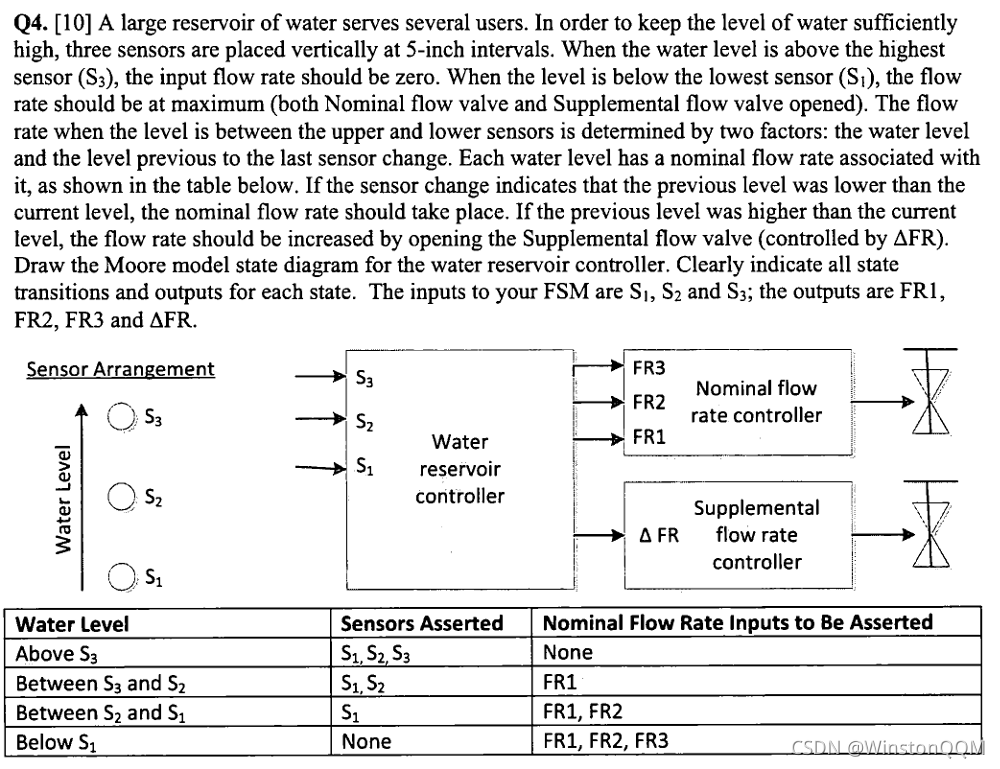
endmodule9、Design a Moore FSM
Problem Statement:
Also include an active-high synchronous reset that resets the state machine to a state equivalent to if the water level had been low for a long time (no sensors asserted, and all four outputs asserted).
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [3:1] s,
output fr3,
output fr2,
output fr1,
output dfr
);
reg [3:0] current_sensor;
reg [3:0] next_sensor;
parameter s1 = 4'b0001;
parameter s1_s2 = 4'b0010;
parameter s2_s3 = 4'b0100;
parameter s3 = 4'b1000;
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
current_sensor <= s1;
else
current_sensor <= next_sensor;
end
always@(*)begin
if(reset)
next_sensor <= s1;
else begin
case(current_sensor)
s1 :
if(s == 3'b001)
next_sensor <= s1_s2;
else
next_sensor <= s1;
s1_s2 :
if(s == 3'b011)
next_sensor <= s2_s3;
else if(s == 3'b000)
next_sensor <= s1;
else
next_sensor <= s1_s2;
s2_s3 :
if(s == 3'b111)
next_sensor <= s3;
else if(s == 3'b001)
next_sensor <= s1_s2;
else if(s == 3'b000)
next_sensor <= s1;
else
next_sensor <= s2_s3;
s3 :
if(s == 3'b011)
next_sensor <= s2_s3;
else if(s == 3'b001)
next_sensor <= s1_s2;
else if(s == 3'b000)
next_sensor <= s1;
else
next_sensor <= s3;
default : ;
endcase
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)begin
fr3 <= 1'b1;
fr2 <= 1'b1;
fr1 <= 1'b1;
dfr <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
case(next_sensor)
s1 : begin
fr3 <= 1'b1;
fr2 <= 1'b1;
fr1 <= 1'b1;
dfr <= 1'b1;
end
s1_s2 : begin
fr3 <= 1'b0;
fr2 <= 1'b1;
fr1 <= 1'b1;
if(current_sensor == s1)
dfr <= 1'b0;
else if(current_sensor == s1_s2)
dfr <= dfr;
else
dfr <= 1'b1;
end
s2_s3 : begin
fr3 <= 1'b0;
fr2 <= 1'b0;
fr1 <= 1'b1;
if(current_sensor &










 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 272
272

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








