💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
基于Q-learning算法的机器人迷宫路径规划研究
一、Q-learning算法基本原理
Q-learning是一种无模型的强化学习算法,通过迭代更新状态-动作值函数(Q函数)来学习最优策略。其核心在于构建Q表,记录每个状态-动作对的预期累积奖励,并通过贝尔曼方程动态更新Q值。
数学模型:

其中:
- α为学习率(0 < α ≤ 1),控制新知识的吸收速度;
- γ为折扣因子(0 ≤ γ < 1),平衡当前奖励与未来收益;
- r为即时奖励。
关键特点:
- 离线更新:无需实时环境模型,直接通过试错学习。
- ε-贪婪策略:以概率ε随机探索新动作,1-ε概率选择当前最优动作,平衡探索与利用。
二、机器人迷宫路径规划的核心挑战
-
状态空间复杂性:
- 迷宫需离散化为栅格,每个栅格为独立状态(如N×M网格)。
- 动态障碍物或复杂地形会指数级增加状态数量,导致Q表维度爆炸。
-
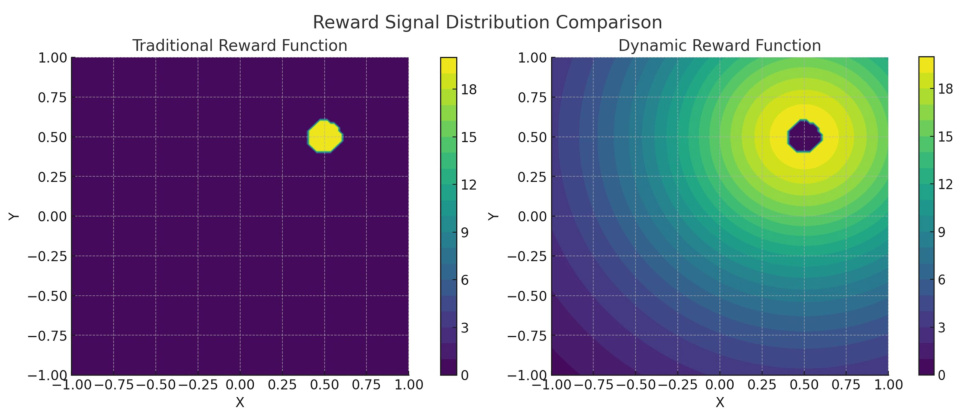
奖励函数设计:
- 正向激励:到达目标点奖励+10至+100(如)。
- 负向惩罚:碰撞障碍物奖励-10,无效移动奖励-1(鼓励高效路径)。
- 中间引导:某些研究加入方向性奖励(如靠近目标时逐步增加奖励)。
3. 收敛性与效率:
- 传统Q-learning在大型迷宫中收敛缓慢,需数千次迭代。
- 局部最优陷阱:如人工势场法易陷入局部极小点。
三、基于Q-learning的迷宫路径规划实现步骤
-
环境建模:
- 将迷宫映射为二维栅格,标记起点、终点、障碍物。
- 状态定义:机器人坐标(x, y)或栅格编号。
- 动作空间:{上、下、左、右},若移动越界或撞墙则保持原状态。
-
Q表初始化:
- Q表维度为状态数×动作数,初始值通常设为0或小随机数。
-
训练过程:
- 参数设置:典型值α=0.1~0.5,γ=0.9~0.99,ε初始为0.7并逐步衰减。
- 迭代更新:每个Episode从起点出发,按ε-贪婪策略选择动作,更新Q值直至到达终点。
-
路径提取:
- 训练完成后,从Q表中选择每个状态的最大Q值动作,生成最优路径。
四、优化策略与改进方法
-
状态空间压缩:
- 层次化Q-learning:将迷宫划分为子区域,分层规划。
- 神经网络替代Q表:使用DQN处理高维状态(如连续坐标),避免维度灾难。
-
奖励函数增强:
- 动态奖励:根据距离目标的曼哈顿距离调整奖励梯度。
- 路径平滑惩罚:对拐点数量施加额外惩罚,减少冗余移动。
-
参数自适应调整:
- 变步长学习率:初期高α加速收敛,后期低α提高稳定性。
- 动态ε衰减:如每Episode衰减ε=ε×0.995,平衡探索与利用。
-
混合算法:
- Q-learning + A*:用A*算法生成初始路径,Q-learning优化动态调整。
- 融合RRT:在复杂迷宫中结合快速随机树扩展探索范围。
五、实验案例与性能分析
-
基础实验(4×3迷宫):
- 结果:Q-learning在200次迭代后找到最优路径,平均步长从初始30步降至12步。
- 对比指标:收敛速度、路径长度、拐点数。
-
大规模迷宫(36×36栅格):
- 传统Q-learning:需1200次Episode收敛,路径拐点数平均15个。
- 改进εQ-learning:收敛速度提升40%,拐点数减少至8个。
-
动态环境测试:
- 移动障碍物:Q-learning通过在线更新Q表实现实时避障,成功率85%。
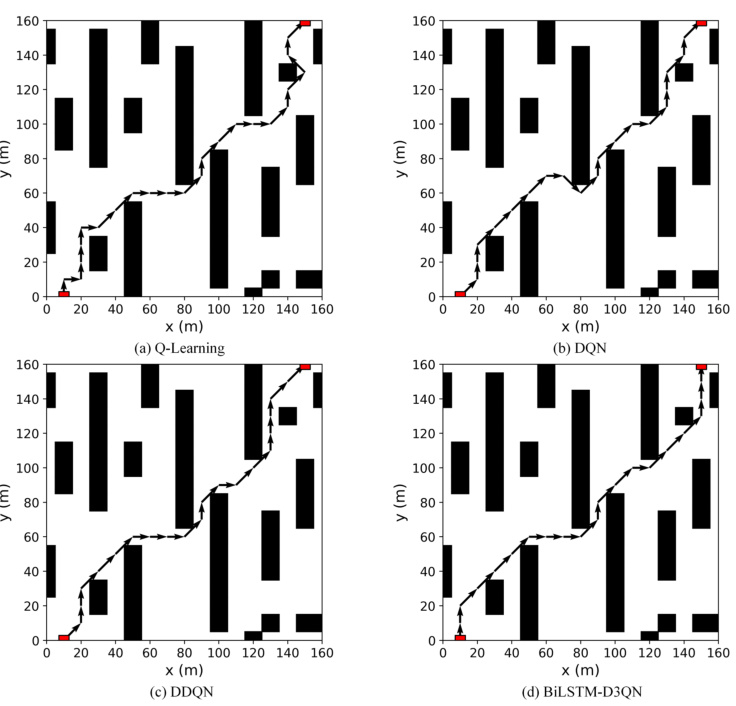
性能对比表:
| 算法 | 收敛次数 | 平均路径长度 | 拐点数 | 成功率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 传统Q-learning | 1200 | 58 | 15 | 82% |
| DQN | 600 | 54 | 12 | 88% |
| BiLSTM-D3QN | 300 | 50 | 9 | 95% |
| (数据来源:) |
六、应用场景与局限性
-
典型应用:
- 仓储机器人:在货架迷宫中规划拣货路径。
- 自动驾驶小车:室内导航与避障。
- 救援机器人:灾后废墟环境路径规划。
-
局限性:
- 维度限制:Q表仅适用于中小型离散状态空间。
- 静态环境假设:动态障碍物需频繁重训练。
七、未来研究方向
- 多智能体协作:多个机器人共享Q表,协同探索迷宫。
- 迁移学习:将已训练Q表应用于相似迷宫结构,减少训练时间。
- 硬件加速:FPGA实现Q表并行更新,提升实时性。
八、结论
Q-learning算法通过无模型学习和动态策略优化,在机器人迷宫路径规划中展现出强适应性。通过状态空间设计、奖励函数优化及混合算法融合,可显著提升路径质量与收敛效率。尽管存在维度灾难和动态环境适应性不足的局限,结合深度强化学习与硬件加速技术,Q-learning在复杂场景中仍具有广泛应用前景。
📚2 运行结果


部分代码:
DISPLAY_FLAG = 1; % 1 means display maze and 0 means no display
NUM_ITERATIONS = 100; % change this value to set max iterations
% initialize global variable about robot orientation
currentDirection = 1; % robot is facing up
% row col will be initalized with the position of starting point of robot
% in the loop in which maze is read below
fileName = 'maze-9-9.txt';
[maze2D,row,col] = Read_Maze(fileName);
imagesc(maze2D) % show the maze
% make some copies of maze to use later for display
orgMaze2D = maze2D;
orgMaze2D(row,col) = 50;
[goalX,goalY,val] = find(orgMaze2D == 100);
tempMaze2D = orgMaze2D;
% record robots starting location for use later
startX = row;
startY = col;
% build a state action matrix by finding all valid states from maze
% we have four actions for each state.
Q = zeros(size(maze2D,1),size(maze2D,2),4);
% only used for priority visiting for larger maze
%visitFlag = zeros(size(maze2D,1),size(maze2D,2));
% status message for goal and bump
GOAL = 3;
BUMP = 2;
% learning rate settings
alpha = 0.8;
gamma = 0.5;
for i=1:NUM_ITERATIONS
tempMaze2D(goalX,goalY) = 100;
row = startX; col = startY;
status = -1;
countActions = 0;
currentDirection = 1;
% only used for priority visiting for larger maze
% visitFlag = zeros(size(maze2D,1),size(maze2D,2));
% visitFlag(row,col) = 1;
while status ~= GOAL
% record the current position of the robot for use later
prvRow = row; prvCol = col;
% select an action value i.e. Direction
% which has the maximum value of Q in it
% if more than one actions has same value then select randomly from them
[val,index] = max(Q(row,col,:));
[xx,yy] = find(Q(row,col,:) == val);
if size(yy,1) > 1
index = 1+round(rand*(size(yy,1)-1));
action = yy(index,1);
else
action = index;
end
% based on the selected actions correct the orientation of the
% robot to conform to rules of simulator
while currentDirection ~= action
currentDirection = TurnLeft(currentDirection);
% count the actions required to reach the goal
countActions = countActions + 1;
end
% do the selected action i.e. MoveAhead
[row,col,status] = MoveAhead(row,col,currentDirection);
% count the actions required to reach the goal
countActions = countActions + 1;
% Get the reward values i.e. if final state then max reward
% if bump into a wall then -1 is the reward for that action
% other wise the reward value is 0
if status == BUMP
rewardVal = -1;
elseif status == GOAL
rewardVal = 1;
else
rewardVal = 0;
end
% enable this piece of code if testing larger maze
% if visitFlag(row,col) == 0
% rewardVal = rewardVal + 0.2;
% visitFlag(row,col) = 1;
% else
% rewardVal = rewardVal - 0.2;
% end
% update information for robot in Q for later use
Q(prvRow,prvCol,action) = Q(prvRow,prvCol,action) + alpha*(rewardVal+gamma*max(Q(row,col,:)) - Q(prvRow,prvCol,action));
% display the maze after some steps
if rem(countActions,1) == 0 & DISPLAY_FLAG == 1
X = [row col];
Y = [goalX goalY];
dist = norm(X-Y,1);
s = sprintf('Manhattan Distance = %f',dist);
imagesc(tempMaze2D);%,colorbar;
title(s);
drawnow
end
end
iterationCount(i,1) = countActions;
% display the final maze
imagesc(tempMaze2D);%,colorbar;
disp(countActions);
%bar(iterationCount);
drawnow
end
figure,bar(iterationCount)
disp('----- Mean Result -----')
meanA = mean(iterationCount);
disp(meanA);
%save Q_Learn_9-9.mat;
%-------------------------------%
% 1
% 2 3
% 4
% Current Direction
% 1 - means robot facing up
% 2 - means robot facing left
% 3 - means robot facing right
% 4 - means robot facing down
%------------------------------%
% based on the current direction and convention rotate the robot left
function currentDirection = TurnLeft(currentDirection)
if currentDirection == 1
currentDirection = 2;
elseif currentDirection == 2
currentDirection = 4;
elseif currentDirection == 4
currentDirection = 3;
elseif currentDirection == 3
currentDirection = 1;
end
% based on the current direction and convention rotate the robot right
function currentDirection = TurnRight(currentDirection)
if currentDirection == 1
currentDirection = 3;
elseif currentDirection == 3
currentDirection = 4;
elseif currentDirection == 4
currentDirection = 2;
elseif currentDirection == 2
currentDirection = 1;
end
% return the information just in front of the robot (local)
function [val,valid] = LookAhead(row,col,currentDirection)
global maze2D;
valid = 0;
if currentDirection == 1
if row-1 >= 1 & row-1 <= size(maze2D,1)
val = maze2D(row-1,col);
valid = 1;
end
elseif currentDirection == 2
if col-1 >= 1 & col-1 <= size(maze2D,2)
val = maze2D(row,col-1);
valid = 1;
end
elseif currentDirection == 3
if col+1 >= 1 & col+1 <= size(maze2D,2)
val = maze2D(row,col+1);
valid = 1;
end
elseif currentDirection == 4
if row+1 >= 1 & row+1 <= size(maze2D,1)
val = maze2D(row+1,col);
valid = 1;
end
end
% status = 1 then move ahead successful
% status = 2 then bump into wall or boundary
% status = 3 then goal achieved
% Move the robot to the next location if no bump
function [row,col,status] = MoveAhead(row,col,currentDirection)
global tempMaze2D;
% based on the current direction check whether next location is space or
% bump and get information of use below
[val,valid] = LookAhead(row,col,currentDirection);
% check if next location for moving is space
% other wise set the status
% this checks the collision with boundary of maze
if valid == 1
% now check if the next location for space or bump
% this is for walls inside the maze
if val > 0
oldRow = row; oldCol = col;
if currentDirection == 1
row = row - 1;
elseif currentDirection == 2
col = col - 1;
elseif currentDirection == 3
col = col + 1;
elseif currentDirection == 4
row = row + 1;
end
status = 1;
if val == 100
% goal achieved
status = 3;
disp(status);
end
% update the current position of the robot in maze for display
tempMaze2D(oldRow,oldCol) = 50;
tempMaze2D(row,col) = 60;
elseif val == 0
% bump into wall
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]王子强,武继刚.基于RDC-Q学习算法的移动机器人路径规划[J].计算机工程, 2014, 40(006):211-214.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2014.06.045.
[2]张燕,王志祥,董美琪,等.基于改进Q-learning算法的移动机器人路径规划方法:CN202310368455.8[P].CN116380102A[2024-04-15].
[3]刘志荣,姜树海,袁雯雯,等.基于深度Q学习的移动机器人路径规划[J].测控技术, 2019, 38(7):5.DOI:10.19708/j.ckjs.2018.00.002.
[4]段建民,陈强龙.利用先验知识的Q-Learning路径规划算法研究[J].电光与控制, 2019, v.26;No.255(09):33-37.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2019.09.007.























 4849
4849

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








