一、action通信
1.概念
应用于机器人导航过程,在行进的过程中连续反馈当前机器人的状态信息。当导航终止时,再返回最终的执行结果。
2.功能包
提供有actionlib功能包集
3.action图解:
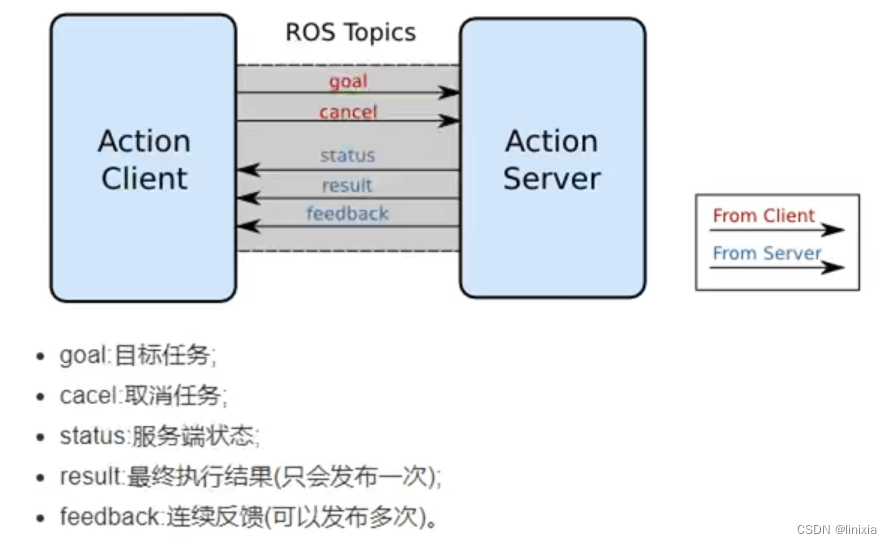
二、自定义action文件
1.创建action文件
(1)功能包有roscpp,rospy,std_msgs,actionlib,actionlib_msgs
(2)添加.action文件
2.编辑配置文件
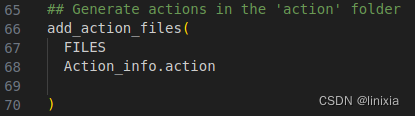
(1)解除第66行注释,并改正.action文件
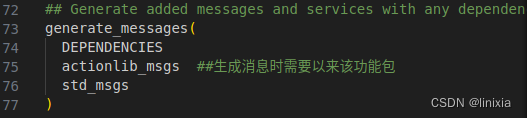
(2)解除第73行注释(生成消息时需要的功能包)
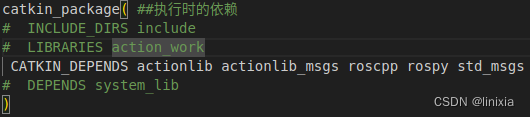
(3)解除第111行注释(执行时的依赖)
3.编译生成中间文件
三、编写C++文件
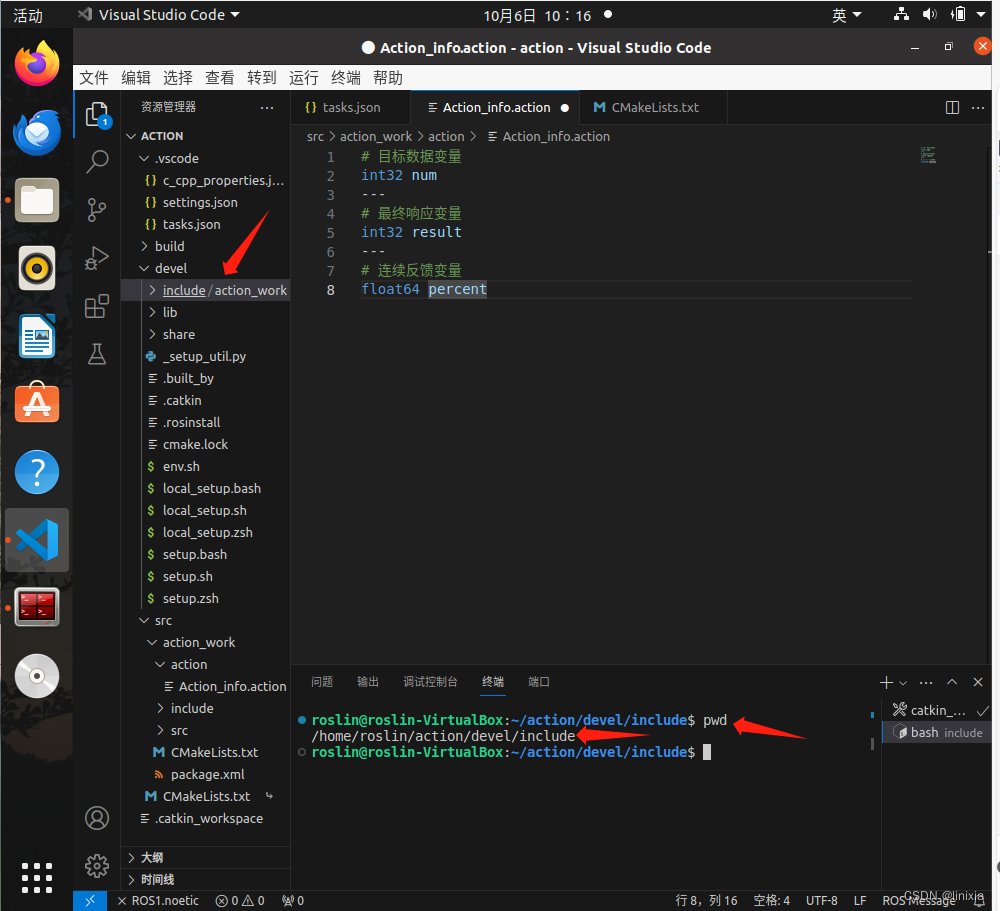
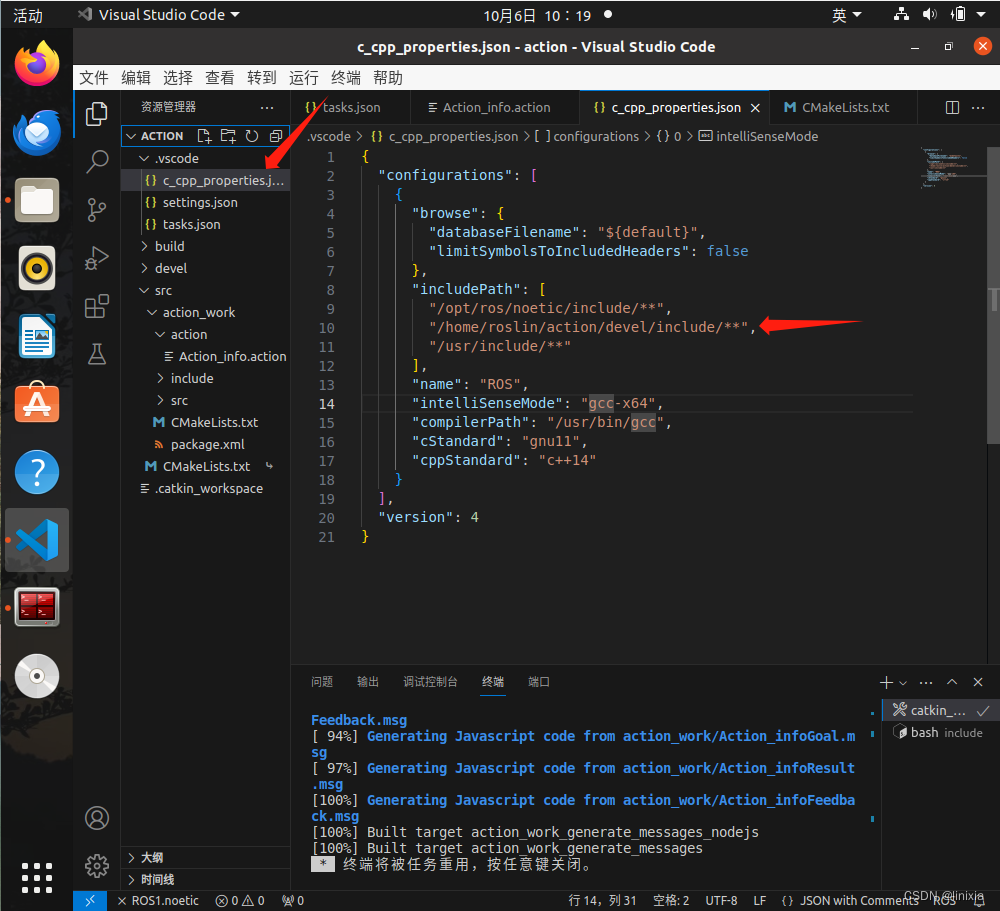
1.修改c_cpp_properies.json文件
(1)在集成终端中打开devel下的include文件,输入pwd获取该文件的路径
(2)添加到c_cpp_properies.json文件中
2.编写action服务端
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "actionlib/server/simple_action_server.h"//创建服务端对象需要用到的头文件
#include "action_work/Action_infoAction.h"
/*
1.包含头文件
2.初始化ROS节点
3.创建NodeHandle
4.创建action服务对象
5.请求处理(回调函数)
a.解析客户端提交的目标值
b.服务端产生连续反馈
c.最终结果响应
6.spin()回旋
*/
//服务对象宏定义为Server
typedef actionlib::SimpleActionServer<action_work::Action_infoAction> Server;
void Check_Callback(const action_work::Action_infoGoalConstPtr &goal,Server* server)
{
int goal_num= goal -> num;
ROS_INFO("零件数为: %d",goal_num);
ros::Rate rate(1); //1Hz,一秒检查一次
int finished=0;
//响应的过程
for(int i=1;i<=goal_num;i++)
{
finished ++;
rate.sleep();
//产生连续反馈
//void publishFeedback(const action_work::Action_infoFeedback &feedback)
action_work::Action_infoFeedback fb;
ROS_INFO("检测%d个零件",i);
fb.percent = (i / (double)goal_num) * 100;
server->publishFeedback(fb);
}
//最终响应结果
action_work::Action_infoResult checkresult;
checkresult.result = finished;
server->setSucceeded(checkresult);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* code */
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
ros::init(argc,argv,"check_server");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
//创建服务对象
//actionlib::SimpleActionServer<action_work::Action_infoAction>;
/*参数: (ros::NodeHandle n,
话题名称 std::string name,
回调函数 boost::function<void (const action_work::Action_infoGoalConstPtr &)> execute_callback,
(boost::bind用于绑定,包括绑定的函数,要传入的参数:_1表示回调函数的第一个参数)
是否自动启动 bool auto_start)
*/
Server server(nh,"check_parts",boost::bind(&Check_Callback,_1,&server),false);
server.start(); //如果上方选择了false,那么需要手动调用该函数来启动服务
ROS_INFO("服务端启动完毕!");
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
3.编写action客户端
#include "ros/ros.h"
#include "actionlib/client/simple_action_client.h"//创建客户端对象所需要的文件
#include "action_work/Action_infoAction.h"
/*
1.包含头文件
2.初始化ROS节点
3.创建NodeHandle
4.创建action客户端对象
5.发送请求
a.连接建立 --- 回调函数
b.处理连续反馈 --- 回调函数
c.处理最终响应 --- 回调函数
6.spin()回旋
*/
//处理最终响应的回调函数:包括状态state和结果result两个参数
void done_cb(const actionlib::SimpleClientGoalState &state, const action_work::Action_infoResultConstPtr &result)
{
if(state.state_ == state.SUCCEEDED)
{
ROS_INFO("检测完成");
}
else{
ROS_INFO("检测失败");
}
}
//处理连接建立的回调函数:
void active_cb()
{
ROS_INFO("客户端和服务端连接建立...");
}
//处理连续反馈的回调
void feedback_cb(const action_work::Action_infoFeedbackConstPtr &feedback)
{
char symbol='%';
ROS_INFO("当前进度为:%.1f%c", feedback->percent,symbol);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* code */
setlocale(LC_ALL,"");
ros::init(argc, argv ,"check_client");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
//创建客户端对象:<>内是功能包下的action文件
actionlib::SimpleActionClient<action_work::Action_infoAction> client(nh,"check_parts");
//发送请求
//等待服务
ROS_INFO("等待服务器启动...");
client.waitForServer();
/*
void sendGoal(const action_work::Action_infoGoal &goal,
处理最终响应 boost::function<void (const actionlib::SimpleClientGoalState &state, const action_work::Action_infoResultConstPtr &result)> done_cb,
处理连接建立 boost::function<void ()> active_cb,
处理连续反馈 boost::function<void (const action_work::Action_infoFeedbackConstPtr &feedback)> feedback_cb)
开始根据参数来设置
*/
action_work::Action_infoGoal goal;
goal.num = 40;
client.sendGoal(goal, &done_cb, &active_cb, &feedback_cb);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}
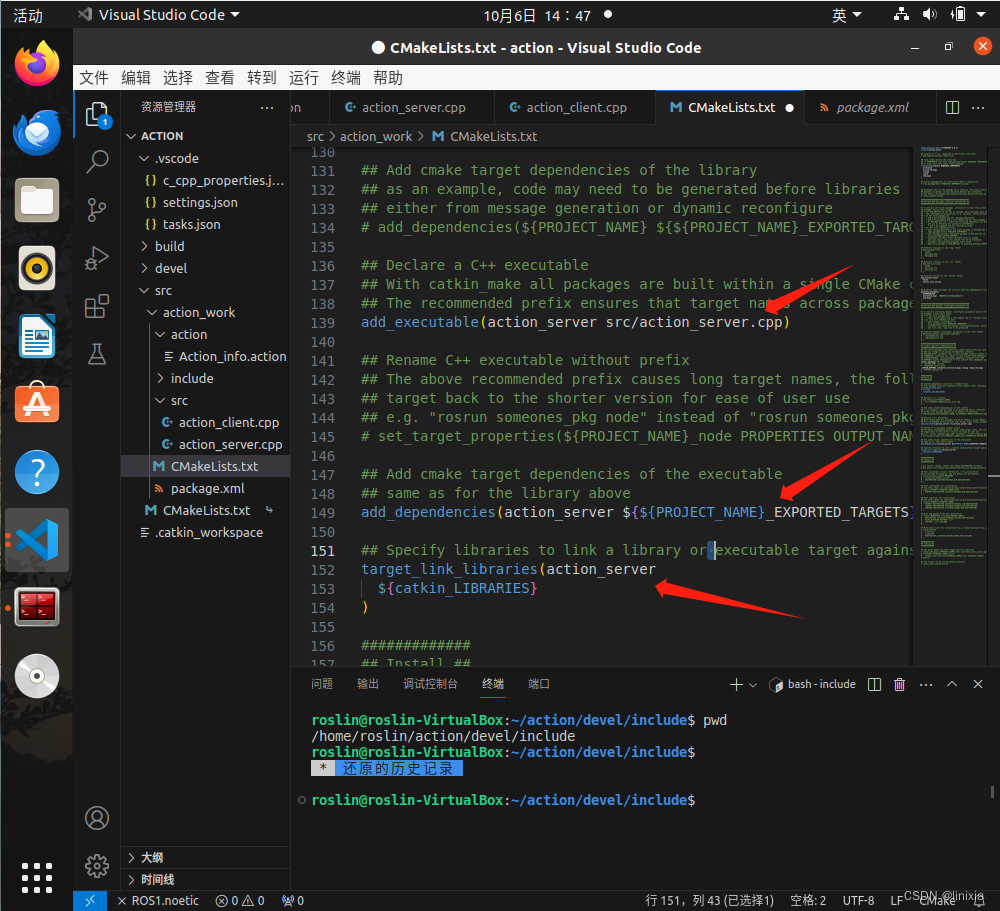
4.编辑CMakeList.txt
(1)第139行和第151行,更换文件名
(2)第149行,更换文件名




















 4459
4459











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








