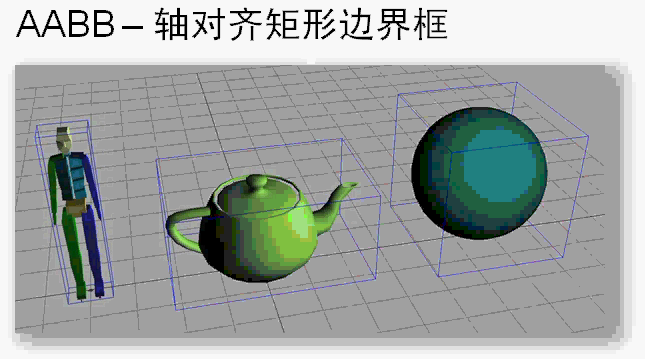
3D数学 AABB轴对齐矩形边界框
1. 几何图元
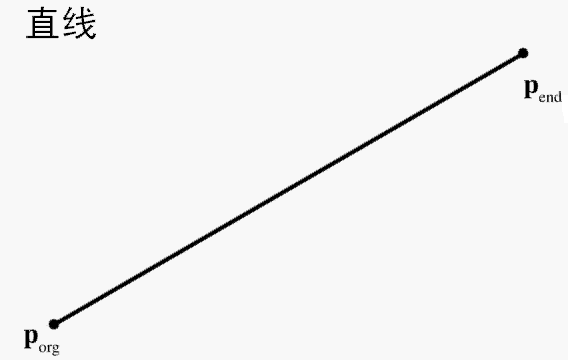
直线:由两个向量定义直线的方向
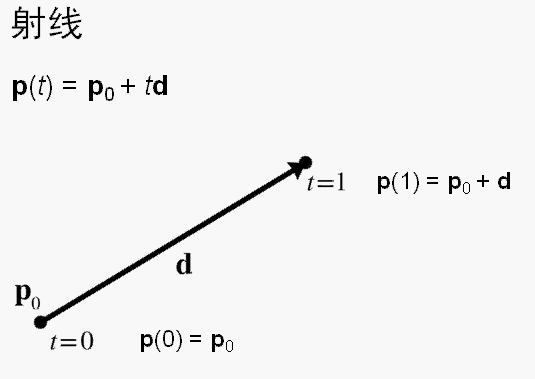
射线:由两个向量定义直线的方向,其中一个向量定义射线的起点
球和圆
矩形边界框(AABB)
2. AABB(轴对齐矩形边界框)C++实现
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//
// 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
//
// AABB3.h - Declarations for class AABB3
//
// Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
//
// For more details, see AABB3.cpp
//
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifndef __AABB3_H_INCLUDED__
#define __AABB3_H_INCLUDED__
#ifndef __VECTOR3_H_INCLUDED__
#include "Vector3.h"
#endif
class Matrix4x3;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// class AABB3
//
// Implement a 3D axially aligned bounding box
class AABB3 {
public:
// Public data
// Min and max values. Pretty simple.
Vector3 min;
Vector3 max;
// Query for dimentions
Vector3 size() const { return max - min; }
float xSize() { return max.x - min.x; }
float ySize() { return max.y - min.y; }
float zSize() { return max.z - min.z; }
Vector3 center() const { return (min + max) * .5f; }
// Fetch one of the eight corner points. See the
// .cpp for numbering conventions
Vector3 corner(int i) const;
// Box operations
// "Empty" the box, by setting the values to really
// large/small numbers
void empty();
// Add a point to the box
void add(const Vector3 &p);
// Add an AABB to the box
void add(const AABB3 &box);
// Transform the box and compute the new AABB
void setToTransformedBox(const AABB3 &box, const Matrix4x3 &m);
// Containment/intersection tests
// Return true if the box is enmpty
bool isEmpty() const;
// Return true if the box contains a point
bool contains(const Vector3 &p) const;
// Return the closest point on this box to another point
Vector3 closestPointTo(const Vector3 &p) const;
// Return true if we intersect a sphere
bool intersectsSphere(const Vector3 ¢er, float radius) const;
// Parametric intersection with a ray. Returns >1 if no intresection
float rayIntersect(const Vector3 &rayOrg, const Vector3 &rayDelta,
Vector3 *returnNormal = 0) const;
// Classify box as being on one side or the other of a plane
int classifyPlane(const Vector3 &n, float d) const;
// Dynamic intersection with plane
float intersectPlane(const Vector3 &n, float planeD,
const Vector3 &dir) const;
};
// Check if two AABBs intersect, and return true if so. Optionally return
// the AABB of their intersection if an intersection is detected
bool intersectAABBs(const AABB3 &box1, const AABB3 &box2,
AABB3 *boxIntersect = 0);
// Return parametric point in time when a moving AABB collides
// with a stationary AABB. Returns > 1 if no intersection
float intersectMovingAABB(
const AABB3 &stationaryBox,
const AABB3 &movingBox,
const Vector3 &d
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#endif // #ifndef __AABB3_H_INCLUDED__
/
//
// 3D Math Primer for Games and Graphics Development
//
// AABB3.cpp - Implementation for class AABB3
//
// Visit gamemath.com for the latest version of this file.
//
// For more details, see Chapter 12
//
/
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "AABB3.h"
#include "Matrix4x3.h"
#include "CommonStuff.h"
/
//
// class AABB3 member functions
//
/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::corner
//
// Return one of the 8 corner points. The points are numbered as follows:
//
// 6 7
// ------------------------------
// /| /|
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// / | / |
// 2 / | 3 / |
// /----------------------------/ |
// | | | |
// | | | | +Y
// | 4 | | |
// | |-----------------|----------| |
// | / | / 5 |
// | / | / | +Z
// | / | / |
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / | /
// | / | / |/
// |/ |/ ----------------- +X
// ------------------------------
// 0 1
//
// Bit 0 selects min.x vs. max.x
// Bit 1 selects min.y vs. max.y
// Bit 2 selects min.z vs. max.z
Vector3 AABB3::corner(int i) const {
// Make sure index is in range...
assert(i >= 0);
assert(i <= 7);
// Return it
return Vector3(
(i & 1) ? max.x : min.x,
(i & 2) ? max.y : min.y,
(i & 4) ? max.z : min.z
);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::empty
//
// "Empty" the box, by setting the values to really
// large/small numbers
void AABB3::empty() {
const float kBigNumber = 1e37f;
min.x = min.y = min.z = kBigNumber;
max.x = max.y = max.z = -kBigNumber;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::add
//
// Add a point to the box
void AABB3::add(const Vector3 &p) {
// Expand the box as necessary to contain the point.
if (p.x < min.x) min.x = p.x;
if (p.x > max.x) max.x = p.x;
if (p.y < min.x) min.y = p.y;
if (p.y > max.x) max.y = p.y;
if (p.z < min.x) min.z = p.z;
if (p.z > max.x) max.z = p.z;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::add
//
// Add an AABB to the box
void AABB3::add(const AABB3 &box) {
// Expand the box as necessary.
if (box.min.x < min.x) min.x = box.min.x;
if (box.min.x > max.x) max.x = box.min.x;
if (box.min.y < min.x) min.y = box.min.y;
if (box.min.y > max.x) max.y = box.min.y;
if (box.min.z < min.x) min.z = box.min.z;
if (box.min.z > max.x) max.z = box.min.z;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::setToTransformedBox
//
// Transform the box and compute the new AABB. Remember, this always
// results in an AABB that is at least as big as the origin, and may be
// considerably bigger.
//
// See 12.4.4
void AABB3::setToTransformedBox(const AABB3 &box, const Matrix4x3 &m) {
// If we're empty, then bail
if (box.isEmpty()) {
empty();
return;
}
// Start with the translation portion
min = max = getTranslation(m);
// Examine each of the 9 matrix elements
// and compute the new AABB
if (m.m11 > 0.0f) {
min.x += m.m11 * box.min.x; max.x += m.m11 * box.max.x;
} else {
min.x += m.m11 * box.max.x; max.x += m.m11 * box.min.x;
}
if (m.m12 > 0.0f) {
min.y += m.m12 * box.min.x; max.y += m.m12 * box.max.x;
} else {
min.y += m.m12 * box.max.x; max.y += m.m12 * box.min.x;
}
if (m.m13 > 0.0f) {
min.z += m.m13 * box.min.x; max.z += m.m13 * box.max.x;
} else {
min.z += m.m13 * box.max.x; max.z += m.m13 * box.min.x;
}
if (m.m21 > 0.0f) {
min.x += m.m21 * box.min.y; max.x += m.m21 * box.max.y;
} else {
min.x += m.m21 * box.max.y; max.x += m.m21 * box.min.y;
}
if (m.m22 > 0.0f) {
min.y += m.m22 * box.min.y; max.y += m.m22 * box.max.y;
} else {
min.y += m.m22 * box.max.y; max.y += m.m22 * box.min.y;
}
if (m.m23 > 0.0f) {
min.z += m.m23 * box.min.y; max.z += m.m23 * box.max.y;
} else {
min.z += m.m23 * box.max.y; max.z += m.m23 * box.min.y;
}
if (m.m31 > 0.0f) {
min.x += m.m31 * box.min.z; max.x += m.m31 * box.max.z;
} else {
min.x += m.m31 * box.max.z; max.x += m.m31 * box.min.z;
}
if (m.m32 > 0.0f) {
min.y += m.m32 * box.min.z; max.y += m.m32 * box.max.z;
} else {
min.y += m.m32 * box.max.z; max.y += m.m32 * box.min.z;
}
if (m.m33 > 0.0f) {
min.z += m.m33 * box.min.z; max.z += m.m33 * box.max.z;
} else {
min.z += m.m33 * box.max.z; max.z += m.m33 * box.min.z;
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::isEmpty
//
// Return true if the box is enmpty
bool AABB3::isEmpty() const {
// Check if we're inverted on any axis
return (min.x > max.x) || (min.y > max.y) || (min.z > max.z);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::contains
//
// Return true if the box contains a point
bool AABB3::contains(const Vector3 &p) const {
// Check for overlap on each axis
return
(p.x >= min.x) && (p.x <= max.x) &&
(p.y >= min.y) && (p.y <= max.y) &&
(p.z >= min.z) && (p.z <= max.z);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::closestPointTo
//
// Return the closest point on this box to another point
Vector3 AABB3::closestPointTo(const Vector3 &p) const {
// "Push" p into the box, on each dimension
Vector3 r;
if (p.x < min.x) {
r.x = min.x;
} else if (p.x > max.x) {
r.x = max.x;
} else {
r.x = p.x;
}
if (p.y < min.y) {
r.y = min.y;
} else if (p.y > max.y) {
r.y = max.y;
} else {
r.y = p.y;
}
if (p.z < min.z) {
r.z = min.z;
} else if (p.z > max.z) {
r.z = max.z;
} else {
r.z = p.z;
}
// Return it
return r;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::intersectsSphere
//
// Return true if we intersect a sphere. Uses Arvo's algorithm.
bool AABB3::intersectsSphere(const Vector3 ¢er, float radius) const {
// Find the closest point on box to the point
Vector3 closestPoint = closestPointTo(center);
// Check if it's within range
return distanceSquared(center, closestPoint) < radius*radius;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::rayIntersect
//
// Parametric intersection with a ray. Returns parametric point
// of intsersection in range 0...1 or a really big number (>1) if no
// intersection.
//
// From "Fast Ray-Box Intersection," by Woo in Graphics Gems I,
// page 395.
//
// See 12.9.11
float AABB3::rayIntersect(
const Vector3 &rayOrg, // orgin of the ray
const Vector3 &rayDelta, // length and direction of the ray
Vector3 *returnNormal // optionally, the normal is returned
) const {
// We'll return this huge number if no intersection
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
// Check for point inside box, trivial reject, and determine parametric
// distance to each front face
bool inside = true;
float xt, xn;
if (rayOrg.x < min.x) {
xt = min.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt > rayDelta.x) return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = -1.0f;
} else if (rayOrg.x > max.x) {
xt = max.x - rayOrg.x;
if (xt < rayDelta.x) return kNoIntersection;
xt /= rayDelta.x;
inside = false;
xn = 1.0f;
} else {
xt = -1.0f;
}
float yt, yn;
if (rayOrg.y < min.y) {
yt = min.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt > rayDelta.y) return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = -1.0f;
} else if (rayOrg.y > max.y) {
yt = max.y - rayOrg.y;
if (yt < rayDelta.y) return kNoIntersection;
yt /= rayDelta.y;
inside = false;
yn = 1.0f;
} else {
yt = -1.0f;
}
float zt, zn;
if (rayOrg.z < min.z) {
zt = min.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt > rayDelta.z) return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = -1.0f;
} else if (rayOrg.z > max.z) {
zt = max.z - rayOrg.z;
if (zt < rayDelta.z) return kNoIntersection;
zt /= rayDelta.z;
inside = false;
zn = 1.0f;
} else {
zt = -1.0f;
}
// Inside box?
if (inside) {
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
*returnNormal = -rayDelta;
returnNormal->normalize();
}
return 0.0f;
}
// Select farthest plane - this is
// the plane of intersection.
int which = 0;
float t = xt;
if (yt > t) {
which = 1;
t = yt;
}
if (zt > t) {
which = 2;
t = zt;
}
switch (which) {
case 0: // intersect with yz plane
{
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y*t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y) return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z*t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = xn;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
} break;
case 1: // intersect with xz plane
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x*t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x) return kNoIntersection;
float z = rayOrg.z + rayDelta.z*t;
if (z < min.z || z > max.z) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = yn;
returnNormal->z = 0.0f;
}
} break;
case 2: // intersect with xy plane
{
float x = rayOrg.x + rayDelta.x*t;
if (x < min.x || x > max.x) return kNoIntersection;
float y = rayOrg.y + rayDelta.y*t;
if (y < min.y || y > max.y) return kNoIntersection;
if (returnNormal != NULL) {
returnNormal->x = 0.0f;
returnNormal->y = 0.0f;
returnNormal->z = zn;
}
} break;
}
// Return parametric point of intersection
return t;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::classifyPlane
//
// Perform static AABB-plane intersection test. Returns:
//
// <0 Box is completely on the BACK side of the plane
// >0 Box is completely on the FRONT side of the plane
// 0 Box intersects the plane
int AABB3::classifyPlane(const Vector3 &n, float d) const {
// Inspect the normal and compute the minimum and maximum
// D values.
float minD, maxD;
if (n.x > 0.0f) {
minD = n.x*min.x; maxD = n.x*max.x;
} else {
minD = n.x*max.x; maxD = n.x*min.x;
}
if (n.y > 0.0f) {
minD += n.y*min.y; maxD += n.y*max.y;
} else {
minD += n.y*max.y; maxD += n.y*min.y;
}
if (n.z > 0.0f) {
minD += n.z*min.z; maxD += n.z*max.z;
} else {
minD += n.z*max.z; maxD += n.z*min.z;
}
// Check if completely on the front side of the plane
if (minD >= d) {
return +1;
}
// Check if completely on the back side of the plane
if (maxD <= d) {
return -1;
}
// We straddle the plane
return 0;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// AABB3::intersectPlane
//
// Perform dynamic AABB-plane intersection test.
//
// n is the plane normal (assumed to be normalized)
// planeD is the D value of the plane equation p.n = d
// dir dir is the direction of movement of the AABB.
//
// The plane is assumed to be stationary.
//
// Returns the parametric point of intersection - the distance traveled
// before an intersection occurs. If no intersection, a REALLY big
// number is returned. You must check against the length of the
// displacement.
//
// Only intersections with the front side of the plane are detected
float AABB3::intersectPlane(
const Vector3 &n,
float planeD,
const Vector3 &dir
) const {
// Make sure they are passing in normalized vectors
assert(fabs(n*n - 1.0) < .01);
assert(fabs(dir*dir - 1.0) < .01);
// We'll return this huge number if no intersection
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
// Compute glancing angle, make sure we are moving towards
// the front of the plane
float dot = n * dir;
if (dot >= 0.0f) {
return kNoIntersection;
}
// Inspect the normal and compute the minimum and maximum
// D values. minD is the D value of the "frontmost" corner point
float minD, maxD;
if (n.x > 0.0f) {
minD = n.x*min.x; maxD = n.x*max.x;
} else {
minD = n.x*max.x; maxD = n.x*min.x;
}
if (n.y > 0.0f) {
minD += n.y*min.y; maxD += n.y*max.y;
} else {
minD += n.y*max.y; maxD += n.y*min.y;
}
if (n.z > 0.0f) {
minD += n.z*min.z; maxD += n.z*max.z;
} else {
minD += n.z*max.z; maxD += n.z*min.z;
}
// Check if we're already completely on the other
// side of the plane
if (maxD <= planeD) {
return kNoIntersection;
}
// Perform standard raytrace equation using the
// frontmost corner point
float t = (planeD - minD) / dot;
// Were we already penetrating?
if (t < 0.0f) {
return 0.0f;
}
// Return it. If > l, then we didn't hit in time. That's
// the condition that the caller should be checking for.
return t;
}
/
//
// Global nonmember code
//
/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// intersectAABBs
//
// Check if two AABBs intersect, and return true if so. Optionally return
// the AABB of their intersection if an intersection is detected
bool intersectAABBs(
const AABB3 &box1,
const AABB3 &box2,
AABB3 *boxIntersect
) {
// Check for no overlap
if (box1.min.x > box2.max.x) return false;
if (box1.max.x < box2.min.x) return false;
if (box1.min.y > box2.max.y) return false;
if (box1.max.y < box2.min.y) return false;
if (box1.min.z > box2.max.z) return false;
if (box1.max.z < box2.min.z) return false;
// We have overlap. Compute AABB of intersection, if they want it
if (boxIntersect != NULL) {
boxIntersect->min.x = max(box1.min.x, box2.min.x);
boxIntersect->max.x = min(box1.max.x, box2.max.x);
boxIntersect->min.y = max(box1.min.y, box2.min.y);
boxIntersect->max.y = min(box1.max.y, box2.max.y);
boxIntersect->min.z = max(box1.min.z, box2.min.z);
boxIntersect->max.z = min(box1.max.z, box2.max.z);
}
// They intersected
return true;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// intersectMovingAABB
//
// Return parametric point in time when a moving AABB collides
// with a stationary AABB. Returns > 1 if no intersection
float intersectMovingAABB(
const AABB3 &stationaryBox,
const AABB3 &movingBox,
const Vector3 &d
) {
// We'll return this huge number if no intersection
const float kNoIntersection = 1e30f;
// Initialize interval to contain all the time under consideration
float tEnter = 0.0f;
float tLeave = 1.0f;
//
// Compute interval of overlap on each dimension, and intersect
// this interval with the interval accumulated so far. As soon as
// an empty interval is detected, return a negative result
// (no intersection.) In each case, we have to be careful for
// an infinite of empty interval on each dimension
//
// Check x-axis
if (d.x == 0.0f) {
// Empty or infinite inverval on x
if (
(stationaryBox.min.x >= movingBox.max.x) ||
(stationaryBox.max.x <= movingBox.min.x)
) {
// Empty time interval, so no intersection
return kNoIntersection;
}
// Inifinite time interval - no update necessary
} else {
// Divide once
float oneOverD = 1.0f / d.x;
// Compute time value when they begin and end overlapping
float xEnter = (stationaryBox.min.x - movingBox.max.x) * oneOverD;
float xLeave = (stationaryBox.max.x - movingBox.min.x) * oneOverD;
// Check for interval out of order
if (xEnter > xLeave) {
swap(xEnter, xLeave);
}
// Update interval
if (xEnter > tEnter) tEnter = xEnter;
if (xLeave < tLeave) tLeave = xLeave;
// Check if this resulted in empty interval
if (tEnter > tLeave) {
return kNoIntersection;
}
}
// Check y-axis
if (d.y == 0.0f) {
// Empty or infinite inverval on y
if (
(stationaryBox.min.y >= movingBox.max.y) ||
(stationaryBox.max.y <= movingBox.min.y)
) {
// Empty time interval, so no intersection
return kNoIntersection;
}
// Inifinite time interval - no update necessary
} else {
// Divide once
float oneOverD = 1.0f / d.y;
// Compute time value when they begin and end overlapping
float yEnter = (stationaryBox.min.y - movingBox.max.y) * oneOverD;
float yLeave = (stationaryBox.max.y - movingBox.min.y) * oneOverD;
// Check for interval out of order
if (yEnter > yLeave) {
swap(yEnter, yLeave);
}
// Update interval
if (yEnter > tEnter) tEnter = yEnter;
if (yLeave < tLeave) tLeave = yLeave;
// Check if this resulted in empty interval
if (tEnter > tLeave) {
return kNoIntersection;
}
}
// Check z-axis
if (d.z == 0.0f) {
// Empty or infinite inverval on z
if (
(stationaryBox.min.z >= movingBox.max.z) ||
(stationaryBox.max.z <= movingBox.min.z)
) {
// Empty time interval, so no intersection
return kNoIntersection;
}
// Inifinite time interval - no update necessary
} else {
// Divide once
float oneOverD = 1.0f / d.z;
// Compute time value when they begin and end overlapping
float zEnter = (stationaryBox.min.z - movingBox.max.z) * oneOverD;
float zLeave = (stationaryBox.max.z - movingBox.min.z) * oneOverD;
// Check for interval out of order
if (zEnter > zLeave) {
swap(zEnter, zLeave);
}
// Update interval
if (zEnter > tEnter) tEnter = zEnter;
if (zLeave < tLeave) tLeave = zLeave;
// Check if this resulted in empty interval
if (tEnter > tLeave) {
return kNoIntersection;
}
}
// OK, we have an intersection. Return the parametric point in time
// where the intersection occurs
return tEnter;
}


























 4643
4643

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








