1. 4位移位寄存器 4-bit shift register
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset, // async active-high reset to zero
input load,
input ena,
input [3:0] data,
output reg [3:0] q);
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset)
begin
if(areset)
q<=4'b0;
else if(load)
q<=data;
else if(ena)
q<={1'b0,q[3:1]};
else
q<=q;
end
endmodulemodule top_module(
input clk,
input areset,
input load,
input ena,
input [3:0] data,
output reg [3:0] q);
// Asynchronous reset: Notice the sensitivity list.
// The shift register has four modes:
// reset
// load
// enable shift
// idle -- preserve q (i.e., DFFs)
always @(posedge clk, posedge areset) begin
if (areset) // reset
q <= 0;
else if (load) // load
q <= data;
else if (ena) // shift is enabled
q <= q[3:1]; // Use vector part select to express a shift.
end
endmodule
2. Left/ right register 左移|右移寄存器(1位)
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [1:0] ena,
input [99:0] data,
output reg [99:0] q);
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(load) // load
q<=data;
else case(ena) // ena
2'b00: q<=q;
2'b01:q<={q[0],q[99:1]}; //右移
2'b10:q<={q[98:0],q[99]}; //左移
2'b11:q<=q;
default;
endcase
end
endmodulemodule top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [1:0] ena,
input [99:0] data,
output reg [99:0] q);
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(load) // load
q<=data;
else case(ena) // ena
2'b00: q<=q;
2'b01:q<={q[0],q[99:1]}; //右移
2'b10:q<={q[98:0],q[99]}; //左移
2'b11:q<=q;
default;
endcase
end
endmodule3. Left/right arithmetic shift by 1 or 8 算数 左移|右移寄存器(1 或8位)




module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input ena,
input [1:0] amount,
input [63:0] data,
output reg [63:0] q);
//左移:算数左移==逻辑左移,丢弃高位,低位补0
//算数右移:丢弃低位,高位补符号位
//逻辑右移:丢弃低位,高位补0
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(load)
q<=data;
else if(ena)
begin
case(amount)
2'b00:q<={q[62:0],1'b0}; //左移,空位补0,丢弃高位,低位补0
2'b01:q<={q[55:0],8'b0}; //左移,空位补0,丢弃高位,低位补0
2'b10:q<={q[63],q[63:1]}; //算数右移,空位补最高位符号位
2'b11:q<={{8{q[63]}},q[63:8]}; //算术右移,空位补最高位符号位
endcase
end
else q<=q;
end
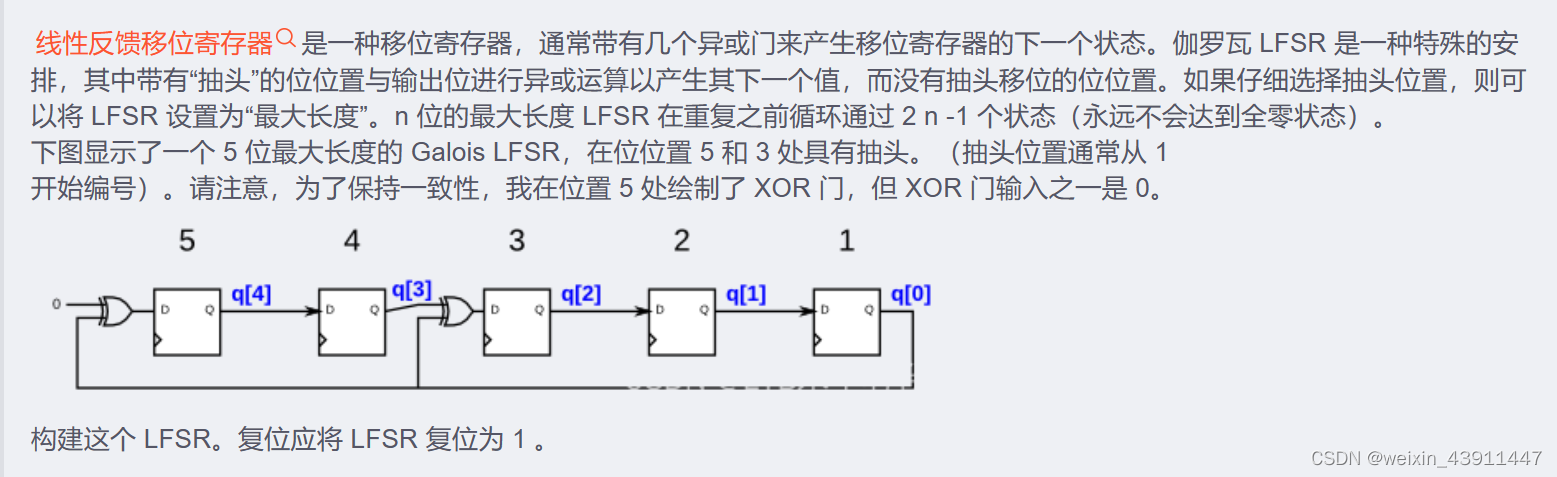
endmodule4. 5-bit LFSR
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset,
output reg [4:0] q);
reg [4:0] q_next; // q_next is not a register
// Convenience: Create a combinational block of logic that computes
// what the next value should be. For shorter code, I first shift
// all of the values and then override the two bit positions that have taps.
// A logic synthesizer creates a circuit that behaves as if the code were
// executed sequentially, so later assignments override earlier ones.
// Combinational always block: Use blocking assignments.
always @(*) begin
q_next = q[4:1]; // Shift all the bits. This is incorrect for q_next[4] and q_next[2]
q_next[4] = q[0]; // Give q_next[4] and q_next[2] their correct assignments
q_next[2] = q[3] ^ q[0];
end
// This is just a set of DFFs. I chose to compute the connections between the
// DFFs above in its own combinational always block, but you can combine them if you wish.
// You'll get the same circuit either way.
// Edge-triggered always block: Use non-blocking assignments.
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 5'h1;
else
q <= q_next;
end
endmodulemodule top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 5'h1
output [4:0] q
);
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset) q<=5'b1;
else
q<={0^q[0],q[4],q[3]^q[0],q[2],q[1]};
end
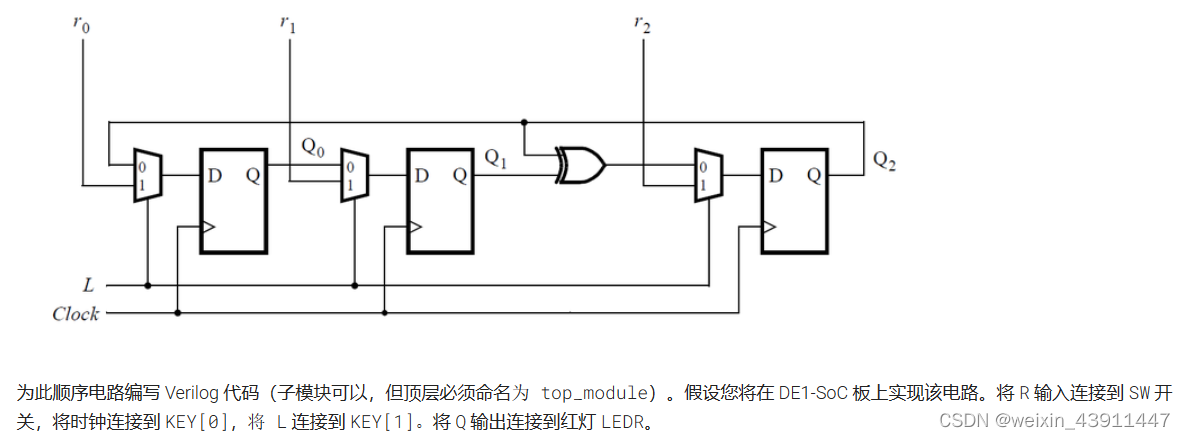
endmodule5. 3-bit LFSR
module top_module (
input [2:0] SW, // R
input [1:0] KEY, // L and clk
output [2:0] LEDR); // Q
LFSR u_0(SW[0],KEY[1],KEY[0],LEDR[2],LEDR[0]);
LFSR u_1(SW[1],KEY[1],KEY[0],LEDR[0],LEDR[1]);
LFSR u_2(SW[2],KEY[1],KEY[0],LEDR[1]^LEDR[2],LEDR[2]);
endmodule
module LFSR(
input r,
input L,
input clk,
input Q,
output q);
always@(posedge clk)
begin
q <= L? r:Q ;
end
endmodulemodule top_module (
input [2:0] SW, // R
input [1:0] KEY, // L and clk
output [2:0] LEDR); // Q
reg ry;
assign ry=LEDR[1]^LEDR[2];
mode_muxdff u0(KEY[0],KEY[1],SW[0],LEDR[2],LEDR[0]);
mode_muxdff u1(KEY[0],KEY[1],SW[1],LEDR[0],LEDR[1]);
mode_muxdff u2(KEY[0],KEY[1],SW[2],ry,LEDR[2]);
endmodule
module mode_muxdff (
input clk,
input L,
input r_in,
input q_in,
output reg Q);
wire D;
assign D=L? r_in:q_in;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
Q<=D;
end
endmodule
6. 32-bit LFSR
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 32'h1
output [31:0] q
);
reg[32:0] q_next;
always@(*) begin
q_next = q[31:1];
q_next[31] = 0^q[0];
q_next[21] = q[22]^q[0];
q_next[1] = q[2]^q[0];
q_next[0] = q[1]^q[0];
end
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(reset)
q<=32'b1;
else
q<=q_next;
end
endmodule
> module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 32'h1
output [31:0] q
);
always@(posedge clk)
begin
if(!reset)begin
q[0]<=q[0]^q[1];
q[1]<=q[0]^q[2];
q[20:2]<=q[21:3];
q[30:22]<=q[31:23];
q[21]<=q[22]^q[0];
q[31]<=q[0]^1'b0;
end
else
q<=32'h1;
end
endmodule
7. Shift register
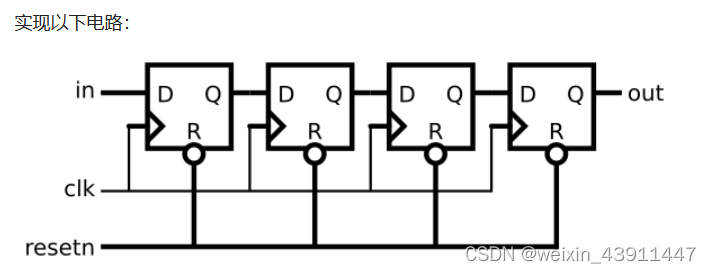
module top_module (
input clk,
input resetn,
input in,
output out
);
reg [3:0] sr;
// Create a shift register named sr. It shifts in "in".
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (~resetn) // Synchronous active-low reset
sr <= 0;
else
sr <= {sr[2:0], in};
end
assign out = sr[3]; // Output the final bit (sr[3])
endmodulemodule top_module (
input clk,
input resetn, // synchronous reset
input in,
output out);
reg [2:0] q;
always@(posedge clk)
begin
if(!resetn)
{out,q}<=4'b0;
else
{out,q[2:0]}<={q[2:0],in};
end
endmodule
8. Shift register
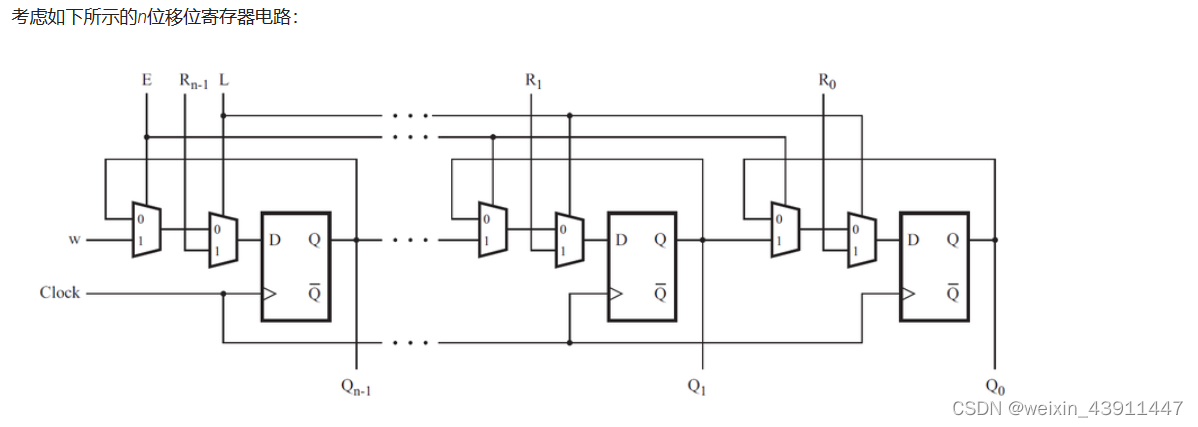

module top_module (
input [3:0] SW, //R
input [3:0] KEY, //0-clk,1-E,2-L,3-w
output [3:0] LEDR //out
); //
MUXDFF u_3(SW[3],KEY[0],KEY[1],KEY[2],KEY[3],LEDR[3]);
MUXDFF u_2(SW[2],KEY[0],KEY[1],KEY[2],LEDR[3],LEDR[2]);
MUXDFF u_1(SW[1],KEY[0],KEY[1],KEY[2],LEDR[2],LEDR[1]);
MUXDFF u_0(SW[0],KEY[0],KEY[1],KEY[2],LEDR[1],LEDR[0]);
endmodule
module MUXDFF (
input R,
input clk,
input E,
input L,
input w,
output q
);
reg w1,d;
always@(posedge clk)
begin
w1 = E?w:q;
d = L?R:w1;
q<=d;
end
endmodule9. 3-input LUT

module top_module (
input clk,
input enable,
input S,
input A, B, C,
output Z );
reg [7:0] q;
always@(posedge clk)
begin
if(enable)
q<={q[6:0],S};
else
q<=q;
end
always@(*)
begin
case({A,B,C})
3'b0:Z=q[0];
3'b001:Z=q[1];
3'b010:Z=q[2];
3'b011:Z=q[3];
3'b100:Z=q[4];
3'b101:Z=q[5];
3'b110:Z=q[6];
3'b111:Z=q[7];
endcase
end
endmodule
module top_module (
input clk,
input enable,
input S,
input A, B, C,
output reg Z
);
reg [7:0] q;
// The final circuit is a shift register attached to a 8-to-1 mux.
// Create a 8-to-1 mux that chooses one of the bits of q based on the three-bit number {A,B,C}:
// There are many other ways you could write a 8-to-1 mux
// (e.g., combinational always block -> case statement with 8 cases).
assign Z = q[ {A, B, C} ];
// Edge-triggered always block: This is a standard shift register (named q) with enable.
// When enabled, shift to the left by 1 (discarding q[7] and and shifting in S).
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (enable)
q <= {q[6:0], S};
end
endmodule




















 8498
8498











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








