作者主页(文火冰糖的硅基工坊):文火冰糖(王文兵)的博客_文火冰糖的硅基工坊_CSDN博客
本文网址:https://blog.csdn.net/HiWangWenBing/article/details/121050469
目录
前言:LeNet网络详解
(1)LeNet网络详解
(2)Pytorch官网对LeNet的定义
第1章 业务领域分析
1.1 步骤1-1:业务领域分析
(1)业务需求

目标要求:
给定任意个手写数字图形,识别出其属于哪个数字?
(2)业务分析
本任务的本质是逻辑分类中的多分类,多分类中的10分类问题,即给定一张图形的特征数据(这里是单个图形的单通道像素值),能够判断其属于哪个数字分类。属于分类问题。
有很多现有的卷积神经网络可以解决分类问题,本文使用LeNet来解决这个简单的分类问题。
这里也有两个思路:
- 直接利用框架自带的LeNet网络完成模型的搭建。
- 自己按照LeNet网络的结构,使用Pytorch提供的卷积核自行搭建该网络。
由于LeNet网络比较简单,也为了熟悉Ptorch的nn网络,我们不妨尝试上述两种方法。
对于后续的复杂网络,我们可以直接利用平台提供的库,直接使用已有的网络,而不再手工搭建。
1.2 步骤1-2:业务建模
其实,这里不需要自己在建立数据模型了,可以直接使用LeNet已有的模型,模型参考如下:


1.3 训练模型

1.4 验证模型

1.5 整体架构

1.6 代码实例前置条件
#环境准备
import numpy as np # numpy数组库
import math # 数学运算库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 画图库
import torch # torch基础库
import torch.nn as nn # torch神经网络库
import torch.nn.functional as F # torch神经网络库
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
print("Hello World")
print(torch.__version__)
print(torch.cuda.is_available())第2章 前向运算模型定义
2.1 步骤2-1:数据集选择
(1)MNIST数据集: http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/

备注 :可以先把样本数据下载本地,以提升程序调试的效率。最终的产品可以远程下载数据。
(2)样本数据与样本标签格式

(3)源代码示例 -- 下载并读入数据
#2-1 准备数据集
train_data = dataset.MNIST(root = "mnist",
train = True,
transform = transforms.ToTensor(),
download = True)
#2-1 准备数据集
test_data = dataset.MNIST(root = "mnist",
train = False,
transform = transforms.ToTensor(),
download = True)
print(train_data)
print("size=", len(train_data))
print("")
print(test_data)
print("size=", len(test_data))Dataset MNIST
Number of datapoints: 60000
Root location: mnist
Split: Train
StandardTransform
Transform: ToTensor()
size= 60000
Dataset MNIST
Number of datapoints: 10000
Root location: mnist
Split: Test
StandardTransform
Transform: ToTensor()
size= 10000
2.2 步骤2-2:数据预处理 - 本案例无需数据预处理
(1)批量数据读取 -- 启动dataloader从数据集中读取Batch数据
# 批量数据读取
train_loader = data_utils.DataLoader(dataset = train_data,
batch_size = 64,
shuffle = True)
test_loader = data_utils.DataLoader(dataset = test_data,
batch_size = 64,
shuffle = True)
print(train_loader)
print(test_loader)
print(len(train_loader), len(train_data)/64)
print(len(test_loader), len(test_data)/64)<torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader object at 0x000002461EF4A1C0> <torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader object at 0x000002461ED66610> 938 937.5 157 156.25
(2)#显示一个batch图片 -- 仅仅用于调试
显示一个batch图片
print("获取一个batch组图片")
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_loader))
print(imgs.shape)
print(labels.shape)
print(labels.size()[0])
print("\n合并成一张三通道灰度图片")
images = utils.make_grid(imgs)
print(images.shape)
print(labels.shape)
print("\n转换成imshow格式")
images = images.numpy().transpose(1,2,0)
print(images.shape)
print(labels.shape)
print("\n显示样本标签")
#打印图片标签
for i in range(64):
print(labels[i], end=" ")
i += 1
#换行
if i%8 == 0:
print(end='\n')
print("\n显示图片")
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()获取一个batch组图片 torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28]) torch.Size([64]) 64 合并成一张三通道灰度图片 torch.Size([3, 242, 242]) torch.Size([64]) 转换成imshow格式 (242, 242, 3) torch.Size([64]) 显示样本标签 tensor(0) tensor(8) tensor(3) tensor(7) tensor(5) tensor(7) tensor(9) tensor(7) tensor(1) tensor(1) tensor(1) tensor(8) tensor(8) tensor(6) tensor(0) tensor(1) tensor(4) tensor(8) tensor(1) tensor(3) tensor(3) tensor(6) tensor(4) tensor(4) tensor(0) tensor(5) tensor(8) tensor(5) tensor(9) tensor(3) tensor(7) tensor(5) tensor(2) tensor(1) tensor(0) tensor(6) tensor(8) tensor(8) tensor(9) tensor(6) tensor(1) tensor(3) tensor(5) tensor(3) tensor(4) tensor(4) tensor(3) tensor(1) tensor(4) tensor(1) tensor(4) tensor(4) tensor(9) tensor(8) tensor(7) tensor(2) tensor(3) tensor(1) tensor(2) tensor(0) tensor(8) tensor(1) tensor(1) tensor(4) 显示图片

2.3 步骤2-3:神经网络建模
(1)模型

LeNet-5 神经网络一共五层,其中卷积层和池化层可以考虑为一个整体,网络的结构为 :
输入 → 卷积 → 池化 → 卷积 → 池化 → 全连接 → 全连接 → 全连接 → 输出。
(2)Pytorch NN Conv2d用法详解
https://blog.csdn.net/HiWangWenBing/article/details/121051650
(3)Pytorch NN MaxPool2d用法详解
https://blog.csdn.net/HiWangWenBing/article/details/121053578
(4)使用Pytorch卷积核构建构建LeNet网络
在 pytorch 中,图像数据集(提供给网络的输入)的存储顺序为:
(batch, channels, height, width),依次为批大小、通道数、高度、宽度。
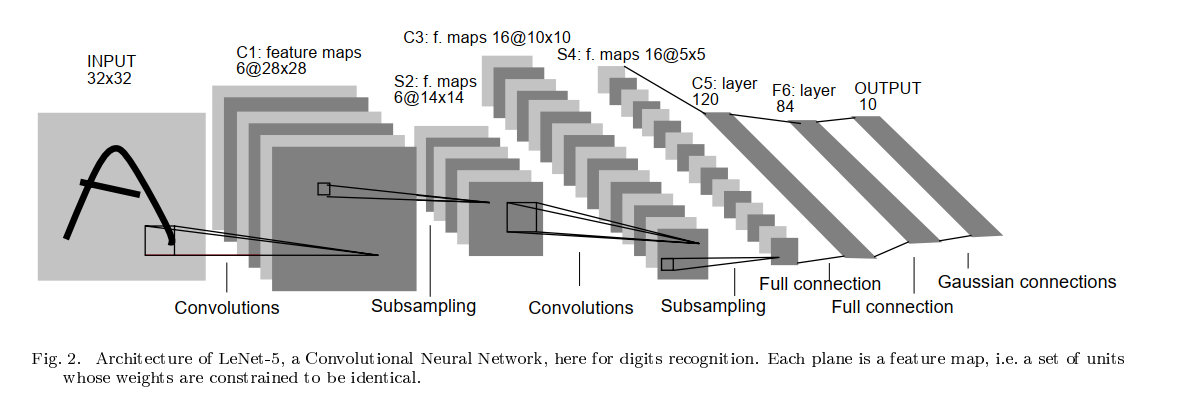
特别提醒:
LeNet-5网络的默认的输入图片的尺寸是32*32, 而Mnist数据集的图片的尺寸是28 * 28。
因此,采用Mnist数据集时,每一层的输出的特征值feature map的尺寸与LeNet-5网络的默认默认的feature map的尺寸是不一样的,需要适当的调整。
具体如何调整,请参考代码的实现:
下面以两种等效的方式定义LeNet神经网络:
- Pytorch官网方式
- 自定义方式
(5)构建LeNet网络结构的代码实例 - 官网
# 来自官网
class LeNet5A(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet5A, self).__init__()
# 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 square convolution kernel
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels = 1, out_channels = 6, kernel_size = 5) # 6 * 24 * 24
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels = 6, out_channels = 16, kernel_size = 5) # 16 * 8 * 8
# an affine operation: y = Wx + b
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features = 16 * 4 * 4, out_features= 120) # 16 * 4 * 4
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features = 120, out_features = 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(in_features = 84, out_features = 10)
def forward(self, x):
# Max pooling over a (2, 2) window
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2))
# If the size is a square, you can specify with a single number
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except the batch dimension
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
#x = F.log_softmax(x,dim=1)
return x(6)构建LeNet网络结构的代码实例 - 自定义
class LeNet5B(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet5B, self).__init__()
self.feature_convnet = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv1', nn.Conv2d (in_channels = 1, out_channels = 6, kernel_size= (5, 5), stride = 1)), # 6 * 24 * 24
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('pool1', nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2))), # 6 * 12 * 12
('conv2', nn.Conv2d (in_channels = 6, out_channels = 16, kernel_size=(5, 5))), # 16 * 8 * 8
('relu2', nn.ReLU()),
('pool2', nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2))), # 16 * 4 * 4
]))
self.class_fc = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('fc1', nn.Linear(in_features = 16 * 4 * 4, out_features = 120)), # 16 * 4 * 4
('relu3', nn.ReLU()),
('fc2', nn.Linear(in_features = 120, out_features = 84)),
('relu4', nn.ReLU()),
('fc3', nn.Linear(in_features = 84, out_features = 10)),
]))
def forward(self, img):
output = self.feature_convnet(img)
output = output.view(-1, 16 * 4 * 4) #相当于Flatten()
output = self.class_fc(output)
return output2.4 步骤2-4:定义神经网络实例以及输出
net_a = LeNet5A()
print(net_a)LeNet5A( (conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1)) (conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1)) (fc1): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=120, bias=True) (fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True) (fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True) )
net_b = LeNet5B()
print(net_b)LeNet5A( (conv1): Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1)) (conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1)) (fc1): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=120, bias=True) (fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True) (fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True) )
# 2-4 定义网络预测输出
# 测试网络是否能够工作
print("定义测试数据")
input = torch.randn(1, 1, 28, 28)
print("")
print("net_a的输出方法1:")
out = net_a(input)
print(out)
print("net_a的输出方法2:")
out = net_a.forward(input)
print(out)
print("")
print("net_b的输出方法1:")
out = net_b(input)
print(out)
print("net_b的输出方法2:")
out = net_b.forward(input)
print(out)第3章 定义反向计算
3.1 步骤3-1:定义loss
# 3-1 定义loss函数:
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print(loss_fn)3.2 步骤3-2:定义优化器
# 3-2 定义优化器
net = net_a
Learning_rate = 0.001 #学习率
# optimizer = SGD: 基本梯度下降法
# parameters:指明要优化的参数列表
# lr:指明学习率
#optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = Learning_rate)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr = Learning_rate, momentum=0.9)
print(optimizer)SGD (
Parameter Group 0
dampening: 0
lr: 0.001
momentum: 0.9
nesterov: False
weight_decay: 0
)
3.3 步骤3-3:模型训练 (epochs = 10)
# 3-3 模型训练
# 定义迭代次数
epochs = 10
loss_history = [] #训练过程中的loss数据
accuracy_history =[] #中间的预测结果
accuracy_batch = 0.0
for i in range(0, epochs):
for j, (x_train, y_train) in enumerate(train_loader):
#(0) 复位优化器的梯度
optimizer.zero_grad()
#(1) 前向计算
y_pred = net(x_train)
#(2) 计算loss
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y_train)
#(3) 反向求导
loss.backward()
#(4) 反向迭代
optimizer.step()
# 记录训练过程中的损失值
loss_history.append(loss.item()) #loss for a batch
# 记录训练过程中的在训练集上该批次的准确率
number_batch = y_train.size()[0] # 训练批次中图片的个数
_, predicted = torch.max(y_pred.data, dim = 1) # 选出最大可能性的预测
correct_batch = (predicted == y_train).sum().item() # 获得预测正确的数目
accuracy_batch = 100 * correct_batch/number_batch # 计算该批次上的准确率
accuracy_history.append(accuracy_batch) # 该批次的准确率添加到log中
if(j % 100 == 0):
print('epoch {} batch {} In {} loss = {:.4f} accuracy = {:.4f}%'.format(i, j , len(train_data)/64, loss.item(), accuracy_batch))
print("\n迭代完成")
print("final loss =", loss.item())
print("final accu =", accuracy_batch)迭代完成 final loss = 0.007419026922434568 final accu = 100.0
3.4 可视化loss迭代过程
#显示loss的历史数据
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel("iters")
plt.ylabel("")
plt.title("loss", fontsize = 12)
plt.plot(loss_history, "r")
plt.show()

3.5 可视化训练批次的精度迭代过程
#显示准确率的历史数据
plt.grid()
plt.xlabel("iters")
plt.ylabel("%")
plt.title("accuracy", fontsize = 12)
plt.plot(accuracy_history, "b+")
plt.show()
第4章 模型性能验证
4.1 手工验证
# 手工检查
index = 0
print("获取一个batch样本")
images, labels = next(iter(test_loader))
print(images.shape)
print(labels.shape)
print(labels)
print("\n对batch中所有样本进行预测")
outputs = net(images)
print(outputs.data.shape)
print("\n对batch中每个样本的预测结果,选择最可能的分类")
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1)
print(predicted.data.shape)
print(predicted)
print("\n对batch中的所有结果进行比较")
bool_results = (predicted == labels)
print(bool_results.shape)
print(bool_results)
print("\n统计预测正确样本的个数和精度")
corrects = bool_results.sum().item()
accuracy = corrects/(len(bool_results))
print("corrects=", corrects)
print("accuracy=", accuracy)
print("\n样本index =", index)
print("标签值 :", labels[index]. item())
print("分类可能性:", outputs.data[index].numpy())
print("最大可能性:",predicted.data[index].item())
print("正确性 :",bool_results.data[index].item())获取一个batch样本
torch.Size([64, 1, 28, 28])
torch.Size([64])
tensor([3, 9, 7, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 6, 7, 7, 2, 3, 9, 4, 3, 7, 8, 8, 1, 5, 0, 3, 1,
3, 7, 9, 8, 9, 0, 3, 7, 3, 6, 6, 6, 4, 8, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 2, 8, 6, 0,
1, 7, 8, 2, 4, 8, 7, 8, 4, 3, 3, 7, 7, 7, 3, 6])
对batch中所有样本进行预测
torch.Size([64, 10])
对batch中每个样本的预测结果,选择最可能的分类
torch.Size([64])
tensor([3, 9, 7, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 7, 7, 2, 3, 9, 4, 3, 7, 8, 8, 1, 5, 0, 3, 1,
3, 7, 9, 8, 9, 0, 3, 2, 3, 6, 6, 6, 4, 8, 5, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 2, 8, 6, 0,
1, 7, 8, 2, 4, 8, 7, 8, 4, 3, 3, 7, 7, 7, 3, 6])
对batch中的所有结果进行比较
torch.Size([64])
tensor([ True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, False, True,
True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, False, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True, True,
True, True, True, True])
统计预测正确样本的个数和精度
corrects= 62
accuracy= 0.96875
样本index = 0
标签值 : 3
分类可能性: [-4.9285274 0.03151219 1.1638378 15.596342 -6.1877465 6.7307224
-7.46734 -2.5457728 4.803236 1.313346 ]
最大可能性: 3
正确性 : True
4.2 整个训练集上的精度验证:精度可达98%
# 对训练后的模型进行评估:测试其在训练集上总的准确率
correct_dataset = 0
total_dataset = 0
accuracy_dataset = 0.0
# 进行评测的时候网络不更新梯度
with torch.no_grad():
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader):
#获取一个batch样本"
images, labels = data
#对batch中所有样本进行预测
outputs = net(images)
#对batch中每个样本的预测结果,选择最可能的分类
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
#对batch中的样本数进行累计
total_dataset += labels.size()[0]
#对batch中的所有结果进行比较"
bool_results = (predicted == labels)
#统计预测正确样本的个数
correct_dataset += bool_results.sum().item()
#统计预测正确样本的精度
accuracy_dataset = 100 * correct_dataset/total_dataset
if(i % 100 == 0):
print('batch {} In {} accuracy = {:.4f}'.format(i, len(train_data)/64, accuracy_dataset))
print('Final result with the model on the dataset, accuracy =', accuracy_dataset)batch 0 In 937.5 accuracy = 96.8750
batch 100 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.9270
batch 200 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8545
batch 300 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8873
batch 400 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8413
batch 500 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.7826
batch 600 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.7901
batch 700 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8134
batch 800 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8269
batch 900 In 937.5 accuracy = 97.8219
Final result with the model on the dataset, accuracy = 97.80833333333334
4.3 整个测试集上的精度验证:精度可达98%
# 对训练后的模型进行评估:测试其在训练集上总的准确率
correct_dataset = 0
total_dataset = 0
accuracy_dataset = 0.0
# 进行评测的时候网络不更新梯度
with torch.no_grad():
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader):
#获取一个batch样本"
images, labels = data
#对batch中所有样本进行预测
outputs = net(images)
#对batch中每个样本的预测结果,选择最可能的分类
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
#对batch中的样本数进行累计
total_dataset += labels.size()[0]
#对batch中的所有结果进行比较"
bool_results = (predicted == labels)
#统计预测正确样本的个数
correct_dataset += bool_results.sum().item()
#统计预测正确样本的精度
accuracy_dataset = 100 * correct_dataset/total_dataset
if(i % 100 == 0):
print('batch {} In {} accuracy = {:.4f}'.format(i, len(test_data)/64, accuracy_dataset))
print('Final result with the model on the dataset, accuracy =', accuracy_dataset)batch 0 In 156.25 accuracy = 98.4375
batch 100 In 156.25 accuracy = 97.5402
Final result with the model on the dataset, accuracy = 97.68
第5章 模型保存
5.1 保存整个模型
#存储模型
torch.save(net, "models/Lenet_cifar10_model.pkl")
5.2 仅保存模型权重
#存储参数
torch.save(net.state_dict() , "models/Lenet_cifar10_model_params.pkl")作者主页(文火冰糖的硅基工坊):文火冰糖(王文兵)的博客_文火冰糖的硅基工坊_CSDN博客
本文网址:https://blog.csdn.net/HiWangWenBing/article/details/121050469
























 2651
2651











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










