1.背景
2024年,B Abdollahzadeh等人受到美洲狮智能行为和生活行为启发,提出了美洲狮优化算法(Puma Optimizer, PO)。

2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
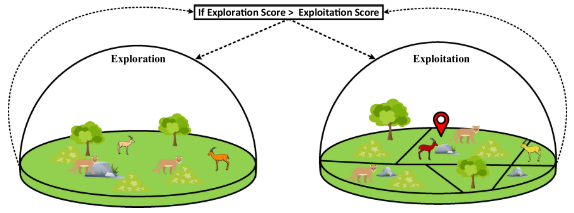
PO基于美洲狮猎食行为,其利用美洲狮的智能和记忆特性,将优化过程分为探索和开发两个阶段。在探索阶段,PO模拟美洲狮探索新领地的行为,寻找潜在的优化方向;在开发阶段,PO则模拟美洲狮返回已知有猎物的地方的行为,深化优化方案。

2.2算法过程
无经验阶段
美洲狮在它的早期生活中没有太多的经验,由于它不熟悉它的生活空间和不知道猎物在它的领土上的位置,它经常在同一时间进行探索:
f
1
E
x
p
l
o
r
=
P
F
1
⋅
(
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
1
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
)
f
1
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
=
P
F
1
⋅
(
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
)
f
2
E
x
p
l
o
r
=
P
F
2
⋅
(
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
+
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
2
+
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
3
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
1
+
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
2
+
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
3
)
f
2
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
=
P
F
2
⋅
(
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
+
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
2
+
S
e
q
C
o
u
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
3
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
1
+
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
2
+
S
e
q
T
i
m
e
3
)
(1)
\begin{aligned}&f1_{Explor}=PF_{1}\cdot\left(\frac{Seq_{CoutExplore}^{1}}{Seq_{Time}}\right)\\&f1_{Exploit}=PF_{1}\cdot\left(\frac{Seq_{CoutExploit}^{1}}{Seq_{Time}}\right)\\&f2_{Explor}=PF_{2}\\&\cdot\left(\frac{Seq_{CoutExploit}^{1}+Seq_{CoutExploit}^{2}+Seq_{CoutExploit}^{3}}{Seq_{Time}^{1}+Seq_{Time}^{2}+Seq_{Time}^{3}}\right)\\&f2_{Exploit}=PF_{2}\\&\cdot\left(\frac{Seq_{CoutExploit}^{1}+Seq_{CoutExploit}^{2}+Seq_{CoutExploit}^{3}}{Seq_{Time}^{1}+Seq_{Time}^{2}+Seq_{Time}^{3}}\right)\end{aligned}\tag{1}
f1Explor=PF1⋅(SeqTimeSeqCoutExplore1)f1Exploit=PF1⋅(SeqTimeSeqCoutExploit1)f2Explor=PF2⋅(SeqTime1+SeqTime2+SeqTime3SeqCoutExploit1+SeqCoutExploit2+SeqCoutExploit3)f2Exploit=PF2⋅(SeqTime1+SeqTime2+SeqTime3SeqCoutExploit1+SeqCoutExploit2+SeqCoutExploit3)(1)
SeqCost的变量值与探索、开发的各个阶段相关,表述为:
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
1
=
∣
C
o
s
t
B
e
s
t
I
n
i
t
i
a
l
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
1
∣
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
2
=
∣
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
2
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
1
∣
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
3
=
∣
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
3
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
2
∣
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
=
∣
C
o
s
t
B
e
s
t
I
n
i
t
i
a
l
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
∣
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
2
=
∣
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
2
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
1
∣
S
e
q
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
3
=
∣
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
3
−
C
o
s
t
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
2
∣
(2)
\begin{aligned}&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExplore}}^{1}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Best}}^{Initial}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Explore}}^{1}\right|\\&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExplore}}^{2}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Explore}}^{2}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Explore}}^{1}\right|\\&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExplore}}^{3}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Explore}}^{3}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Explore}}^{2}\right|\\&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExploit}}^{1}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Best}}^{Initial}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Exploit}}^{1}\right|\\&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExploit}}^{2}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Exploit}}^{2}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Exploit}}^{1}\right|\\&\mathrm{Seq}_{\mathrm{CostExploit}}^{3}=\left|\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Exploit}}^{3}-\mathrm{Cost}_{\mathrm{Exploit}}^{2}\right|\end{aligned}\tag{2}
SeqCostExplore1=
CostBestInitial−CostExplore1
SeqCostExplore2=
CostExplore2−CostExplore1
SeqCostExplore3=
CostExplore3−CostExplore2
SeqCostExploit1=
CostBestInitial−CostExploit1
SeqCostExploit2=
CostExploit2−CostExploit1
SeqCostExploit3=
CostExploit3−CostExploit2
(2)
由于其他的美洲狮都有令人愉快的经历,需要在两个阶段中选择一个,计算探索与开发阶段:
S
c
o
r
e
E
x
p
l
o
r
e
=
(
P
F
1
⋅
f
1
E
x
p
l
o
r
)
+
(
P
F
2
⋅
f
2
E
x
p
l
o
r
)
S
c
o
r
e
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
=
(
P
F
1
⋅
f
1
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
)
+
(
P
F
2
⋅
f
2
E
x
p
l
o
i
t
)
(3)
Score_{Explore}=(PF_{1}\cdot f1_{Explor})+(PF_{2}\cdot f2_{Explor})\\Score_{Exploit}=(PF_{1}\cdot f1_{Exploit})+(PF_{2}\cdot f2_{Exploit})\tag{3}
ScoreExplore=(PF1⋅f1Explor)+(PF2⋅f2Explor)ScoreExploit=(PF1⋅f1Exploit)+(PF2⋅f2Exploit)(3)
有经验阶段
经过三代之后,美洲狮有了可以接受的经验来决定更换阶段,并且在迭代的延续中,只选择一个阶段进行优化操作:
f
1
t
e
x
p
l
o
i
t
=
P
F
1
⋅
∣
C
o
s
t
o
l
d
e
x
p
l
o
i
t
−
C
o
s
t
n
e
w
e
x
p
l
o
i
t
T
t
e
x
p
l
o
i
t
∣
f
1
t
e
x
p
l
o
r
e
=
P
F
1
⋅
∣
C
o
s
t
o
l
d
e
x
p
l
o
r
e
−
C
o
s
t
n
e
w
e
x
p
l
o
r
e
T
t
e
x
p
l
o
r
e
∣
(4)
f_{1t}^{exploit}=PF_{1}\cdot\left|\frac{Cost_{old}^{exploit}-Cost_{new}^{exploit}}{T_{t}^{exploit}}\right|\\f_{1t}^{explore}=PF_{1}\cdot\left|\frac{Cost_{old}^{explore}-Cost_{new}^{explore}}{T_{t}^{explore}}\right|\tag{4}
f1texploit=PF1⋅
TtexploitCostoldexploit−Costnewexploit
f1texplore=PF1⋅
TtexploreCostoldexplore−Costnewexplore
(4)
探索阶段
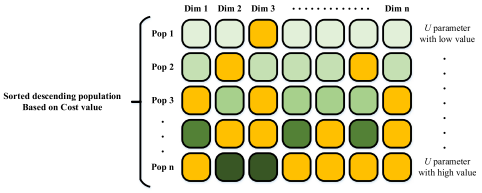
美洲狮经常在它们的领地内长途漫游,寻找食物和狩猎。这种搜索可以是到他以前有机会找到猎物的领土点,或者他可以对他的领土上的新地方进行搜索,并且在该地区没有获得猎物和食物。。在这个阶段,美洲狮在它们的领地内随机搜索寻找食物,或者随机接近其他美洲狮并利用它们的猎物。因此,美洲狮会随机跳入搜索空间或在美洲狮之间的空间寻找食物。首先对整个种群进行升序排序:
i
f
r
a
n
d
1
>
0.5
,
Z
i
,
G
=
R
D
i
m
∗
(
U
b
−
L
b
)
+
L
b
O
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
,
Z
i
,
G
=
X
a
,
G
+
G
⋅
(
X
a
,
G
−
X
b
,
G
)
+
G
⋅
(
(
(
X
a
,
G
−
X
b
,
G
)
)
)
X
b
,
G
)
−
(
X
c
,
G
−
X
d
,
G
)
)
+
(
(
X
c
,
G
−
X
d
,
G
)
−
(
X
e
,
G
−
X
f
,
G
)
)
)
G
=
2
⋅
r
a
n
d
2
−
1
(5)
\begin{aligned} &\mathrm{if} rand_{1}>0.5, Z_{i,G}=R_{Dim}*(Ub-Lb)+Lb \\ &\mathrm{Otherwise},\quad Z_{i,G}=X_{a,G}+G\cdot(X_{a,G}-X_{b,G})+G\cdot\left(\left(\left(X_{a,G}-X_{b,G}\right)\right)\right) \\ &X_{b,G})-\left(X_{c,G}-X_{d,G}\right))+\left(\left(X_{c,G}-X_{d,G}\right)-\left(X_{e,G}-X_{f,G}\right)\right)) \\ &G=2\cdot rand_{2}-1 \end{aligned}\tag{5}
ifrand1>0.5,Zi,G=RDim∗(Ub−Lb)+LbOtherwise,Zi,G=Xa,G+G⋅(Xa,G−Xb,G)+G⋅(((Xa,G−Xb,G)))Xb,G)−(Xc,G−Xd,G))+((Xc,G−Xd,G)−(Xe,G−Xf,G)))G=2⋅rand2−1(5)
根据现有条件将生成的新解用于改进当前解。
X
n
e
w
=
{
Z
i
,
G
,
i
f
j
=
j
r
a
n
d
o
r
r
a
n
d
3
≤
U
X
a
,
G
,
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
N
C
=
1
−
U
p
=
N
C
N
p
o
p
i
f
C
o
s
t
X
n
e
w
<
C
o
s
t
X
i
,
U
=
U
+
p
(6)
\begin{aligned} &\left.X_{new}=\left\{\begin{array}{c}{Z_{i,G},ifj=\mathrm{j}_{rand}orrand_{3}\leq U}\\{X_{a,G},otherwise}\end{array}\right.\right. \\ &NC=1-U \\ &p={\frac{NC}{Npop}} \\ &ifCostX_{new}<CostX_{i},U=U+p \end{aligned}\tag{6}
Xnew={Zi,G,ifj=jrandorrand3≤UXa,G,otherwiseNC=1−Up=NpopNCifCostXnew<CostXi,U=U+p(6)
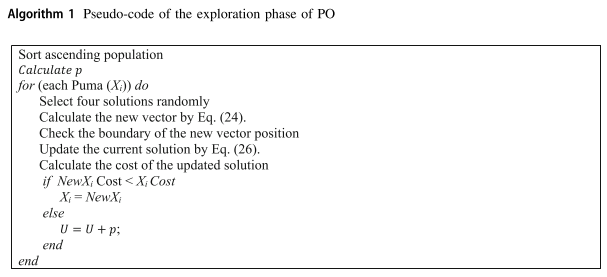
开发阶段
在开发阶段,该算法利用两种不同的算子来改进解,这两种机制是基于美洲狮的伏击和冲刺两种狩猎行为:
X
n
e
w
=
{
i
f
r
a
n
d
4
≥
0.5
,
X
n
e
w
=
(
m
e
a
n
(
S
o
l
t
o
t
a
l
)
N
p
o
p
)
⋅
X
1
r
−
(
−
1
)
β
×
X
i
1
+
(
α
⋅
r
a
n
d
5
)
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
,
i
f
r
a
n
d
6
≥
L
,
X
n
e
w
=
P
u
n
a
m
a
l
e
+
(
2
⋅
r
a
n
d
7
)
⋅
e
x
p
(
r
a
n
d
n
1
)
⋅
X
2
r
−
X
i
o
t
h
e
r
w
i
s
e
,
X
n
e
w
=
(
2
×
r
a
n
d
8
)
×
(
F
1
⋅
R
⋅
X
(
i
)
+
F
2
⋅
(
1
−
R
)
⋅
P
u
n
a
m
a
l
e
)
(
2
⋅
r
a
n
d
9
−
1
+
r
a
n
d
n
2
)
−
P
u
m
a
m
a
l
e
(7)
\begin{aligned}&X_{new}=\begin{cases} if rand_4\geq0.5,X_{new}=\frac{\left(\frac{mean(Sol_{total})}{Npop}\right)\cdot X_1^r-(-1)^\beta\times X_i}{1+(\alpha\cdot rand_5)}\\ otherwise, if rand_6\geq L,X_{new}=Puna_{male}+(2\cdot rand_7)\cdot exp(randn_1)\cdot X_2^r-X_i\\ otherwise, X_{new}=(2\times rand_8)\times\frac{(F_1\cdot R\cdot X(i)+F2\cdot(1-R)\cdot Puna_{male})}{(2\cdot rand_9-1+randn_2)}-Puma_{male}\end{cases}\end{aligned}\tag{7}
Xnew=⎩
⎨
⎧ifrand4≥0.5,Xnew=1+(α⋅rand5)(Npopmean(Soltotal))⋅X1r−(−1)β×Xiotherwise,ifrand6≥L,Xnew=Punamale+(2⋅rand7)⋅exp(randn1)⋅X2r−Xiotherwise,Xnew=(2×rand8)×(2⋅rand9−1+randn2)(F1⋅R⋅X(i)+F2⋅(1−R)⋅Punamale)−Pumamale(7)
第一种用于模拟美洲狮向其他美洲狮的猎物进行短距离跳跃,第二种用于向最佳美洲狮的猎物进行长距离跳跃。
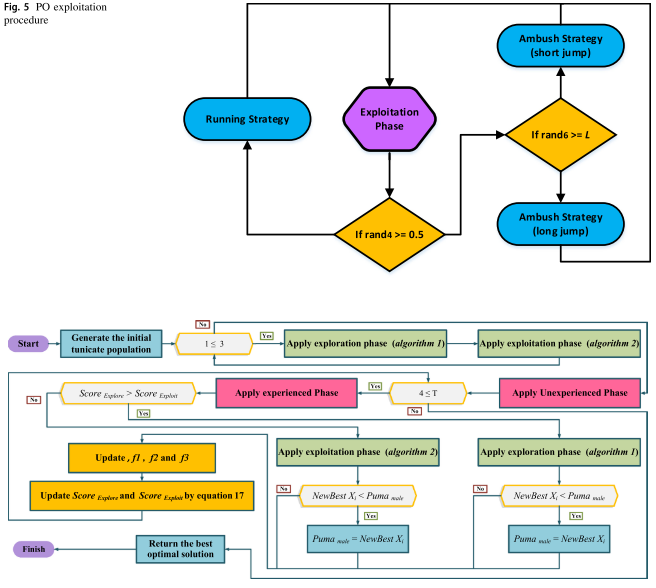
参数表述:
R
=
2
⋅
r
a
n
d
11
−
1
F
1
=
r
a
n
d
n
3
⋅
e
x
p
(
2
−
I
t
e
r
⋅
(
2
M
a
x
I
t
e
r
)
)
(8)
\begin{aligned}&R=2\cdot rand_{11}-1\\&F_{1}=randn_{3}\cdot exp\biggl(2-Iter\cdot\biggl(\frac{2}{MaxIter}\biggr)\biggr)\end{aligned}\tag{8}
R=2⋅rand11−1F1=randn3⋅exp(2−Iter⋅(MaxIter2))(8)

伪代码

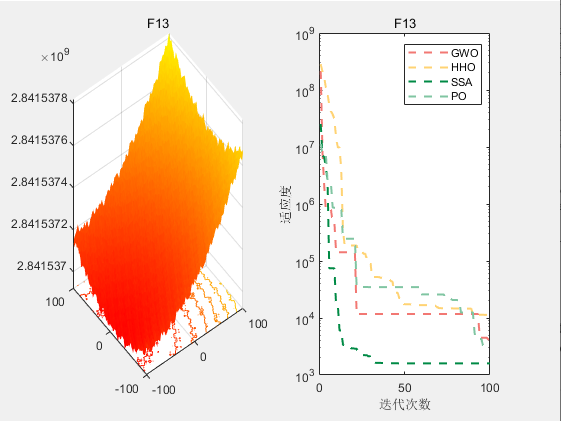
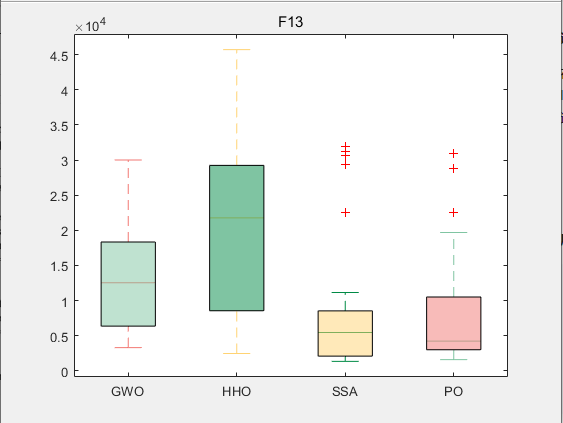
3.结果展示
使用测试框架,测试PO性能 一键run.m
CEC2017-F13

4.参考文献
[1] Abdollahzadeh B, Khodadadi N, Barshandeh S, et al. Puma optimizer (PO): A novel metaheuristic optimization algorithm and its application in machine learning[J]. Cluster Computing, 2024: 1-49.























 286
286











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










