1.MAmmoTH-VL: Eliciting Multimodal Reasoning with Instruction Tuning at Scale
Authors: Jarvis Guo, Tuney Zheng, Yuelin Bai, Bo Li, Yubo Wang, King Zhu, Yizhi Li, Graham Neubig, Wenhu Chen, Xiang Yue
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.05237
论文摘要
Open-source multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown significant potential in a broad range of multimodal tasks. However, their reasoning capabilities remain constrained by existing instruction-tuning datasets, which are predominantly repurposed from academic datasets such as VQA, AI2D, and ChartQA. These datasets focus on simplistic tasks and only provide phrase-level answers without any intermediate rationales. To address these challenges, we introduce a scalable and cost-effective method to construct a large-scale multimodal instruction-tuning dataset with rich intermediate rationales designed to elicit chain-of-thought reasoning. Using only open models, we created a dataset containing 12M instruction-response pairs to cover diverse and reasoning-intensive tasks with detailed and faithful rationales. Experiments demonstrate that training MLLMs on this dataset significantly improves reasoning capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art performance on benchmarks such as MathVerse (+8.1%), MMMU-Pro (+7%), and MuirBench (+13.3%). Additionally, the model shows notable improvements of up to 4% on non-reasoning-based benchmarks. Ablation studies further highlight the importance of key components, such as rewriting and self-filtering, in the dataset construction process.
论文简评
本文主要介绍了MAmmoTH-VL,一个用于提升大规模语言模型(如大型语言模型)推理能力的多模态可扩展教学数据集。作者描述了一个包含收集、链式思考推理重写以及质量过滤的三步生成流程的数据生成方法。实验结果显示在多个基准测试中取得了显著性能改进,表明了提出的数据集的有效性。
该文有效解决了大型语言模型在处理复杂任务时面临的挑战,并提出了一种新的数据生成策略,旨在促进多模态AI的发展。通过与开源模型的合作,可以增加数据的多样性,从而提高模型的泛化能力和理解能力。此外,该研究还展示了MMLMs在多种基准测试中的良好性能,进一步验证了其有效性。因此,本文对于推动多模态AI技术的进步具有重要意义。

2.Socio-Emotional Response Generation: A Human Evaluation Protocol for LLM-Based Conversational Systems
Authors: Lorraine Vanel, Ariel R. Ramos Vela, Alya Yacoubi, Chloé Clavel
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.04492
论文摘要
Conversational systems are now capable of producing impressive and generally relevant responses. However, we have no visibility nor control of the socio-emotional strategies behind state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs), which poses a problem in terms of their transparency and thus their trustworthiness for critical applications. Another issue is that current automated metrics are not able to properly evaluate the quality of generated responses beyond the dataset’s ground truth. In this paper, we propose a neural architecture that includes an intermediate step in planning socio-emotional strategies before response generation. We compare the performance of open-source baseline LLMs to the outputs of these same models augmented with our planning module. We also contrast the outputs obtained from automated metrics and evaluation results provided by human annotators. We describe a novel evaluation protocol that includes a coarse-grained consistency evaluation, as well as a finer-grained annotation of the responses on various social and emotional criteria. Our study shows that predicting a sequence of expected strategy labels and using this sequence to generate a response yields better results than a direct end-to-end generation scheme. It also highlights the divergences and the limits of current evaluation metrics for generated content. The code for the annotation platform and the annotated data are made publicly available for the evaluation of future models.
论文简评
该篇论文提出了一种神经架构来生成对话AI系统的社会情感响应,该构想整合了一个计划模块以指导社会情感策略。同时,文中引入了人机评估协议来评估回应质量,这是当前自动指标所无法比拟的。论文的核心在于解决对话AI系统中社会情感响应生成的关键问题,并通过提出一种结构化的解决方案,强调情感输出的可控性和透明度,从而超越传统的端到端模型。此外,论文还提供了详尽的人机评估协议,涵盖逻辑、情绪和社会一致性等多个方面,这些都标志着对现有评估方法的一大进步。综上所述,该文不仅为对话AI系统的发展提供了一种新颖且有效的解决办法,其研究思路具有创新性和前瞻性,值得进一步深入探讨和应用。

3.TACO: Learning Multi-modal Action Models with Synthetic Chains-of-Thought-and-Action
Authors: Zixian Ma, Jianguo Zhang, Zhiwei Liu, Jieyu Zhang, Juntao Tan, Manli Shu, Juan Carlos Niebles, Shelby Heinecke, Huan Wang, Caiming Xiong, Ranjay Krishna, Silvio Savarese
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.05479
论文摘要
While open-source multi-modal language models perform well on simple question answering tasks, they often fail on complex questions that require multiple capabilities, such as fine-grained recognition, visual grounding, and reason ing, and that demand multi-step solutions. We present TACO, a family of multi-modal large action models de signed to improve performance on such complex, multi step and multi-modal tasks. During inference, TACO pro duces chains-of-thought-and–action (CoTA), executes in termediate steps by invoking external tools such as OCR, depth estimation and calculator, then integrates both the thoughts and action outputs to produce coherent responses. To train TACO, we create a large dataset of 1M+ synthetic CoTA traces generated with GPT-4o and Python programs. We then experiment with various data filtering and mixing techniques and obtain a final subset of 293K high-quality CoTA examples. This dataset enables TACO to learn com plex reasoning and action paths, surpassing existing mod els trained on instruct tuning data with only direct answers. Our model TACO outperforms the instruction-tuned base line across 8 benchmarks, achieving a 3.6% improvement on average, with gains up to 15% in MMVet tasks involv ing OCR, mathematical reasoning and spatial reasoning. Training on high-quality CoTA traces sets a new standard for complex multi-modal reasoning, highlighting the need for structured, multi-step instruction tuning in advancing open-source mutli-modal models’ capabilities.
论文简评
本文提出了TACO框架,以解决多模态语言模型面临的挑战——如何有效处理复杂、多步骤的任务。作者利用生成的合成CoTA数据集(Chain-of-Thought-and-Action)对现有模型进行了比较,发现TACO在多个基准测试中表现出色,特别是在OCR和数学推理任务上。该研究不仅解决了当前AI领域的一个重要问题,也为未来的研究提供了宝贵的参考案例。综上所述,TACO是一个具有创新性的多模态语言模型训练方法,它展示了其在实际应用中的潜力,并为解决复杂的多步任务提供了一种有效的方法。

4.Show, Don’t Tell: Uncovering Implicit Character Portrayal using LLMs
Authors: Brandon Jaipersaud, Zining Zhu, Frank Rudzicz, Elliot Creager
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.04576
论文摘要
Tools for analyzing character portrayal in fiction are valuable for writers and literary scholars in developing and interpreting compelling stories. Existing tools, such as visualization tools for analyzing fictional characters, primarily rely on explicit textual indicators of character attributes. However, portrayal is often implicit, revealed through actions and behaviors rather than explicit statements. We address this gap by leveraging large language models (LLMs) to uncover implicit character portrayals. We start by generating a dataset for this task with greater cross-topic similarity, lexical diversity, and narrative lengths than existing narrative text corpora such as TinyStories and WritingPrompts. We then introduce LIIPA (LLMs for Inferring Implicit Portrayal for Character Analysis), a framework for prompting LLMs to uncover character portrayals. LIIPA can be configured to use various types of intermediate computation (character attribute word lists, chain-of-thought) to infer how fictional characters are portrayed in the source text. We find that LIIPA outperforms existing approaches and is more robust to increasing character counts (number of unique persons depicted) due to its ability to utilize full narrative context. Lastly, we investigate the sensitivity of portrayal estimates to character demographics, identifying a fairness-accuracy tradeoff among methods in our LIIPA framework – a phenomenon familiar within the algorithmic fairness literature. Despite this tradeoff, all LIIPA variants consistently outperform non-LLM baselines in both fairness and accuracy. Our work demonstrates the potential benefits of using LLMs to analyze complex characters and to better understand how implicit portrayal biases may manifest in narrative texts.
论文简评
本文通过引入名为LIIPA的框架,利用大型语言模型揭示叙事中的隐性人物刻画。它提出了一种新的数据集ImPortPrompts,其多样性和代表性远超现有数据集。该框架在与先前方法的竞争中显示出改进的表现,尤其是在处理复杂故事中有多个角色的情况下。此外,论文还讨论了LLM输出中的公平-准确性权衡问题,并将其视为文学分析和算法公平性研究的重要贡献。总之,本文提供了对叙事中隐性人物刻画的全面概述,展示了LIIPA框架如何有效解决这一问题,以及它在理解和解释算法偏见方面的潜在作用。

5.IterNorm: Fast Iterative Normalization
Authors: ChangMin Ye, Yonguk Sim, Youngchae Kim, SeongMin Jin, Doo Seok Jeong
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.04778
论文摘要
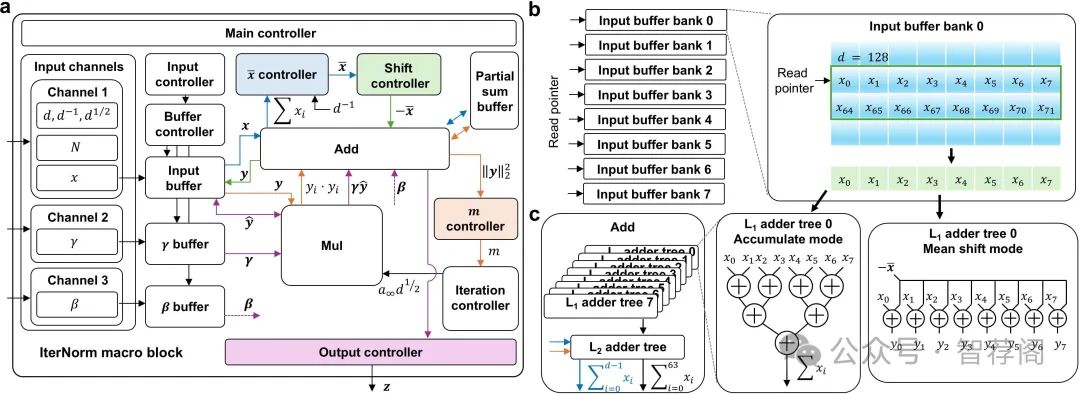
Transformer-based large language models are a memory-bound model whose operation is based on a large amount of data that are marginally reused. Thus, the data movement between a host and accelerator likely dictates the total wall-clock time. Layer normalization is one of the key workloads in the transformer model, following each of multi-head attention and feed-forward network blocks. To reduce data movement, layer normalization needs to be performed on the same chip as the matrix-matrix multiplication engine. To this end, we introduce an iterative L2-normalization method for 1D input (IterNorm), ensuring fast convergence to the steady-state solution within five iteration steps and high precision, outperforming the fast inverse square root algorithm in six out of nine cases for FP32 and five out of nine for BFloat16 across the embedding lengths used in the OPT models. Implemented in 32/28nm CMOS, the IterNorm macro normalizes-dimensional vectors, where, with a latency of 112-227 cycles at 100MHz/1.05V.
论文简评
这篇论文介绍了一种名为IterNorm的快速迭代归一化方法,用于Transformer基的大型语言模型(LLM)中的层归一化。其目标是在芯片上执行归一化操作,以避免昂贵的数据移动和操作延迟。该方法基于坚实的理论框架,并展现出良好的性能,尤其是在输入长度和浮点格式方面。实验结果表明,IterNorm在精度和收敛速度方面优于现有方法。总的来说,这篇文章提供了对这一问题的深入理解和改进方法的有效性证明。
如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
























 1007
1007

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








