目录
💥1 概述
📚2 运行结果
🎉3 参考文献
👨💻4 Matlab代码
💥1 概述
本文运用基于双目立体视觉的技术,提出一种快速非接触测量目标物体的体积方法。此方法将适用于多种场景下的目标体积测量,具有测量精度较高、测量成本低和灵活等优点。
📚2 运行结果
主函数部分代码:
%%
% 清理空间
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% 导入立体标定参数
load stereoParams.mat
% 立体参数的可视化
% figure;
% showExtrinsics(stereoParams);
%% 导入数据
frameLeft = imread('images/left007.bmp');
frameRight = imread('images/right007.bmp');
[frameLeftRect, frameRightRect] = rectifyStereoImages(frameLeft, frameRight, stereoParams);
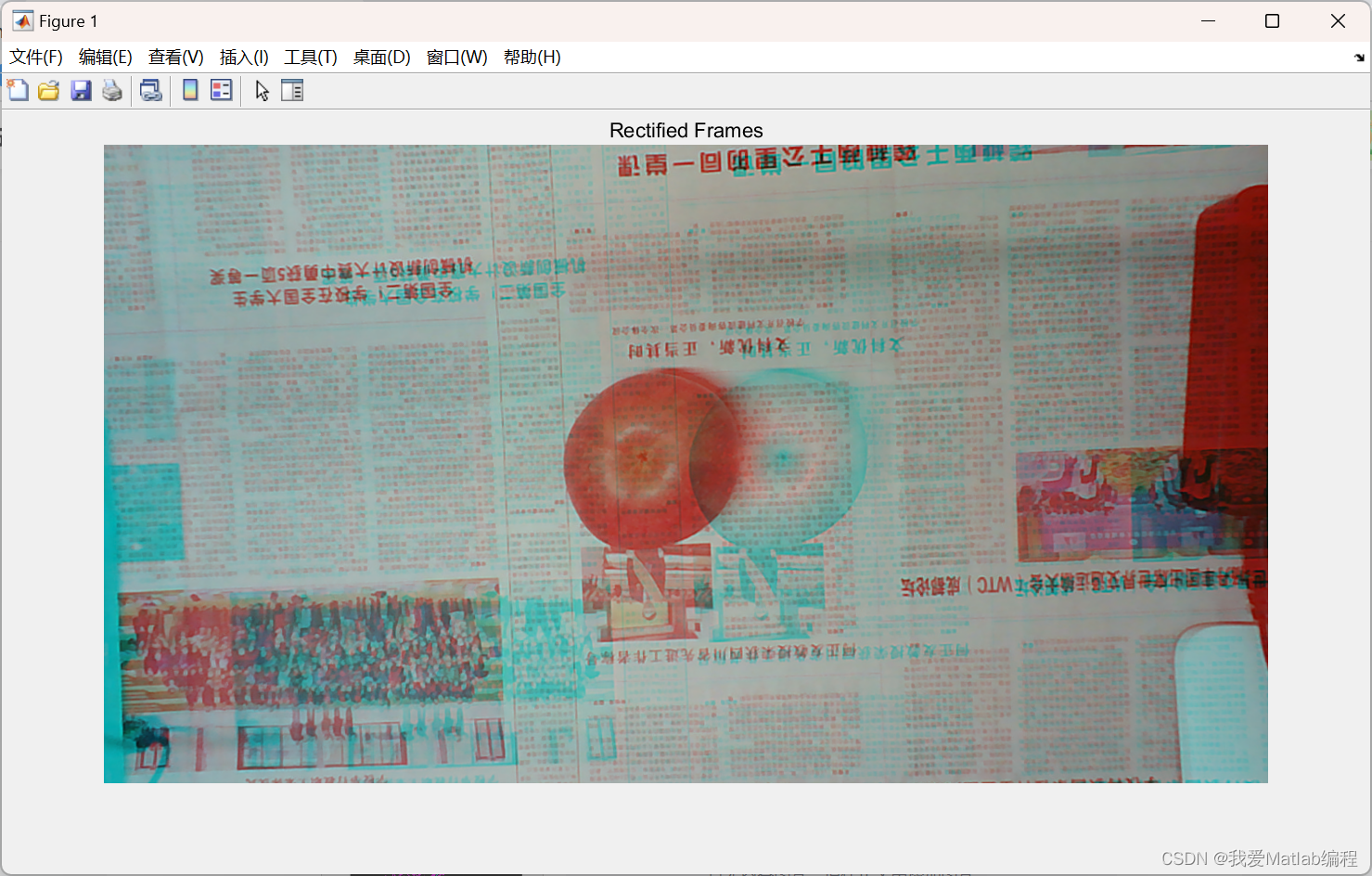
figure;
imshow(stereoAnaglyph(frameLeftRect, frameRightRect));
title('Rectified Frames');
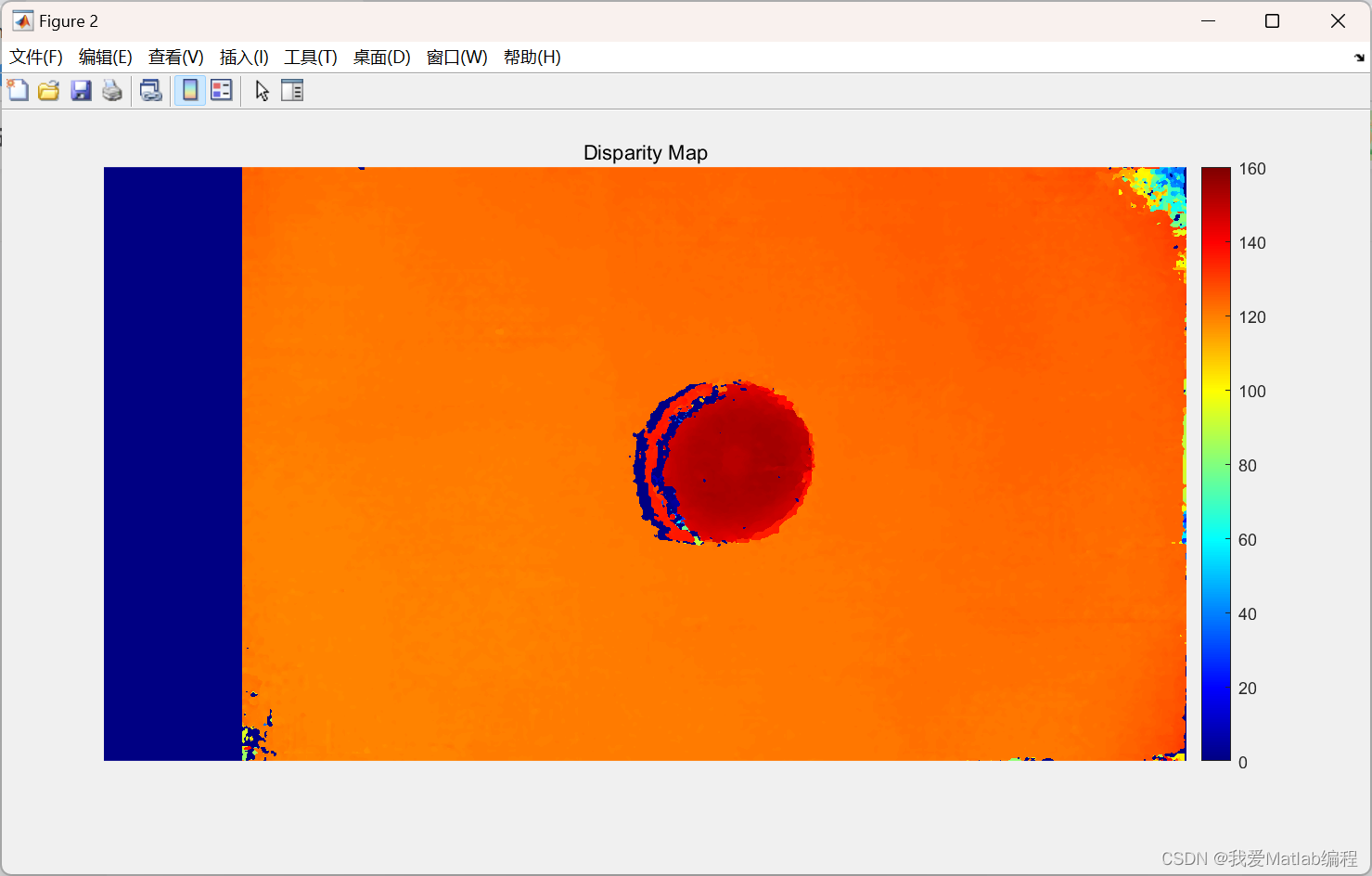
%% 视差计算
frameLeftGray = rgb2gray(frameLeftRect);
frameRightGray = rgb2gray(frameRightRect);
DisparityRange = [0, 160];
disparityMap = disparity(frameLeftGray, frameRightGray, 'Method','SemiGlobal','DisparityRange',DisparityRange,'BlockSize',5,'ContrastThreshold', 0.5,'UniquenessThreshold',0);
figure;
imshow(disparityMap, DisparityRange);
title('Disparity Map');
colormap jet
colorbar
%% 三维重建
points3D = reconstructScene(disparityMap, stereoParams);
% 单位为mm
points3D = points3D(:, 400:1000, :);
ptCloud = pointCloud(points3D);
figure;
pcshow(ptCloud);
% title('Original Data');
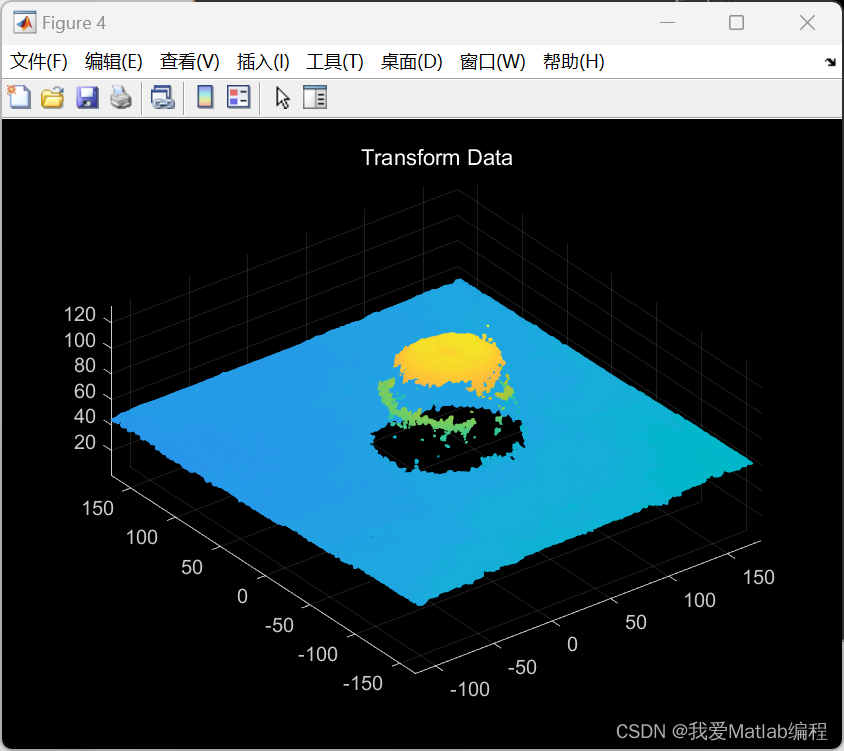
%% 空间位置变换
% 将有序点云变化为无序点云
ptCloudA= removeInvalidPoints(ptCloud);
% 坐标转换
Temp(:, 1) = ptCloudA.Location(:, 1);
Temp(:, 2) = ptCloudA.Location(:, 2);
Temp(:, 3) = -ptCloudA.Location(:, 3) + 400;
% 去除位置不合理的点
[i, j]=find(Temp(:, 3) < 0 | Temp(:, 3) > 500);
Temp(i, :) = [];
ptCloudB = pointCloud(Temp);
figure;
pcshow(ptCloudB);
title('Transform Data');
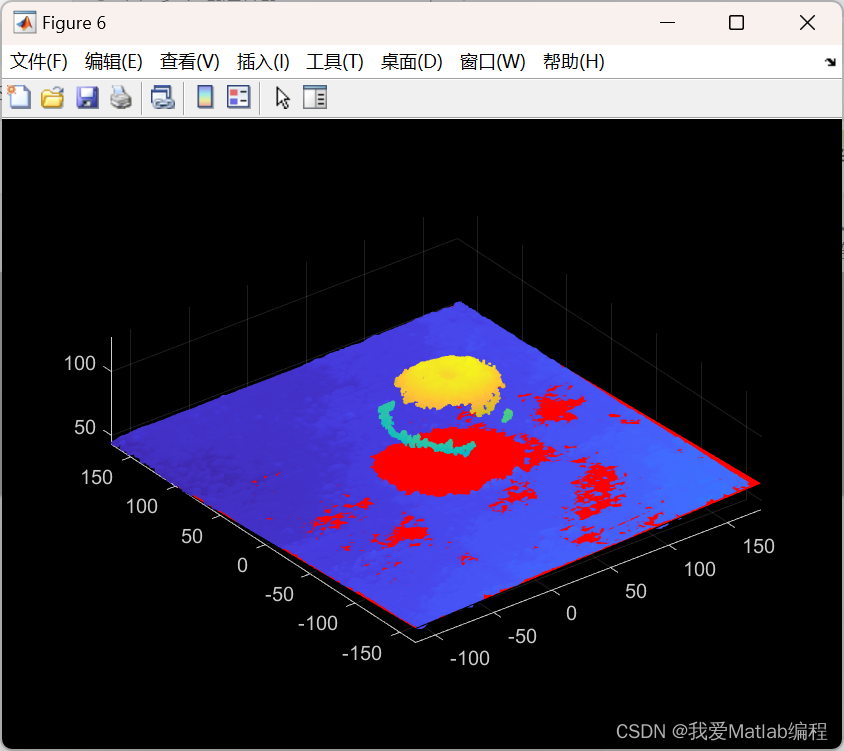
%% 去噪
% Threshold为离群值阈值,阈值为与选定点到邻居点的距离值的一个标准差,大于指定的阈值,则认为该点是异常值。
ptCloudC = pcdenoise(ptCloudB, 'NumNeighbors', 100, 'Threshold', 1); %1~6此实验Threshold=1,第7次Threshold=10
figure;
pcshow(ptCloudC);
% title('Denoised Data');
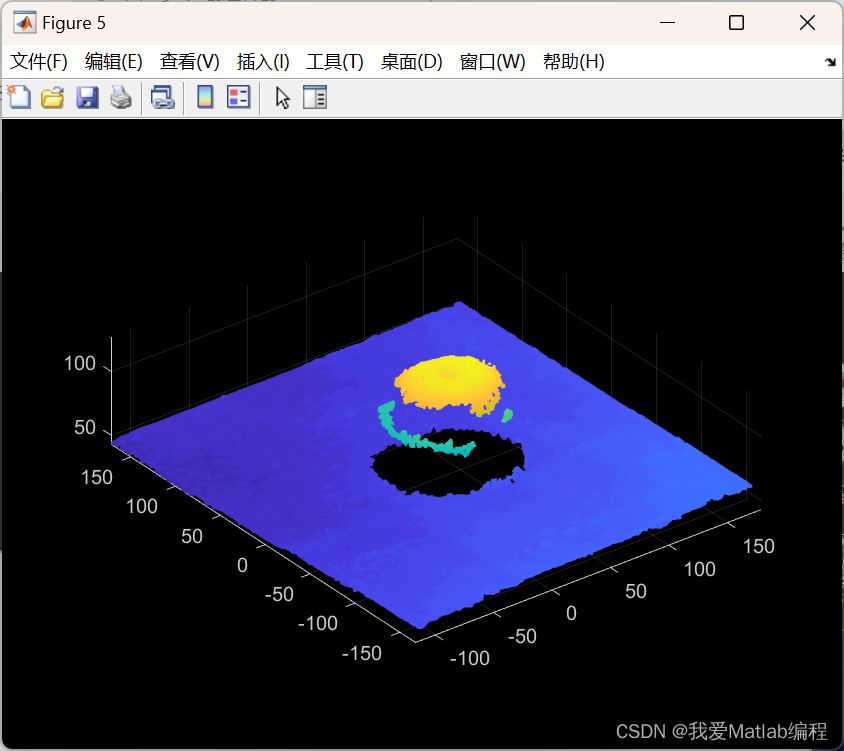
%% 点云分割
% maxDistance:从一个内点到平面标量值的最大距离
maxDistance = 10;
referenceVector = [0, 0, 1];
% 拟合平面的法线向量和参考方向之间的最大绝对角距离,以度为单位指定为标量值。
maxAngularDistance = 5;
[model, inlierIndices, outlierIndices] = pcfitplane(ptCloudC, maxDistance, referenceVector, maxAngularDistance);
ptCloudPlane = select(ptCloudC, inlierIndices);
ptCloudD = select(ptCloudC, outlierIndices);
figure;
pcshow(ptCloudC);
% title('Splitting1 Data');
hold on
plot(model);
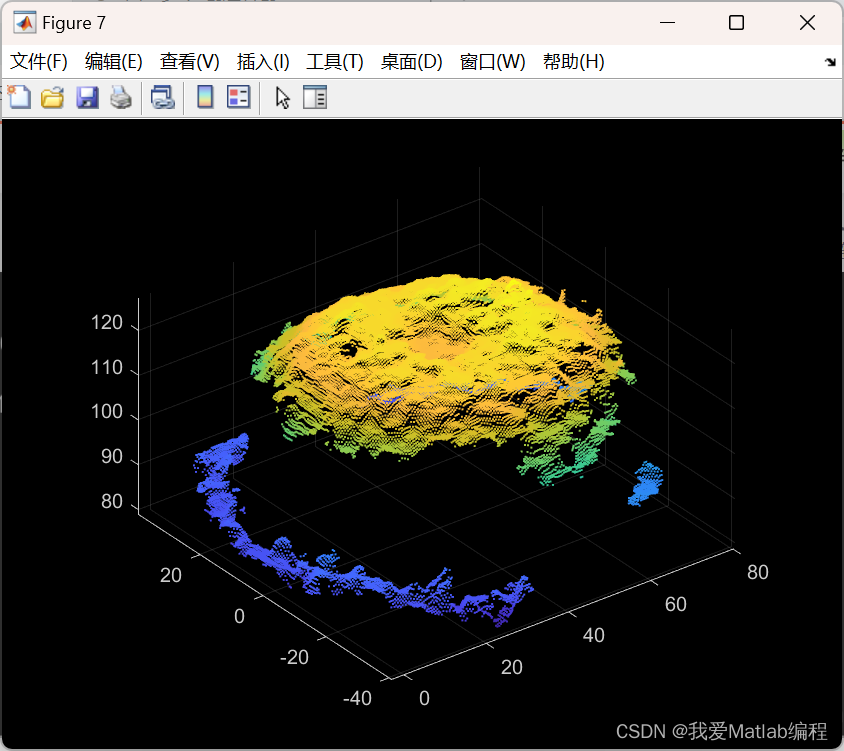
figure;
pcshow(ptCloudD);
% title('Part1 Data');
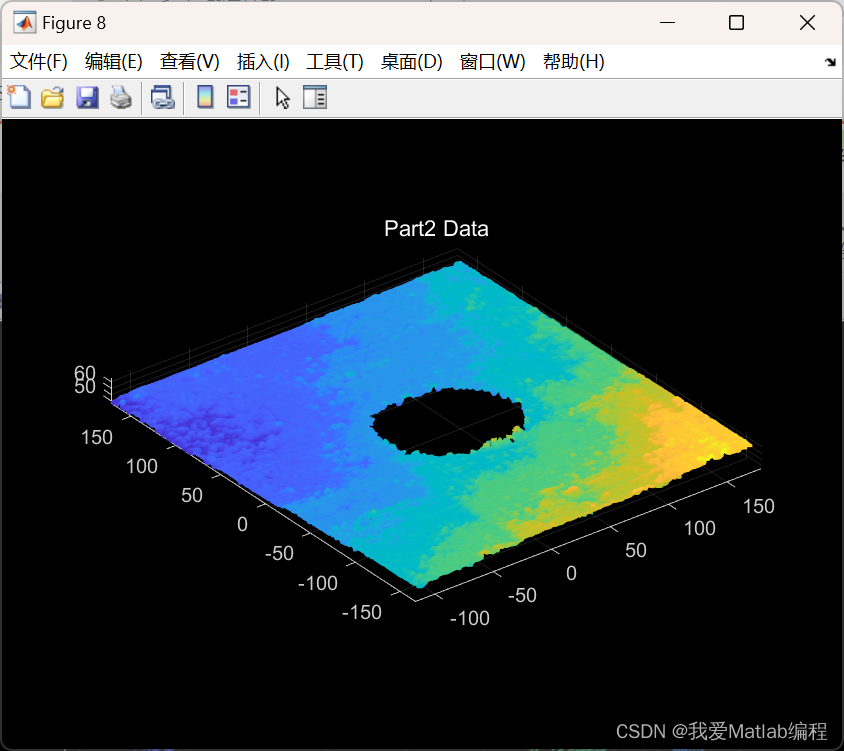
figure;
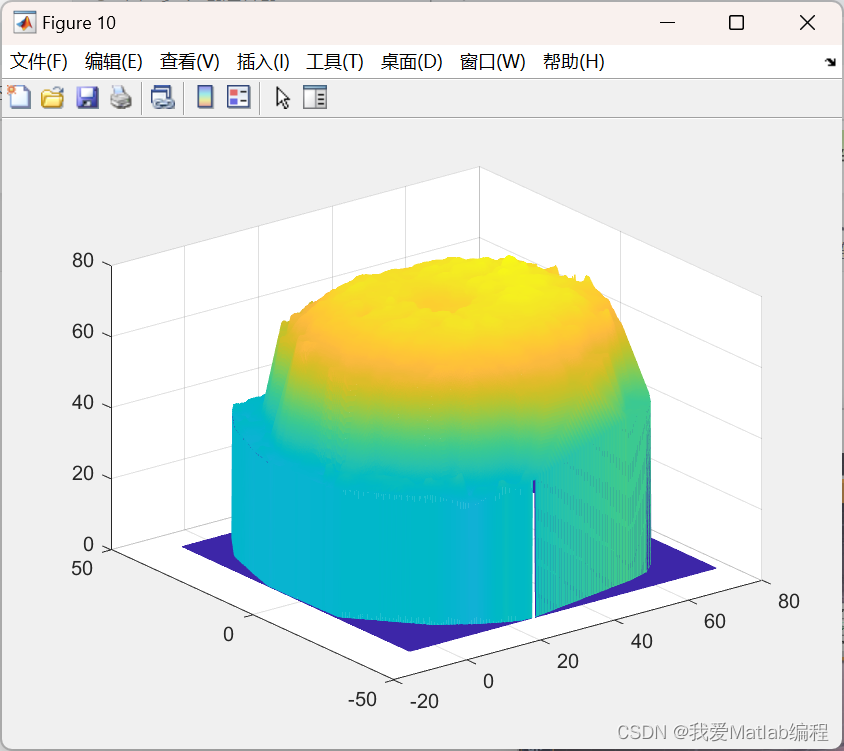
pcshow(ptCloudPlane);
title('Part2 Data');
%% 空间位置校正
ptCloudE = pcTransform(ptCloudD, model);
figure;
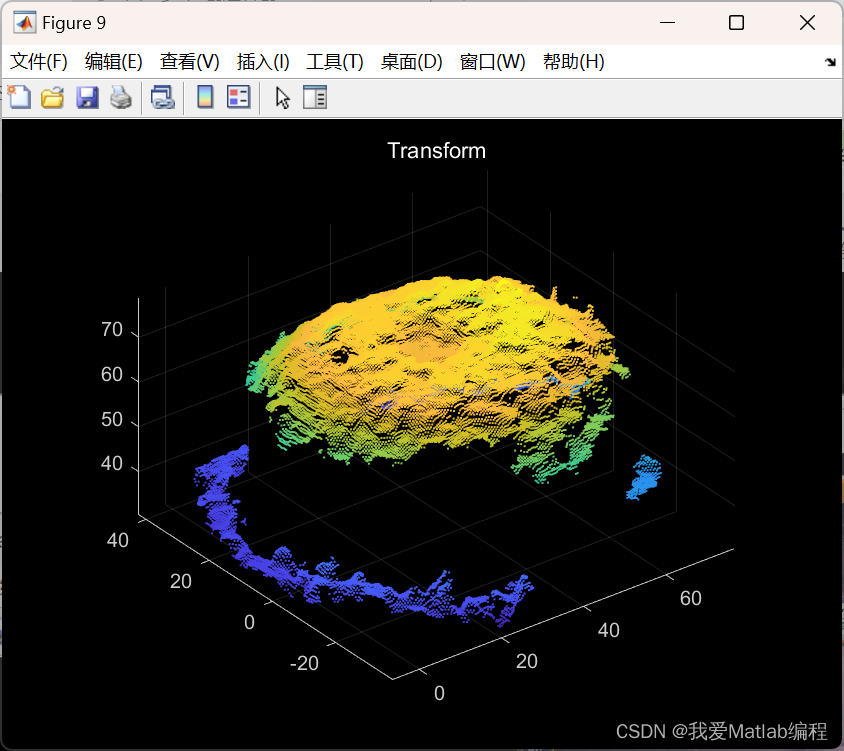
pcshow(ptCloudE);
title('Transform');
🎉3 参考文献
[1]隋婧,金伟其.双目立体视觉技术的实现及其进展[J].电子技术应用,2004(10):4-6+12.
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。






















 2193
2193











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








