GITHUB HUGGING FACE MODELSCOPE DEMO DISCORD
简介
在 Qwen2 发布后的过去三个月里,许多开发者基于 Qwen2 语言模型构建了新的模型,并为我们提供了宝贵的反馈。在这段时间里,我们专注于创建更智能、更博学的语言模型。今天,我们很高兴地向大家介绍 Qwen 家族的最新成员:Qwen2.5。
我们将要宣布的可能是历史上最大的开源发布!让我们开始这场盛会吧!
我们的最新发布包括了语言模型 Qwen2.5,以及专门针对编程的 Qwen2.5-Coder 和数学的 Qwen2.5-Math 模型。所有开放权重的模型都是稠密的、decoder-only的语言模型,提供多种不同规模的版本,包括:
- Qwen2.5: 0.5B, 1.5B, 3B, 7B, 14B, 32B, 以及72B;
- Qwen2.5-Coder: 1.5B, 7B, 以及即将推出的32B;
- Qwen2.5-Math: 1.5B, 7B, 以及72B。
除了3B和72B的版本外,我们所有的开源模型都采用了 Apache 2.0 许可证。您可以在相应的 Hugging Face 仓库中找到许可证文件。除此之外,我们还通过 Model Studio 提供了旗舰语言模型 Qwen-Plus 和 Qwen-Turbo 的 API,诚邀您来体验和使用!此外,我们还开源了相比上个月发布的版本有性能提升的 Qwen2-VL-72B。
如需了解更多关于 Qwen2.5、Qwen2.5-Coder 和 Qwen2.5-Math 的详细信息,请随时访问以下链接:
Qwen2.5 LLM Qwen2.5-Coder Qwen2.5-Math
准备好迎接我们全面的模型系列所带来的无限可能吧!我们非常高兴能够与您分享这些前沿模型,并期待看到您使用它们所取得的非凡成就!
要点总结
就 Qwen2.5 语言模型而言,所有模型都在我们最新的大规模数据集上进行了预训练,该数据集包含多达 18T tokens。相较于 Qwen2,Qwen2.5 获得了显著更多的知识(MMLU:85+),并在编程能力(HumanEval 85+)和数学能力(MATH 80+)方面有了大幅提升。此外,新模型在指令执行、生成长文本(超过 8K 标记)、理解结构化数据(例如表格)以及生成结构化输出特别是 JSON 方面取得了显著改进。 Qwen2.5 模型总体上对各种system prompt更具适应性,增强了角色扮演实现和聊天机器人的条件设置功能。与 Qwen2 类似,Qwen2.5 语言模型支持高达 128K tokens,并能生成最多 8K tokens的内容。它们同样保持了对包括中文、英文、法文、西班牙文、葡萄牙文、德文、意大利文、俄文、日文、韩文、越南文、泰文、阿拉伯文等 29 种以上语言的支持。 我们在下表中提供了有关模型的基本信息。
专业领域的专家语言模型,即用于编程的 Qwen2.5-Coder 和用于数学的 Qwen2.5-Math,相比其前身 CodeQwen1.5 和 Qwen2-Math 有了实质性的改进。 具体来说,Qwen2.5-Coder 在包含 5.5 T tokens 编程相关数据上进行了训练,使即使较小的编程专用模型也能在编程评估基准测试中表现出媲美大型语言模型的竞争力。 同时,Qwen2.5-Math 支持 中文 和 英文,并整合了多种推理方法,包括CoT(Chain of Thought)、PoT(Program of Thought)和 TIR(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)。

API
除了我们的开源模型之外,我们还通过 API 服务提供了更多的模型。您可以访问 阿里云百炼平台 获取更多详情,包括定价信息。关于 API 模型的性能,请参阅接下来的模型性能部分。
| 模型 | 模型名称 | 描述 | 定价 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen-Plus | qwen-plus-latest, qwen-plus-0919 | Qwen2.5 的旗舰模型,在广泛的任务中实现了顶级性能,适用于需要高级推理和深刻理解的复杂任务。 | 0.0008 /0.002 |
| Qwen-Turbo | qwen-turbo-latest, qwen-turbo-0919 | Qwen2.5 的均衡模型,提供快速且准确度高的响应,非常适合实时应用。 | 0.0003 /0.0006 |
| Qwen-VL-Max | qwen-vl-max-latest, qwen-vl-max-0919 | Qwen VL 的旗舰模型, 具有优秀的图像理解和视频推理能力,可以更好地识别图片中的多语言文字和手写体的文字。 | 0.02 / 0.02 |
对于每个模型,我们提供两个不同的模型名称。第一个名称通常是带有最新模型的相对稳定的服务。然而,为了确保服务的稳定性,我们通常首先在以 -latest 结尾的模型名称上部署我们的最新模型,并且还有一个以日期(如 -0919)结尾的快照版本。在定价方面,我们提供输入和输出标记的价格(¥ / 千 tokens)
这些模型针对不同的应用场景进行了优化,允许您选择最适合您特定需求的模型。无论您需要顶级性能、快速响应时间,还是两者之间的平衡,我们的 API 服务都能满足您的需求。
模型性能
Qwen2.5
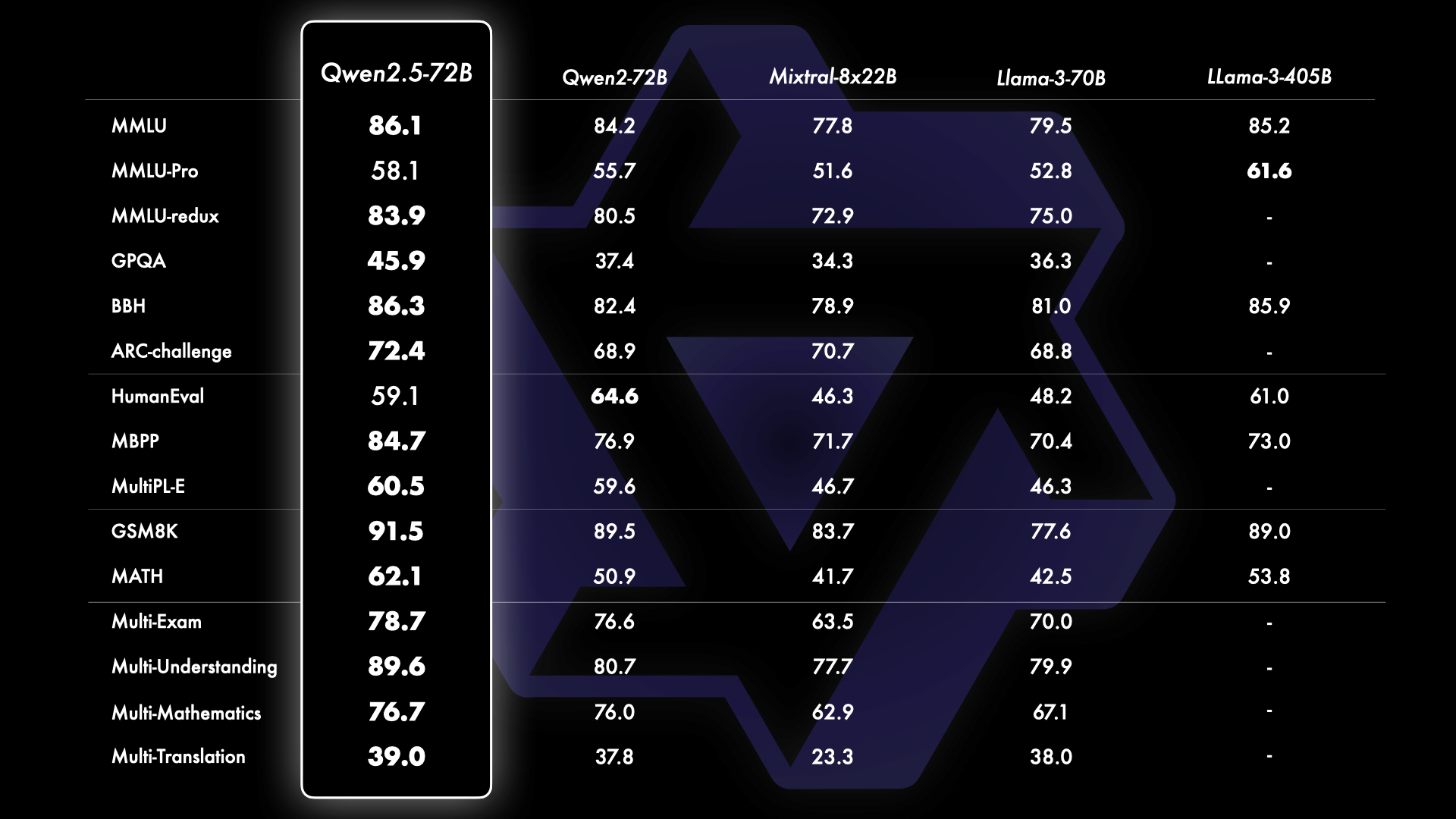
为了展示 Qwen2.5 的能力,我们用我们最大的开源模型 Qwen2.5-72B —— 一个拥有 720 亿参数的稠密 decoder-only 语言模型——与领先的开源模型如 Llama-3.1-70B 和 Mistral-Large-V2进行了基准测试。我们在多个基准测试中展示了经过指令调优的版本的综合结果,评估了模型的能力和人类偏好。
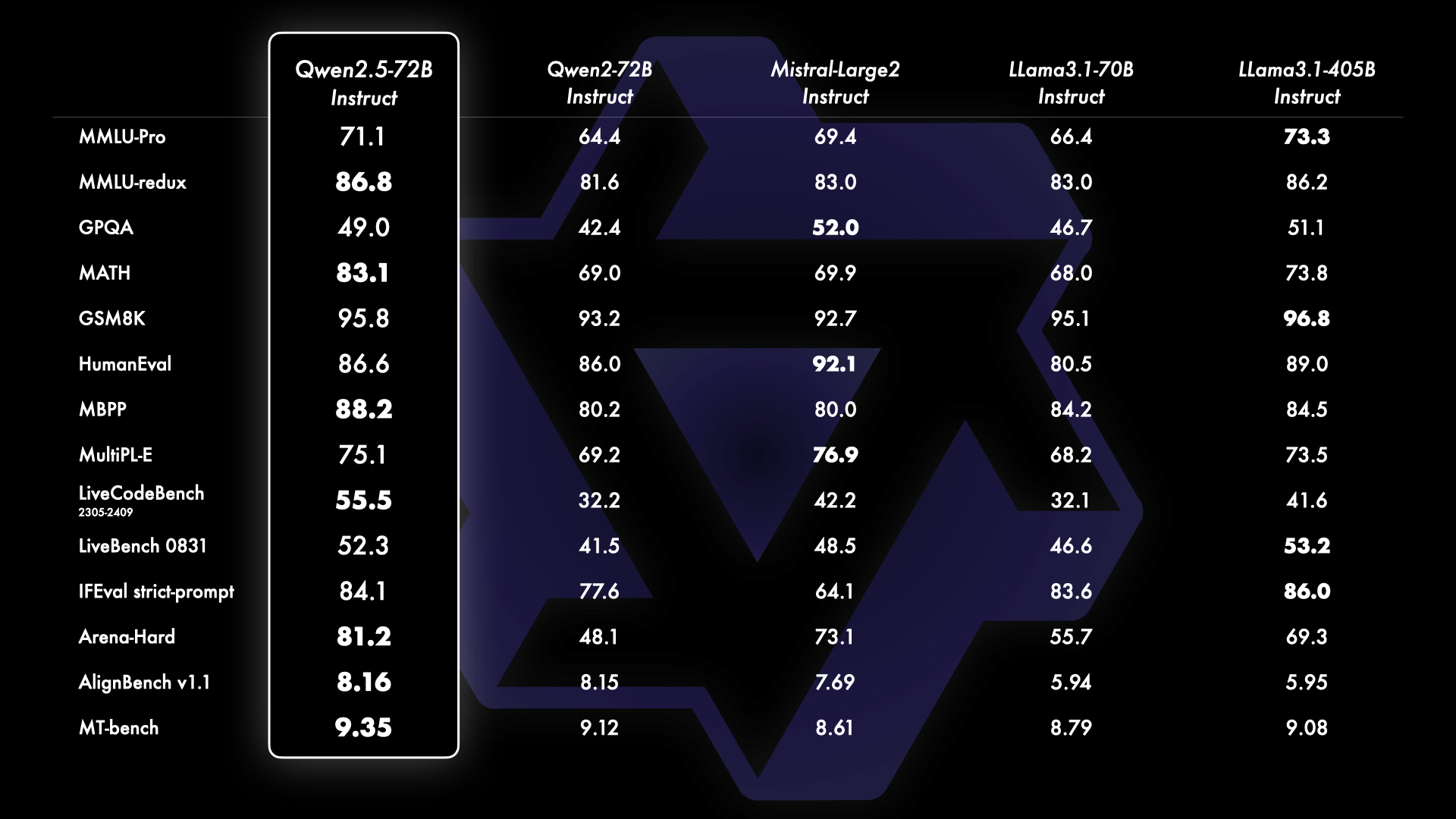
除了指令微调的模型之外,我们还发现,我们的旗舰开源模型 Qwen2.5-72B 的基础语言模型性能达到了顶级水准,即便是在与 Llama-3-405B 这样更大的模型对比时也是如此。
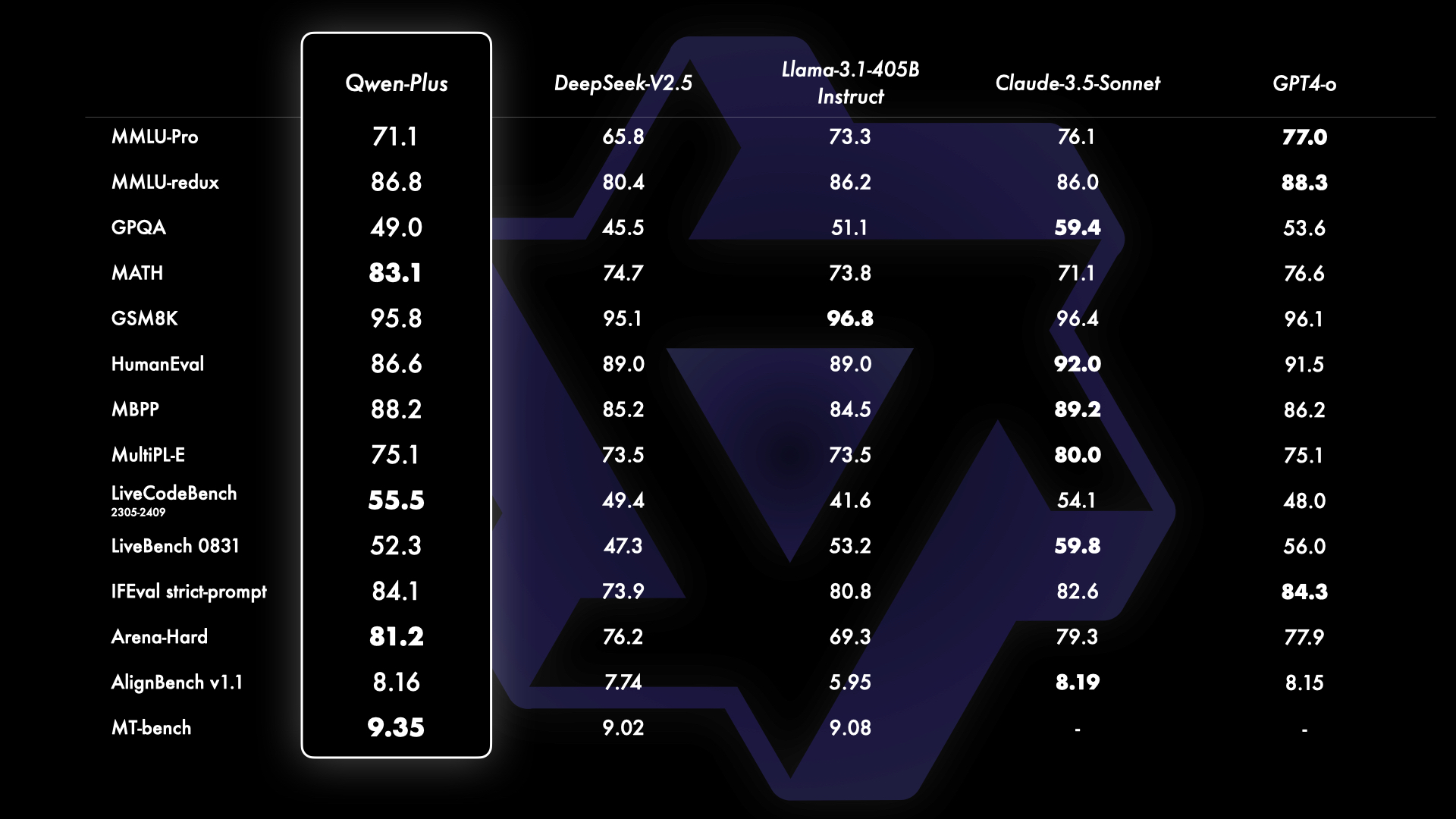
此外,我们将基于 API 的模型 Qwen-Plus 与领先的专有和开源模型进行了对比,包括 GPT4-o、Claude-3.5-Sonnet、Llama-3.1-405B 和 DeepSeek-V2.5。这一对比展示了 Qwen-Plus 在当前大型语言模型领域中的竞争地位。结果显示,Qwen-Plus 显著优于 DeepSeek-V2.5,并且在与 Llama-3.1-405B 的竞争中表现出了竞争力,尽管在某些方面仍不及 GPT4-o 和 Claude-3.5-Sonnet。 这次基准测试不仅突显了 Qwen-Plus 的优势,也指出了未来需要改进的地方,进一步强化了我们在大型语言模型领域持续改进和创新的承诺。
Qwen2.5-14B 和 Qwen2.5-32B
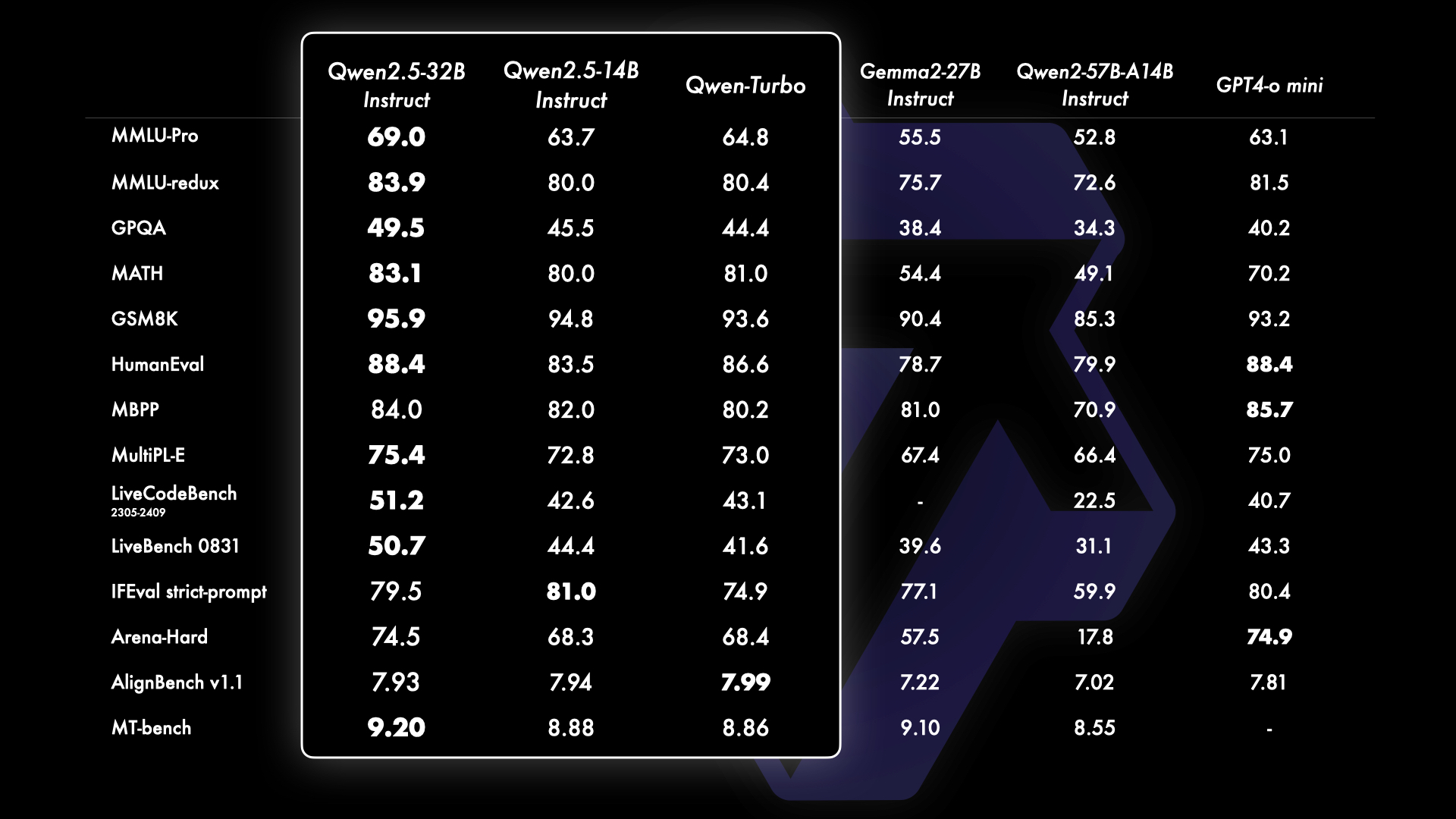
Qwen2.5 的一个重要更新是重新引入了我们的 140 亿参数和 320 亿参数模型,即 Qwen2.5-14B 和 Qwen2.5-32B。这些模型在多样化的任务中超越了同等规模或更大规模的基线模型,例如 Phi-3.5-MoE-Instruct 和 Gemma2-27B-IT。 它们在模型大小和能力之间达到了最佳平衡,提供了匹配甚至超过一些较大模型的性能。此外,我们的基于 API 的模型 Qwen2.5-Turbo 相比这两个开源模型提供了极具竞争力的性能,同时提供了成本效益高且快速的服务。
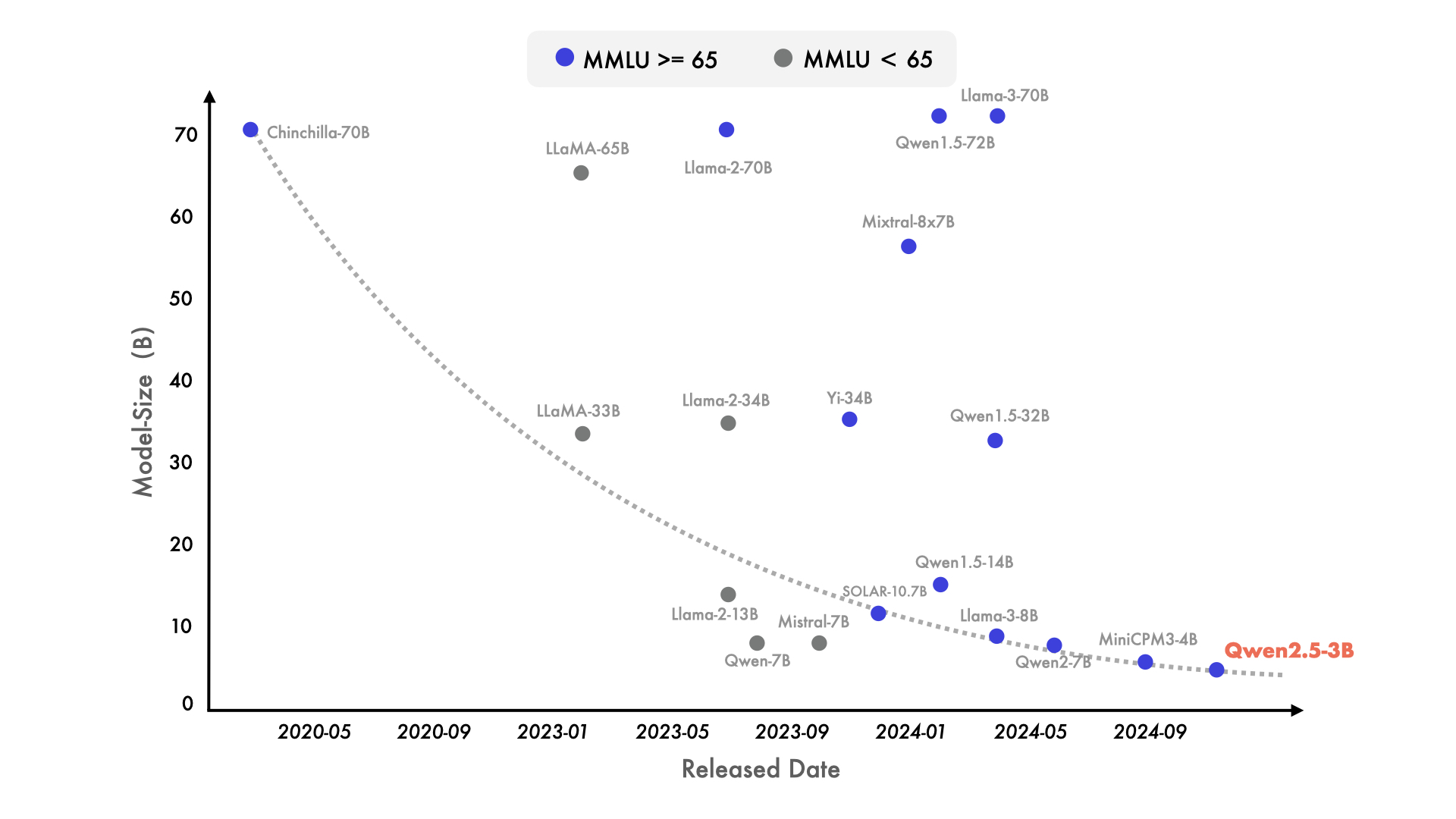
近来也出现了明显的转向小型语言模型(SLMs)的趋势。尽管历史上小型语言模型(SLMs)的表现一直落后于大型语言模型(LLMs),但二者之间的性能差距正在迅速缩小。值得注意的是,即使是只有大约 30 亿参数的模型现在也能取得高度竞争力的结果。附带的图表显示了一个重要的趋势:在 MMLU 中得分超过 65 的新型模型正变得越来越小,这凸显了语言模型的知识密度增长速度加快。特别值得一提的是,我们的 Qwen2.5-3B 成为这一趋势的一个典型例子,它仅凭约 30 亿参数就实现了令人印象深刻的性能,展示了其相对于前辈模型的高效性和能力。
除了在基准评估中取得的显著增强外,我们还改进了我们的后训练方法。我们的四个主要更新包括支持最长可达 8K 标记的长文本生成,大幅提升了对结构化数据的理解能力,生成结构化输出(尤其是 JSON 格式)更加可靠,并且在多样化的系统提示下的表现得到了加强,这有助于有效进行角色扮演。请查阅 LLM 博客了解如何利用这些功能的详细信息。
Qwen2.5-Coder
自从推出 CodeQwen1.5 以来,我们吸引了大量依赖该模型完成各种编程任务的用户,这些任务包括调试、回答编程相关的问题以及提供代码建议。我们最新的迭代版本 Qwen2.5-Coder 特别为编程应用而设计。在本节中,我们展示了 Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct 的性能结果,并将其与领先的开源模型进行了基准测试,其中包括那些参数量大得多的模型。
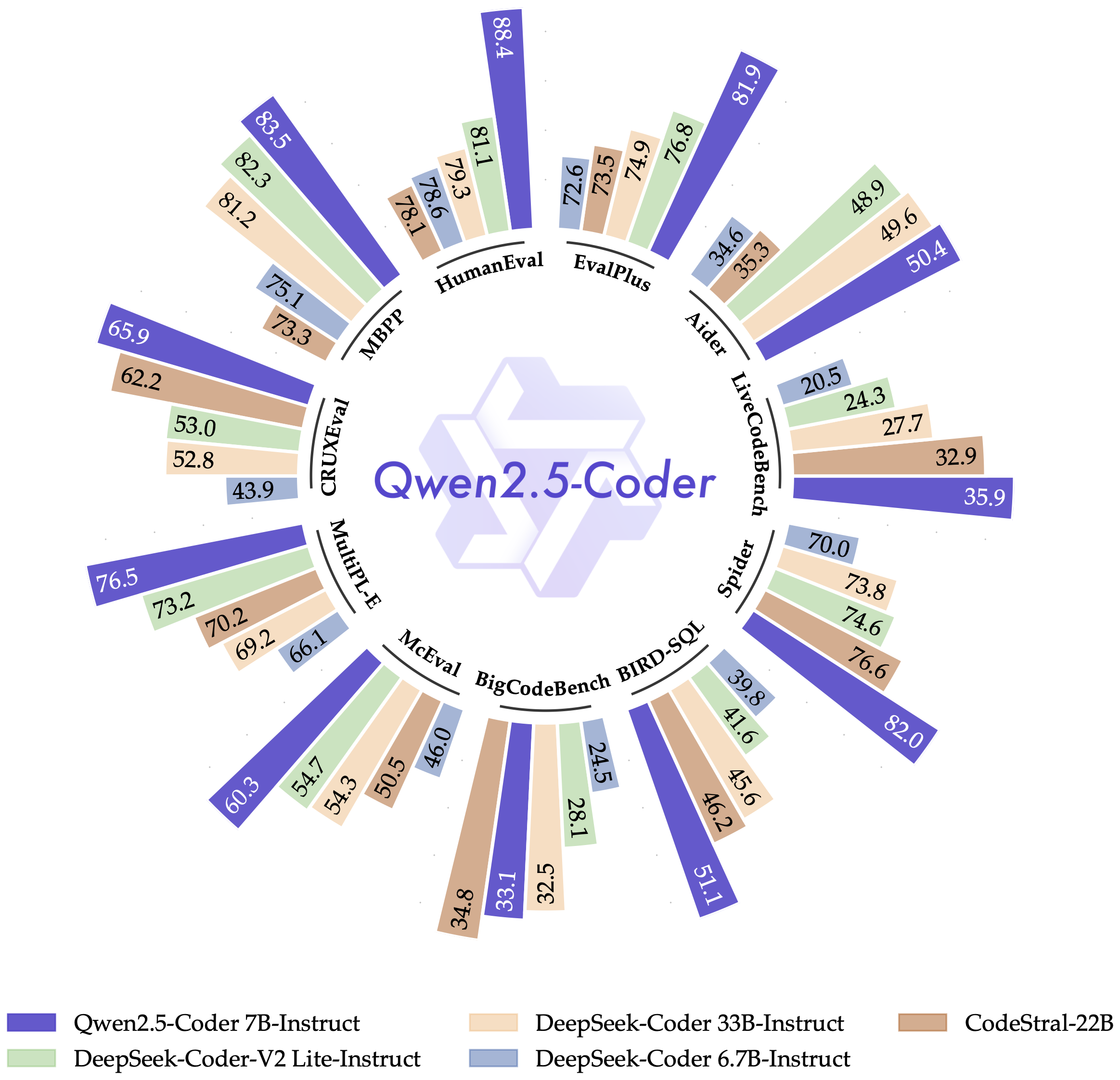
我们认为 Qwen2.5-Coder 是您个人编程助手的优秀选择。尽管它的体积较小,但在多种编程语言和任务中,它的表现超过了众多大型语言模型,展现了其卓越的编程能力。
Qwen2.5-Math
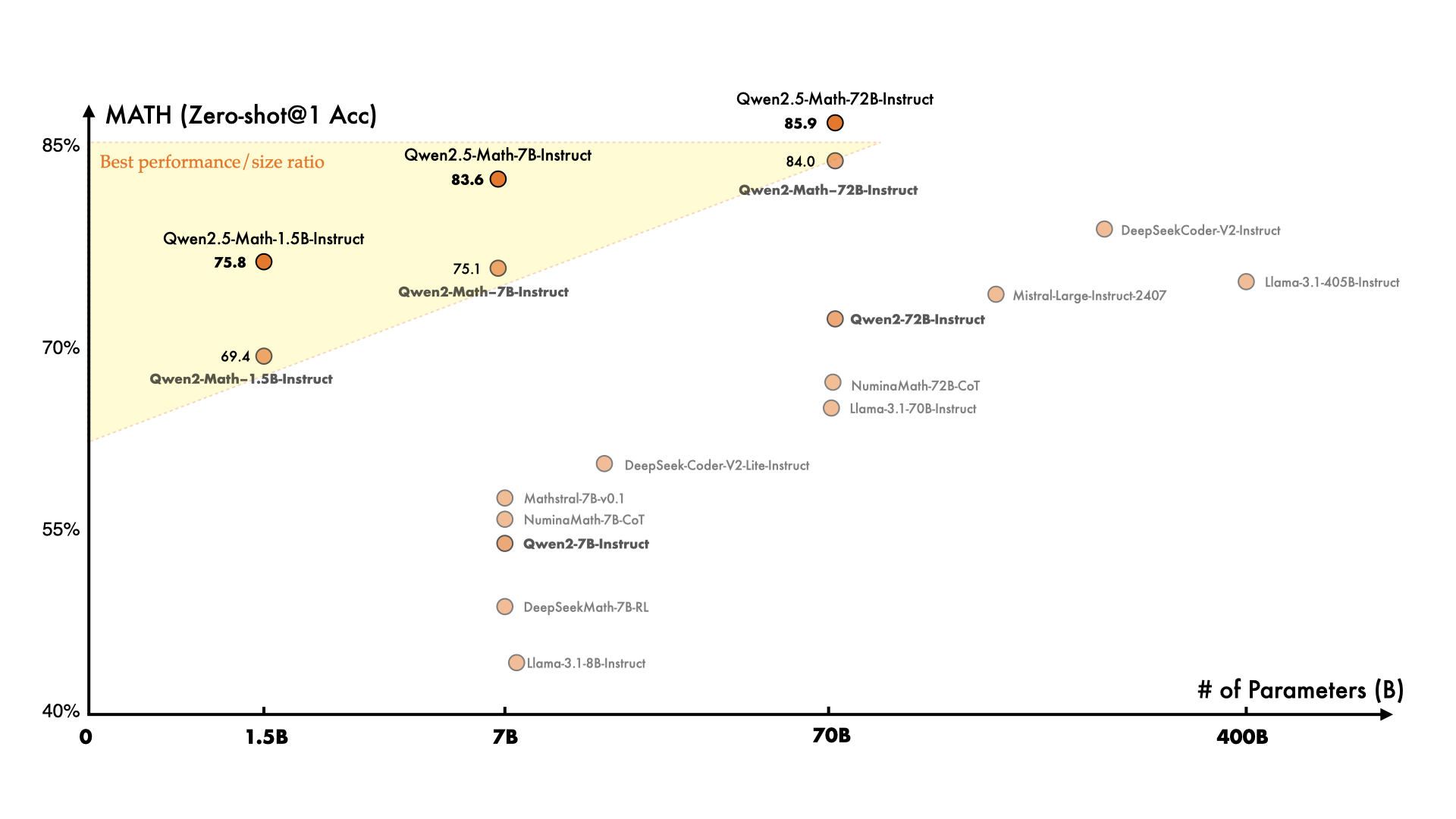
在数学专用语言模型方面,我们上个月发布了首批模型 Qwen2-Math,而这一次,相比于 Qwen2-Math,Qwen2.5-Math 在更大规模的数学相关数据上进行了预训练,包括由 Qwen2-Math 生成的合成数据。 此外,这一次我们增加了对中文的支持,并通过赋予其进行 CoT(Chain of Thought)、PoT(Program of Thought)和 TIR(Tool-Integrated Reasoning)的能力来加强其推理能力。 Qwen2.5-Math-72B-Instruct 的整体性能超越了 Qwen2-Math-72B-Instruct 和 GPT4-o,甚至是非常小的专业模型如 Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B-Instruct 也能在与大型语言模型的竞争中取得高度竞争力的表现。
使用 Qwen2.5
最简单的方法使用过阿里云百炼平台提供的通义千问 API 来使用 阿里云百炼平台,百炼平台已经兼容 OpenAI 接口规范。
from openai import OpenAI
import os
client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("YOUR_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
)
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="qwen-plus-latest",
messages=[
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Tell me something about large language models.'}
]
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)
通过 Hugging Face Transformers 库来使用,正如在model card中演示的那样:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=512
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
要使用 vLLM 运行 Qwen2.5 并部署一个与 OpenAI API 兼容的服务,可以运行如下命令:
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
如果你使用的是vllm>=0.5.3,可以使用 vllm serve 命令。然后你就可以通过 curl 来与 Qwen2.5 进行对话了:
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me something about large language models."}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"top_p": 0.8,
"repetition_penalty": 1.05,
"max_tokens": 512
}'
此外,Qwen2.5 支持 vLLM 内置的工具调用功能。此功能要求 vllm>=0.6。如果您想启用此功能,请使用以下命令启动 vLLM 的 OpenAI API 兼容服务:
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct --enable-auto-tool-choice --tool-call-parser hermes
之后你可以像使用 GPT’s tool calling 那样来使用它。
Qwen2.5 同样支持 Ollama’s tool calling.你可以通过启动Ollama的OpenAI兼容服务,并以与使用GPT的工具调用相同的方式来使用它。
Qwen2.5 的聊天模板中也包含了一个工具调用模板,这意味着你可以使用 Hugging Face transformers’ tool calling support.
vLLM / Ollama / Transformers 的工具调用支持使用受 Nous’ Hermes 的格式启发的工具调用模板。 此前Qwen-Agent 提供了使用Qwen2自己的工具调用模板的工具调用支持(这较难与vllm和Ollama集成),而 Qwen2.5 既保持了与 Qwen2 模板和 Qwen-Agent 的兼容性。
Qwen 的朋友们
💗 Qwen系列取得的成功离不开开源社区的支持!因此,衷心感谢这些老朋友和新朋友们的支持:
-
Finetuning: ChatLearn, Llama-Factory, Axolotl, Firefly, Swift, XTuner, Unsloth, Liger Kernel
-
Quantization: AutoGPTQ, AutoAWQ, Neural Compressor
-
Deployment: vLLM, SGL, SkyPilot, TensorRT-LLM, OpenVino, TGI
-
API Platforms: Together, Fireworks, OpenRouter
-
Agent and RAG Frameworks: Dify, LlamaIndex, CrewAI
-
Evaluation: LMSys, OpenCompass, Open LLM Leaderboard
我们要向所有为 Qwen 做出贡献的团队和个人表示衷心的感谢,即使他们没有被特别提及。你们的支持是无价的,我们热忱邀请更多的朋友加入我们这一激动人心的旅程。共同合作,我们可以推动开源 AI 社区的研究与发展,使其比以往任何时候都更加强大和充满创新。
下一步是什么?
虽然我们很高兴能够同时推出众多高质量的模型,但我们认识到仍然存在重大的挑战。近期的发布表明了我们在语言、视觉-语言和音频-语言领域开发强大基础模型的决心。然而,将这些不同的模态整合到单一模型中以实现三种信息的无缝端到端处理仍然是至关重要的。此外,尽管我们在通过数据扩展来增强推理能力方面已经取得了进展,但最近在强化学习(例如,o1)方面的进步也激励着我们,我们致力于通过扩展推理计算来进一步提高模型的推理能力。我们期待着很快向大家介绍下一代模型!敬请关注更多精彩进展!
Citation
我们即将发布 Qwen2.5 的技术报告。在报告发布之前,您可以引用我们的 Qwen2 论文以及这篇博客。
@misc{qwen2.5,
title = {Qwen2.5: A Party of Foundation Models},
url = {https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen2.5/},
author = {Qwen Team},
month = {September},
year = {2024}
}
@article{qwen2,
title={Qwen2 technical report},
author={Yang, An and Yang, Baosong and Hui, Binyuan and Zheng, Bo and Yu, Bowen and Zhou, Chang and Li, Chengpeng and Li, Chengyuan and Liu, Dayiheng and Huang, Fei and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.10671},
year={2024}
}Qwen2.5: A Party of Foundation Models!
September 19, 2024 · 9 min · 1738 words · Qwen Team | Translations:
GITHUB HUGGING FACE MODELSCOPE DEMO DISCORD
Introduction
In the past three months since Qwen2’s release, numerous developers have built new models on the Qwen2 language models, providing us with valuable feedback. During this period, we have focused on creating smarter and more knowledgeable language models. Today, we are excited to introduce the latest addition to the Qwen family: Qwen2.5. We are announcing what might be the largest opensource release in history! Let’s get the party started!
Our latest release features the LLMs Qwen2.5, along with specialized models for coding, Qwen2.5-Coder, and mathematics, Qwen2.5-Math. All open-weight models are dense, decoder-only language models, available in various sizes, including:
- Qwen2.5: 0.5B, 1.5B, 3B, 7B, 14B, 32B, and 72B
- Qwen2.5-Coder: 1.5B, 7B, and 32B on the way
- Qwen2.5-Math: 1.5B, 7B, and 72B.
All our open-source models, except for the 3B and 72B variants, are licensed under Apache 2.0. You can find the license files in the respective Hugging Face repositories. In addition to these models, we offer APIs for our flagship language models: Qwen-Plus and Qwen-Turbo through Model Studio, and we encourage you to explore them! Furthermore, we have also open-sourced the Qwen2-VL-72B, which features performance enhancements compared to last month’s release.
For more details about Qwen2.5, Qwen2.5-Coder, and Qwen2.5-Math, feel free to visit the following links:
Qwen2.5 LLM Qwen2.5-Coder Qwen2.5-Math
Get ready to unlock a world of possibilities with our extensive lineup of models! We’re excited to share these cutting-edge models with you, and we can’t wait to see the incredible things you’ll achieve with them!
Takeaways
In terms of Qwen2.5, the language models, all models are pretrained on our latest large-scale dataset, encompassing up to 18 trillion tokens. Compared to Qwen2, Qwen2.5 has acquired significantly more knowledge (MMLU: 85+) and has greatly improved capabilities in coding (HumanEval 85+) and mathematics (MATH 80+). Additionally, the new models achieve significant improvements in instruction following, generating long texts (over 8K tokens), understanding structured data (e.g, tables), and generating structured outputs especially JSON. Qwen2.5 models are generally more resilient to the diversity of system prompts, enhancing role-play implementation and condition-setting for chatbots. Like Qwen2, the Qwen2.5 language models support up to 128K tokens and can generate up to 8K tokens. They also maintain multilingual support for over 29 languages, including Chinese, English, French, Spanish, Portuguese, German, Italian, Russian, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, Thai, Arabic, and more. Below, we provide basic information about the models and details of the supported languages.
The specialized expert language models, namely Qwen2.5-Coder for coding and Qwen2.5-Math for mathematics, have undergone substantial enhancements compared to their predecessors, CodeQwen1.5 and Qwen2-Math. Specifically, Qwen2.5-Coder has been trained on 5.5 trillion tokens of code-related data, enabling even smaller coding-specific models to deliver competitive performance against larger language models on coding evaluation benchmarks. Meanwhile, Qwen2.5-Math supports both Chinese and English and incorporates various reasoning methods, including Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Program-of-Thought (PoT), and Tool-Integrated Reasoning (TIR).

Performance
Qwen2.5
To showcase Qwen2.5’s capabilities, we benchmark our largest open-source model, Qwen2.5-72B - a 72B-parameter dense decoder-only language model - against leading open-source models like Llama-3.1-70B and Mistral-Large-V2. We present comprehensive results from instruction-tuned versions across various benchmarks, evaluating both model capabilities and human preferences.

Besides the instruction-tuned language models, we figure out that the base language model of our flagship opensource model Qwen2.5-72B reaches top-tier performance even against larger models like Llama-3-405B.

Furthermore, we benchmark the latest version of our API-based model, Qwen-Plus, against leading proprietary and open-source models, including GPT4-o, Claude-3.5-Sonnet, Llama-3.1-405B, and DeepSeek-V2.5. This comparison showcases Qwen-Plus’s competitive standing in the current landscape of large language models. We show that Qwen-Plus significantly outcompetes DeepSeek-V2.5 and demonstrates competitive performance against Llama-3.1-405B, while still underperforming compared to GPT4-o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet in some aspects. This benchmarking not only highlights Qwen-Plus’s strengths but also identifies areas for future improvement, reinforcing our commitment to continuous enhancement and innovation in the field of large language models.

A significant update in Qwen2.5 is the reintroduction of our 14B and 32B models, Qwen2.5-14B and Qwen2.5-32B. These models outperform baseline models of comparable or larger sizes, such as Phi-3.5-MoE-Instruct and Gemma2-27B-IT, across diverse tasks. They achieve an optimal balance between model size and capability, delivering performance that matches or exceeds some larger models. Additionally, our API-based model, Qwen-Turbo, offers highly competitive performance compared to the two open-source models, while providing a cost-effective and rapid service.

In recent times, there has been a notable shift towards small language models (SLMs). Although SLMs have historically trailed behind their larger counterparts (LLMs), the performance gap is rapidly diminishing. Remarkably, even models with just 3 billion parameters are now delivering highly competitive results. The accompanying figure illustrates a significant trend: newer models achieving scores above 65 in MMLU are increasingly smaller, underscoring the accelerated growth in knowledge density among language models. Notably, our Qwen2.5-3B stands out as a prime example, achieving impressive performance with only around 3 billion parameters, showcasing its efficiency and capability compared to its predecessors.

In addition to the notable enhancements in benchmark evaluations, we have refined our post-training methodologies. Our four key updates include support for long text generation of up to 8K tokens, significantly improved comprehension of structured data, more reliable generation of structured outputs, particularly in JSON format, and enhanced performance across diverse system prompts, which facilitates effective role-playing. Check the LLM blog for details about how to leverage these capabilities.
Qwen2.5-Coder
Since the launch of CodeQwen1.5, we have attracted numerous users who rely on this model for various coding tasks, such as debugging, answering coding-related questions, and providing code suggestions. Our latest iteration, Qwen2.5-Coder, is specifically designed for coding applications. In this section, we present the performance results of Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct, benchmarked against leading open-source models, including those with significantly larger parameter sizes.

We believe that Qwen2.5-Coder is an excellent choice as your personal coding assistant. Despite its smaller size, it outperforms many larger language models across a range of programming languages and tasks, demonstrating its exceptional coding capabilities.
Qwen2.5-Math
In terms of the math specific language models, we released the first models, Qwen2-Math, last month, and this time, compared to Qwen2-Math, Qwen2.5-Math has been pretrained larger-scale of math related data, including the synthetic data generated by Qwen2-Math. Additionally we extend the support of Chinese this time and we also strengthen its reasoning capabilities by endowing it with the abilities to perform CoT, PoT, and TIR. The general performance of Qwen2.5-Math-72B-Instruct surpasses both Qwen2-Math-72B-Instruct and GPT4-o, and even very small expert model like Qwen2.5-Math-1.5B-Instruct can achieve highly competitive performance against large language models.

Develop with Qwen2.5
The simplest way to use is through Hugging Face Transfomer as demonstrated in the model card:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=512
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
To use Qwen2.5 with vLLM, running the following command can deploy an OpenAI API compatible service:
python -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
or use vllm serve if you use vllm>=0.5.3. Then you can communicate with Qwen2.5 via curl:
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"model": "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "Tell me something about large language models."}
],
"temperature": 0.7,
"top_p": 0.8,
"repetition_penalty": 1.05,
"max_tokens": 512
}'
Furthermore, Qwen2.5 supports vllm’s built-in tool calling. This functionality requires vllm>=0.6. If you want to enable this functionality, please start vllm’s OpenAI-compatible service with:
vllm serve Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct --enable-auto-tool-choice --tool-call-parser hermes
You can then use it in the same way you use GPT’s tool calling.
Qwen2.5 also supports Ollama’s tool calling. You can use it by starting Ollama’s OpenAI-compatible service and using it in the same way you use GPT’s tool calling.
Qwen2.5’s chat template also includes a tool calling template, meaning that you can use Hugging Face transformers’ tool calling support.
The vllm / Ollama / transformers tool calling support uses a tool calling template inspired by Nous’ Hermes. Historically, Qwen-Agent provided tool calling support using Qwen2’s own tool calling template (which is harder to be integrated with vllm and Ollama), and Qwen2.5 maintains compatibility with Qwen2’s template and Qwen-Agent as well.
Friends of Qwen
💗 Qwen is nothing without its friends! So many thanks to the support of these old buddies and new friends :
-
Finetuning: Peft, ChatLearn, Llama-Factory, Axolotl, Firefly, Swift, XTuner, Unsloth, Liger Kernel
-
Quantization: AutoGPTQ, AutoAWQ, Neural Compressor
-
Deployment: vLLM, SGL, SkyPilot, TensorRT-LLM, OpenVino, TGI, Xinference
-
API Platforms: Together, Fireworks, OpenRouter, Sillicon Flow
-
Agent and RAG Frameworks: Dify, LlamaIndex, CrewAI
-
Evaluation: LMSys, OpenCompass, Open LLM Leaderboard
We would like to extend our heartfelt gratitude to the numerous teams and individuals who have contributed to Qwen, even if they haven’t been specifically mentioned. Your support is invaluable, and we warmly invite more friends to join us in this exciting journey. Together, we can enhance collaboration and drive forward the research and development of the open-source AI community, making it stronger and more innovative than ever before.
What’s Next?
While we are thrilled to launch numerous high-quality models simultaneously, we recognize that significant challenges remain. Our recent releases demonstrate our commitment to developing robust foundation models across language, vision-language, and audio-language domains. However, it is crucial to integrate these different modalities into a single model to enable seamless end-to-end processing of information across all three. Additionally, although we have made strides in enhancing reasoning capabilities through data scaling, we are inspired by the recent advancements in reinforcement learning (e.g., o1) and are dedicated to further improving our models’ reasoning abilities by scaling inference compute. We look forward to introducing you to the next generation of models soon! Stay tuned for more exciting developments!
Citation
We are going to release the technical report for Qwen2.5 very soon. Before the release, feel free to cite our Qwen2 paper as well as this blog
@misc{qwen2.5,
title = {Qwen2.5: A Party of Foundation Models},
url = {https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen2.5/},
author = {Qwen Team},
month = {September},
year = {2024}
}
@article{qwen2,
title={Qwen2 technical report},
author={Yang, An and Yang, Baosong and Hui, Binyuan and Zheng, Bo and Yu, Bowen and Zhou, Chang and Li, Chengpeng and Li, Chengyuan and Liu, Dayiheng and Huang, Fei and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.10671},
year={2024}
}

























 1051
1051

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










