点击关注,桓峰基因
桓峰基因
生物信息分析,SCI文章撰写及生物信息基础知识学习:R语言学习,perl基础编程,linux系统命令,Python遇见更好的你
108篇原创内容
公众号
桓峰基因的教程不但教您怎么使用,还会定期分析一些相关的文章,学会教程只是基础,但是如果把分析结果整合到文章里面才是目的,觉得我们这些教程还不错,并且您按照我们的教程分析出来不错的结果发了文章记得告知我们,并在文章中感谢一下我们哦!
公司英文名称:Kyoho Gene Technology (Beijing) Co.,Ltd.
如果您觉得这些确实没基础,需要专业的生信人员帮助分析,直接扫码加微信nihaoooo123,我们24小时在线!!
前两期简单介绍了 R 语言基础,比较简单粗略,然后介绍了 R 语言中表格的转换,因为现在绘图基本以及舍弃了基本绘图的方式,都会选择 ggplot2 来作图,这期SCI绘图介绍一下柱状图!
前言
柱状图一般用于,当我们都有一组分类变量以及每个类别的定量值,而我们关注的主要重点是定量值的大小时。应该在柱状图背景保留横网格线,便于比较我们关注的值。
基础参数介绍
当分类label过长时,最好选择横向柱状图,避免出现旋转label,保持文字阅读方向与图形方向的统一性。
应该注意对柱状图进行排序(大小,分类变量,分布)。
基础参数
ggplot2中柱状图的基本绘制函数有两个,如下:
geom_bar() 产生的柱状图映射是经过统计变换的(count, …prop…);
geom_col()是不经过统计变换的,代表的就是该分类变量的实际值。
柱状图使用高度来表示一个值,因此必须始终显示柱状图的底部,以产生有效的视觉比较。使用柱状图转换后的刻度时要小心。始终使用有意义的参考点作为杆的底部是很重要的。例如,对于日志转换,参考点是1。事实上,当使用对数尺度时,geom_bar()会自动将杆的底置为1。
柱状图绘制
1. 软件包安装
if (!require(ggplot2)) install.packages("ggplot2")
library(ggplot2)
2. 数据读取
data(mpg)
head(mpg)
## # A tibble: 6 x 11
## manufacturer model displ year cyl trans drv cty hwy fl class
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <int> <int> <chr> <chr>
## 1 audi a4 1.8 1999 4 auto(l5) f 18 29 p compa~
## 2 audi a4 1.8 1999 4 manual(m5) f 21 29 p compa~
## 3 audi a4 2 2008 4 manual(m6) f 20 31 p compa~
## 4 audi a4 2 2008 4 auto(av) f 21 30 p compa~
## 5 audi a4 2.8 1999 6 auto(l5) f 16 26 p compa~
## 6 audi a4 2.8 1999 6 manual(m5) f 18 26 p compa~
3. 简单柱状图
以每个x在数据集中出现的总数为y轴。
# geom_bar is designed to make it easy to create bar charts that show counts
# (or sums of weights)
ggplot(mpg, aes(class)) + geom_bar() + theme_bw()

4. 简单柱状图排序
ggplot2中一般数据和视觉元素映射是分开的,如果需要对柱状图排序,就需要对数据进行排序处理。数据的处理及转换可以参考公众号FigDraw 3. SCI 文章绘图必备 R 数据转换
library(dplyr)
library(forcats)
data_sorted <- mpg %>%
group_by(class) %>%
summarise(count = n()) %>%
mutate(class = fct_reorder(class, count))
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = data_sorted, aes(x = class, y = count), stat = "identity") +
theme_bw()
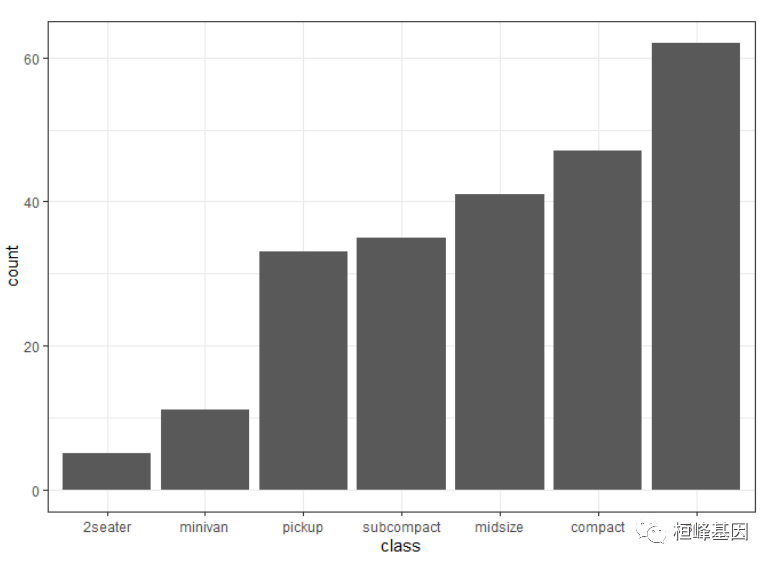
5. 外框颜色和填充颜色
参数color控制外框颜色,fill控制填充颜色。
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = data_sorted, aes(x = class, y = count), stat = "identity",
fill = "blue", colour = "red")+theme_bw()

6. 水平柱状图
当数据分组标签名字过长时,有一种方法是将label旋转,这样它们就不会互相重叠。
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = data_sorted, aes(x = class, y = count), stat = "identity",
width = 0.5, position = position_dodge(width = 0.9)) + theme(panel.grid.major.x = element_line(colour = "black"),
panel.background = element_blank(), axis.line.y = element_blank(), axis.title.y = element_blank()) +
coord_flip()

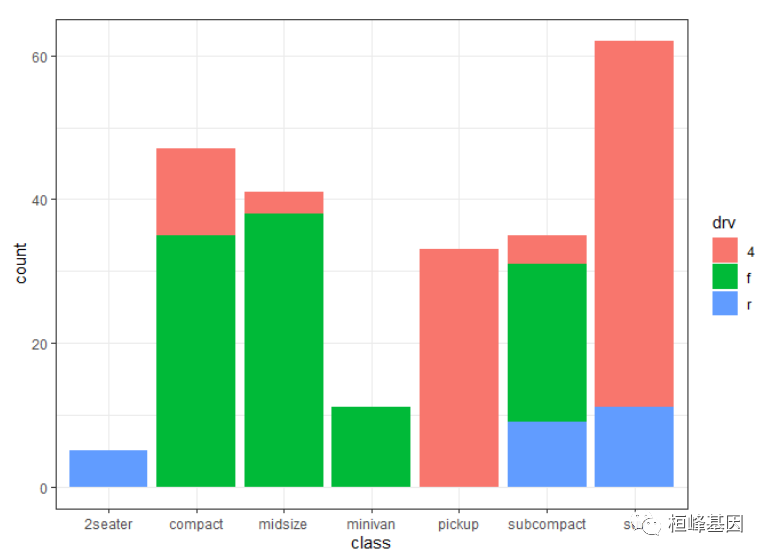
7.堆叠柱状图
分组作图的默认position 是 position = “stack”,fill参数表示将数据映射为填充颜色,color参数表示将数据映射为外框颜色。
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = mpg, aes(x = class, fill = drv), stat = "count") + theme_bw()
利用lwd参数增加外框线宽度,然后将外框线颜色和背景色统一,就可以形成堆叠间有间隔的柱状图。
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = mpg, aes(x = class, group = drv, fill = drv), stat = "count",
lwd = 1.5, colour = "white") + theme_classic() + theme_bw()

8. 百分比堆叠图
比较各组中每个类别出现次数在该组中占的百分比
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = mpg, aes(x = class, fill = factor(cyl)), position = "fill") +
theme_bw()

比较各组中每个类别实际值在该组中占的百分比。由于数据集data中的count就是数据集mpg中每个组别的出现次数,因此图片是一样的。
data <- mpg %>%
group_by(class, cyl) %>%
summarise(count = n())
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = data, aes(x = class, y = count, fill = factor(cyl)), stat = "identity",
position = "fill") + theme_bw()

9. 并排柱状图
在aes()内部的width控制柱子的宽度,position = position_dodge()中的width控制的是一组中各柱子的间隔宽度。
ggplot() + geom_bar(data = mpg, aes(x = class, fill = factor(cyl)), position = "dodge") +
theme_bw()

10. 添加误差线
并排的柱状图误差线和单个的相同,但需要注意一些参数。用position_dodge() 产生的并排柱状图,需要给误差线一个分组依据,然后进行的potion调试。
data <- mpg %>%
group_by(class, cyl) %>%
summarise(count = n())
ggplot() + geom_col(data = data, aes(x = class, y = count, fill = factor(cyl)), position = position_dodge()) +
geom_errorbar(data = data, aes(x = class, ymin = count - 1, ymax = count + 1,
group = factor(cyl)), width = 0.2, position = position_dodge(0.9)) + theme_bw()

11. 金字塔图
金字塔图的核心就是找到需要分开的变量,然后以它为依据对数据进行正和负变换,然后将正负坐标轴强制设置成对应的正值。
mpg$displ <- ifelse(mpg$year == "1999", mpg$displ, -mpg$displ)
ggplot(data = mpg) + geom_col(aes(x = factor(manufacturer), y = displ, fill = factor(year))) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = seq(from = -100, to = 100, by = 20), labels = c(seq(100,
0, -20), seq(20, 100, 20))) + coord_flip() + theme_bw()

12. 坐标轴中断
当柱状图非常高,展示时可以选择截断坐标轴,形成只有底部和上部的中断柱状图。创建y轴截断的plot,如下:
require(patchwork)
theme_1 <- theme(axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.title = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank(),
axis.line = element_line(colour = "black"))
theme_2 <- theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(),
axis.ticks.x = element_blank(),
axis.title = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank(),
axis.line = element_line(colour = "black"))
p1 <- ggplot(data = data_sorted, aes(x = class, y = count)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "stack") +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(0,30)) + theme_1
#设置下面一半
p2 <- ggplot(data = data_sorted, aes(x = class, y = count)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", position = "stack") +
coord_cartesian(ylim = c(32,65)) +
scale_y_continuous(breaks = # 按值设置breaks
seq(from = 32, to = 65, by = 5)) +
labs( title = "Broken y axis")+
theme_2
p2 /p1

























 836
836

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








