aciton 是 ROS 中异步通信的一种形式。 操作客户端向操作服务器发送目标请求。 动作服务器将目标反馈和结果发送给动作客户端。
先决条件:
将需要上一个 教程创建操作action_tutorials_interfaces中定义的包和接口。Fibonacci.action
步骤1:
1.1 创建action_tutorials_cpp包
cd ~/ros2_study/src
ros2 pkg create --dependencies action_tutorials_interfaces rclcpp rclcpp_action rclcpp_components -- action_tutorials_cpp
1.2添加可见性控制
为了使该包能够在 Windows 上编译并运行,我们需要添加一些“可见性控制”。实验阶段可忽视
打开action_tutorials_cpp/include/action_tutorials_cpp/visibility_control.h,并输入以下代码:
#ifndef ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP__VISIBILITY_CONTROL_H_
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP__VISIBILITY_CONTROL_H_
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
// This logic was borrowed (then namespaced) from the examples on the gcc wiki:
// https://gcc.gnu.org/wiki/Visibility
#if defined _WIN32 || defined __CYGWIN__
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_EXPORT __attribute__ ((dllexport))
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_IMPORT __attribute__ ((dllimport))
#else
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_EXPORT __declspec(dllexport)
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_IMPORT __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
#ifdef ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_BUILDING_DLL
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_EXPORT
#else
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_IMPORT
#endif
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC_TYPE ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_LOCAL
#else
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_EXPORT __attribute__ ((visibility("default")))
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_IMPORT
#if __GNUC__ >= 4
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC __attribute__ ((visibility("default")))
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_LOCAL __attribute__ ((visibility("hidden")))
#else
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_LOCAL
#endif
#define ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC_TYPE
#endif
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif // ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP__VISIBILITY_CONTROL_H_
2. 编写action 动作服务器端
动作服务器需要完成 一下 6 个操作:
-
模板化操作类型名称:Fibonacci。
-
将操作添加到的 ROS 2 节点
-
实例化 动作名称:‘fibonacci’.
-
用于处理目标的回调函数:handle_goal
-
用于处理取消的回调函数:handle_cancel。
-
用于处理目标accept:的回调函数handle_accept。
2.1编写动作服务器代码
打开action_tutorials_cpp/src/fibonacci_action_server.cpp,并输入以下代码:
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <thread>
#include "action_tutorials_interfaces/action/fibonacci.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_components/register_node_macro.hpp"
#include "action_tutorials_cpp/visibility_control.h"
namespace action_tutorials_cpp
{
class FibonacciActionServer : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
using Fibonacci = action_tutorials_interfaces::action::Fibonacci;
using GoalHandleFibonacci = rclcpp_action::ServerGoalHandle<Fibonacci>;
ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_PUBLIC
explicit FibonacciActionServer(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options = rclcpp::NodeOptions())
: Node("fibonacci_action_server", options)
{
using namespace std::placeholders;
this->action_server_ = rclcpp_action::create_server<Fibonacci>(
this,
"fibonacci",
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_goal, this, _1, _2),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_cancel, this, _1),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_accepted, this, _1));
}
private:
rclcpp_action::Server<Fibonacci>::SharedPtr action_server_;
rclcpp_action::GoalResponse handle_goal(
const rclcpp_action::GoalUUID & uuid,
std::shared_ptr<const Fibonacci::Goal> goal)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received goal request with order %d", goal->order);
(void)uuid;
return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE;
}
rclcpp_action::CancelResponse handle_cancel(
const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received request to cancel goal");
(void)goal_handle;
return rclcpp_action::CancelResponse::ACCEPT;
}
void handle_accepted(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
using namespace std::placeholders;
// this needs to return quickly to avoid blocking the executor, so spin up a new thread
std::thread{std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::execute, this, _1), goal_handle}.detach();
}
void execute(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Executing goal");
rclcpp::Rate loop_rate(1);
const auto goal = goal_handle->get_goal();
auto feedback = std::make_shared<Fibonacci::Feedback>();
auto & sequence = feedback->partial_sequence;
sequence.push_back(0);
sequence.push_back(1);
auto result = std::make_shared<Fibonacci::Result>();
for (int i = 1; (i < goal->order) && rclcpp::ok(); ++i) {
// Check if there is a cancel request
if (goal_handle->is_canceling()) {
result->sequence = sequence;
goal_handle->canceled(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal canceled");
return;
}
// Update sequence
sequence.push_back(sequence[i] + sequence[i - 1]);
// Publish feedback
goal_handle->publish_feedback(feedback);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Publish feedback");
loop_rate.sleep();
}
// Check if goal is done
if (rclcpp::ok()) {
result->sequence = sequence;
goal_handle->succeed(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal succeeded");
}
}
}; // class FibonacciActionServer
} // namespace action_tutorials_cpp
RCLCPP_COMPONENTS_REGISTER_NODE(action_tutorials_cpp::FibonacciActionServer)
2.2 代码解释
#include 的前几行包含我们需要编译的所有标头。
主要三部分:c++ 库,ros2 库,以及我们自定义的action 实体类
接下来我们创建一个类,它是以下类的派生类rclcpp::Node:
class FibonacciActionServer : public rclcpp::Node
该类的构造函数FibonacciActionServer将节点名称初始化为fibonacci_action_server:
explicit FibonacciActionServer(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options = rclcpp::NodeOptions())
: Node("fibonacci_action_server", options)
构造函数还实例化一个新的操作服务器:
this->action_server_ = rclcpp_action::create_server(
this,
“fibonacci”,
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_goal, this, _1, _2),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_cancel, this, _1),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::handle_accepted, this, _1));
处理新目标的回调开始:
rclcpp_action::GoalResponse handle_goal(
const rclcpp_action::GoalUUID & uuid,
std::shared_ptr<const Fibonacci::Goal> goal)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received goal request with order %d", goal->order);
(void)uuid;
return rclcpp_action::GoalResponse::ACCEPT_AND_EXECUTE;
}
此实现仅接受所有目标。
接下来是处理取消的回调:
rclcpp_action::CancelResponse handle_cancel(
const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Received request to cancel goal");
(void)goal_handle;
return rclcpp_action::CancelResponse::ACCEPT;
}
此实现只是告诉客户端它接受取消。
最后一个回调接受一个新目标并开始处理它:
void handle_accepted(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
using namespace std::placeholders;
// this needs to return quickly to avoid blocking the executor, so spin up a new thread
std::thread{std::bind(&FibonacciActionServer::execute, this, _1), goal_handle}.detach();
}
由于执行是一个长时间运行的操作,因此我们生成一个线程来完成实际工作并handle_accepted快速返回。
execute 执行方法,所有进一步的处理和更新都在新线程的方法中完成:
void execute(const std::shared_ptr<GoalHandleFibonacci> goal_handle)
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Executing goal");
rclcpp::Rate loop_rate(1);
const auto goal = goal_handle->get_goal();
auto feedback = std::make_shared<Fibonacci::Feedback>();
auto & sequence = feedback->partial_sequence;
sequence.push_back(0);
sequence.push_back(1);
auto result = std::make_shared<Fibonacci::Result>();
for (int i = 1; (i < goal->order) && rclcpp::ok(); ++i) {
// Check if there is a cancel request
if (goal_handle->is_canceling()) {
result->sequence = sequence;
goal_handle->canceled(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal canceled");
return;
}
// Update sequence
sequence.push_back(sequence[i] + sequence[i - 1]);
// Publish feedback
goal_handle->publish_feedback(feedback);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Publish feedback");
loop_rate.sleep();
}
// Check if goal is done
if (rclcpp::ok()) {
result->sequence = sequence;
goal_handle->succeed(result);
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal succeeded");
}
}
该工作线程每秒处理一个斐波那契数列的序列号,并为每个步骤发布一个反馈更新。当处理完成后,它将标记goal_handle为成功并退出。
2.3 编译动作服务器
首先,我们需要设置 CMakeLists.txt 以便编译操作服务器。打开action_tutorials_cpp/CMakeLists.txt,并在调用后添加以下内容find_package:
add_library(action_server SHARED
src/fibonacci_action_server.cpp)
target_include_directories(action_server PRIVATE
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>)
target_compile_definitions(action_server
PRIVATE "ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_BUILDING_DLL")
ament_target_dependencies(action_server
"action_tutorials_interfaces"
"rclcpp"
"rclcpp_action"
"rclcpp_components")
rclcpp_components_register_node(action_server PLUGIN "action_tutorials_cpp::FibonacciActionServer" EXECUTABLE fibonacci_action_server)
install(TARGETS
action_server
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin)
具体位置看如下截图:
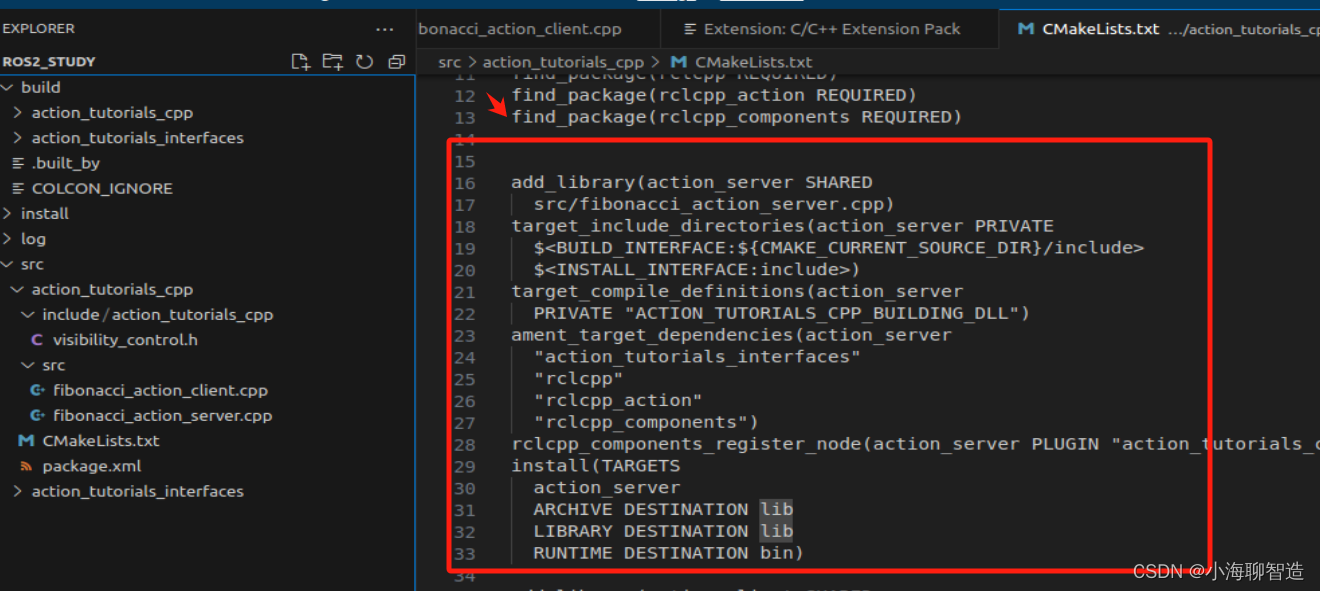
编译
现在我们可以编译这个包了。转到 的顶层ros2_study ,然后运行:
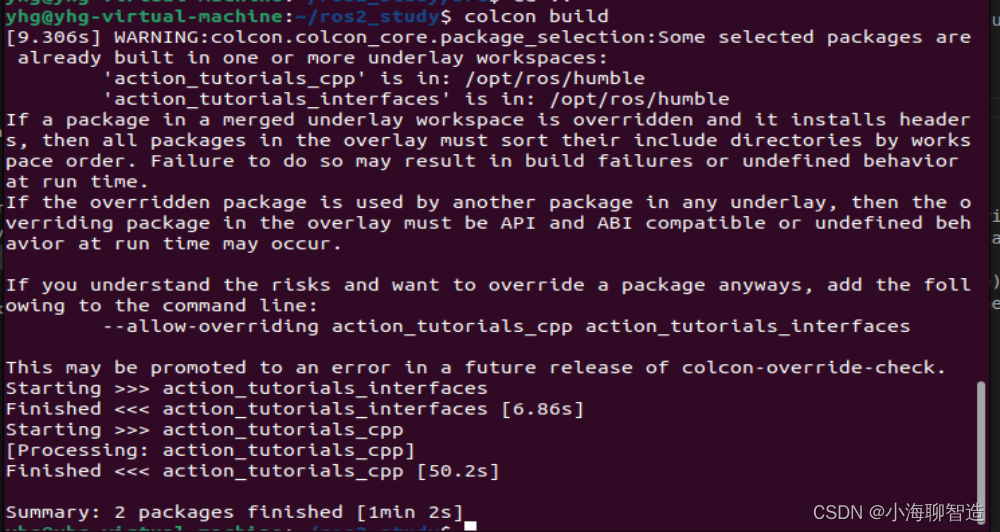
2.4 运行动作服务器
现在我们已经构建了操作服务器,我们可以运行它了
ros2 run action_tutorials_cpp fibonacci_action_server
通过查看action fibonacci已经有一个服务起来了
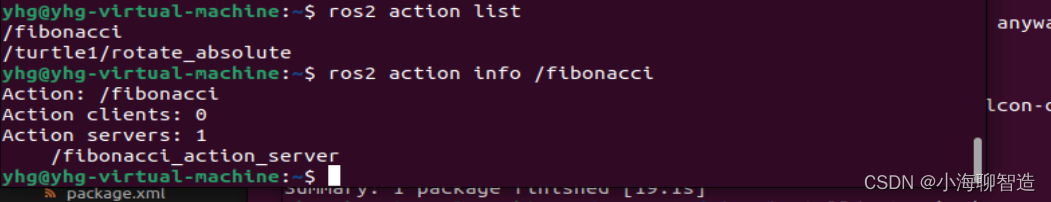
3 编写客户端
在 action_tutorials_cpp/src 下新建 fibonacci_action_client.cpp,具体代码如下:
#include <functional>
#include <future>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include "action_tutorials_interfaces/action/fibonacci.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_components/register_node_macro.hpp"
namespace action_tutorials_cpp
{
class FibonacciActionClient : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
using Fibonacci = action_tutorials_interfaces::action::Fibonacci;
using GoalHandleFibonacci = rclcpp_action::ClientGoalHandle<Fibonacci>;
explicit FibonacciActionClient(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options)
: Node("fibonacci_action_client", options)
{
this->client_ptr_ = rclcpp_action::create_client<Fibonacci>(
this,
"fibonacci");
this->timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::milliseconds(500),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::send_goal, this));
}
void send_goal()
{
using namespace std::placeholders;
this->timer_->cancel();
if (!this->client_ptr_->wait_for_action_server()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Action server not available after waiting");
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
auto goal_msg = Fibonacci::Goal();
goal_msg.order = 10;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Sending goal");
auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action::Client<Fibonacci>::SendGoalOptions();
send_goal_options.goal_response_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::goal_response_callback, this, _1);
send_goal_options.feedback_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::feedback_callback, this, _1, _2);
send_goal_options.result_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::result_callback, this, _1);
this->client_ptr_->async_send_goal(goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
private:
rclcpp_action::Client<Fibonacci>::SharedPtr client_ptr_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
void goal_response_callback(const GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr & goal_handle)
{
if (!goal_handle) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was rejected by server");
} else {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal accepted by server, waiting for result");
}
}
void feedback_callback(
GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr,
const std::shared_ptr<const Fibonacci::Feedback> feedback)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Next number in sequence received: ";
for (auto number : feedback->partial_sequence) {
ss << number << " ";
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), ss.str().c_str());
}
void result_callback(const GoalHandleFibonacci::WrappedResult & result)
{
switch (result.code) {
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::SUCCEEDED:
break;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::ABORTED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was aborted");
return;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::CANCELED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was canceled");
return;
default:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Unknown result code");
return;
}
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Result received: ";
for (auto number : result.result->sequence) {
ss << number << " ";
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), ss.str().c_str());
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
}; // class FibonacciActionClient
} // namespace action_tutorials_cpp
RCLCPP_COMPONENTS_REGISTER_NODE(action_tutorials_cpp::FibonacciActionClient)
3.1 代码解释
#include 部分为项目依赖引入
#include <functional>
#include <future>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include "action_tutorials_interfaces/action/fibonacci.hpp"
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_components/register_node_macro.hpp"
新增类FibonacciActionClient 继承 ros 的node
class FibonacciActionClient : public rclcpp::Node
构造FibonacciActionClient 类 初始化一个节点,并命名fibonacci_action_client
explicit FibonacciActionClient(const rclcpp::NodeOptions & options)
: Node("fibonacci_action_client", options)
初始化一个新的action 对象
this->client_ptr_ = rclcpp_action::create_client<Fibonacci>(
this,
"fibonacci");
aciton 客户端 主要定义以下几个主要步骤:
- 定义action 类的名称
- 增加一个action 客户端节点
- 配置action 的名称
定义一个时间定时方法
this->timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::milliseconds(500),
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::send_goal, this));
当时间过期就是调用send_goal 方法,接下来让我们来实现send_goal 方法中分内容
void send_goal()
{
using namespace std::placeholders;
this->timer_->cancel();
if (!this->client_ptr_->wait_for_action_server()) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Action server not available after waiting");
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
auto goal_msg = Fibonacci::Goal();
goal_msg.order = 10;
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Sending goal");
auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action::Client<Fibonacci>::SendGoalOptions();
send_goal_options.goal_response_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::goal_response_callback, this, _1);
send_goal_options.feedback_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::feedback_callback, this, _1, _2);
send_goal_options.result_callback =
std::bind(&FibonacciActionClient::result_callback, this, _1);
this->client_ptr_->async_send_goal(goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
以上代码主要实现:
- 取消定时
- 等待action 服务起来
- 初始化一个新的Fibonacci::Goal
- 设置返回,结果的回调方法
- 发送参数给action 服务
当action server 收到 参数请求后,它会发送一个反馈给客户端,这个反馈就 进入到这个方法中goal_response_callback
void goal_response_callback(const GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr & goal_handle)
{
if (!goal_handle) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was rejected by server");
} else {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "Goal accepted by server, waiting for result");
}
}
当action server 进入开始处理,它会发松反馈给客户端,这个反馈就进入到feedback_callback 这个方法中
void feedback_callback(
GoalHandleFibonacci::SharedPtr,
const std::shared_ptr<const Fibonacci::Feedback> feedback)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Next number in sequence received: ";
for (auto number : feedback->partial_sequence) {
ss << number << " ";
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), ss.str().c_str());
}
当action server 服务处理完成后,就会将结果 反馈给客户端,结果由result_callback 来处理;
void result_callback(const GoalHandleFibonacci::WrappedResult & result)
{
switch (result.code) {
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::SUCCEEDED:
break;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::ABORTED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was aborted");
return;
case rclcpp_action::ResultCode::CANCELED:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Goal was canceled");
return;
default:
RCLCPP_ERROR(this->get_logger(), "Unknown result code");
return;
}
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Result received: ";
for (auto number : result.result->sequence) {
ss << number << " ";
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), ss.str().c_str());
rclcpp::shutdown();
}
};
3.2 编译action 客户端
首先,我们需要设置 CMakeLists.txt 以便编译操作客户端。打开action_tutorials_cpp/CMakeLists.txt,将下面的配置贴到 之前配置服务端的下面
add_library(action_client SHARED
src/fibonacci_action_client.cpp)
target_include_directories(action_client PRIVATE
$<BUILD_INTERFACE:${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/include>
$<INSTALL_INTERFACE:include>)
target_compile_definitions(action_client
PRIVATE "ACTION_TUTORIALS_CPP_BUILDING_DLL")
ament_target_dependencies(action_client
"action_tutorials_interfaces"
"rclcpp"
"rclcpp_action"
"rclcpp_components")
rclcpp_components_register_node(action_client PLUGIN "action_tutorials_cpp::FibonacciActionClient" EXECUTABLE fibonacci_action_client)
install(TARGETS
action_client
ARCHIVE DESTINATION lib
LIBRARY DESTINATION lib
RUNTIME DESTINATION bin)
现在我们可以编译这个包了。转到 的顶层ros2_study,然后运行:
colcon build
3.3 运行客户端
ros2 run action_tutorials_cpp fibonacci_action_client
运行后效果如下:
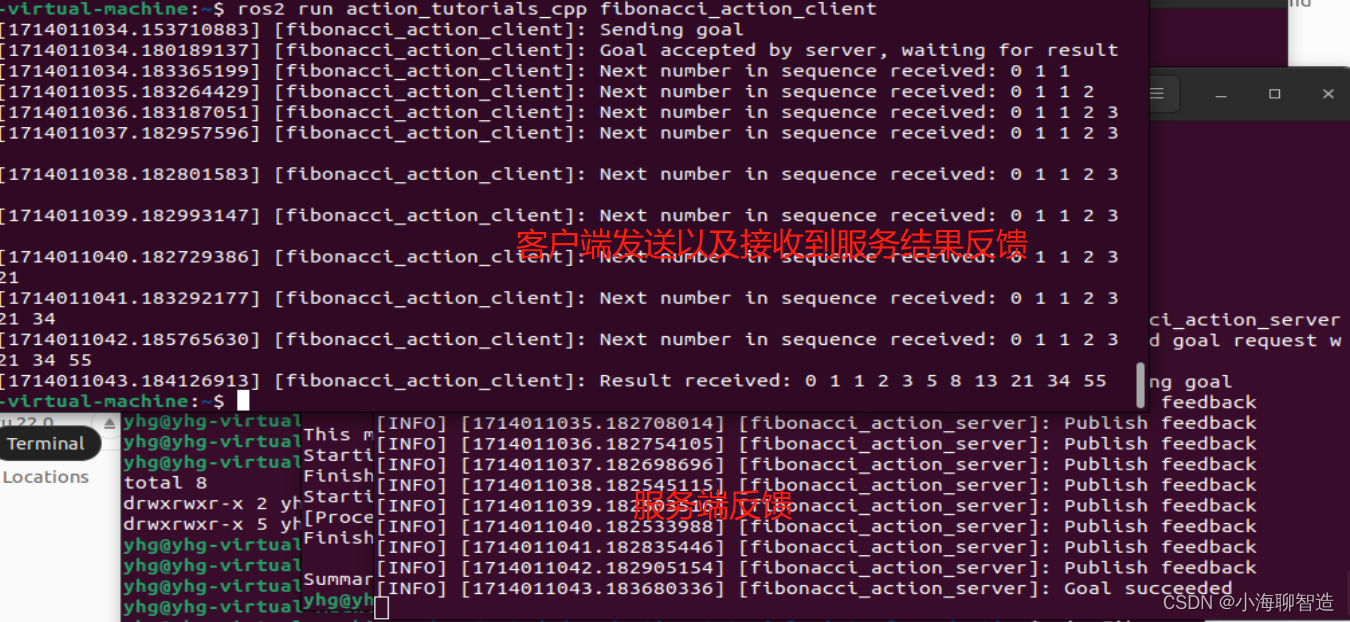
有多种方法可以用 C++ 编写操作服务器和客户端;查看ros2官方示例 ros2/examples存储库中的minimal_action_server和软件包minimal_action_client。



























 1536
1536

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










