考虑这样一些数据:
x = np.array([0, 3, 9, 14, 15, 19, 20, 21, 30, 35,
40, 41, 42, 43, 54, 56, 67, 69, 72, 88])
# x
# x_i
y = np.array([33, 68, 34, 34, 37, 71, 37, 44, 48, 49,
53, 49, 50, 48, 56, 60, 61, 63, 44, 71])
# y
# y_i
e = np.array([3.6, 3.9, 2.6, 3.4, 3.8, 3.8, 2.2, 2.1, 2.3, 3.8,
2.2, 2.8, 3.9, 3.1, 3.4, 2.6, 3.4, 3.7, 2.0, 3.5])
# e
# e_i作如下的可视化:
plt.errorbar(x, y, e, fmt='ok', ecolor='gray', alpha=.4)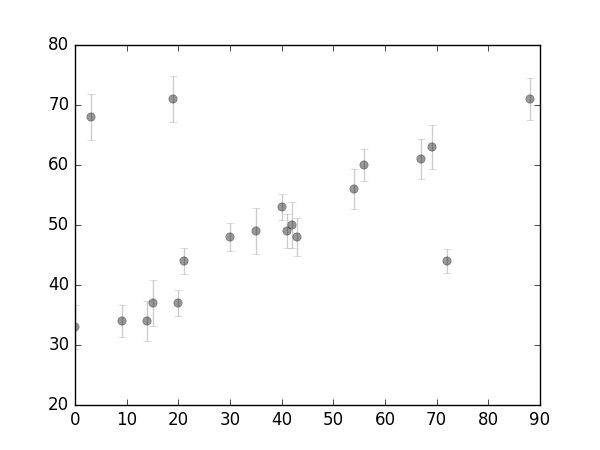
上图可见数据中存在一些离群点(outliers)。
作如下的简单建模(linear model):
y^(x|θ)=θ0+θ1x
在这一模型下(Given this model),我们可以分别对每一个点计算高斯型似然(Gaussian Likelihood):
p(xi,yi,ei|θ)∝exp(−12e2i(yi−y^(xi|θ))2)
则全体样本
D
的对数似然为:
logL(D|θ)=const−∑i=1n12e2i(yi−y^(xi|θ))2
所谓最大似然,即是maximum 这一对数似然值,已获得相关参数。从优化的观点看,最大化该似然函数,等价于最小化和式项(summation term),该项被称为损失函数:
L=∑i=1n12e2i(yi−y^(xi|θ))2
该表达式即是著名的平方误差(squared loss),也即我们从高斯对数似然(Gaussian Log Likelihood)推导出了经典的平方误差(Squared Loss)的形式。
接下来我们使用两种方式进行目标函数的求解:
法一:使用scipy的最优化工具箱optimize:
from scipy import optimize
def squared_loss(theta, x=x, y=y, e=e):
dy = (y-(theta[0]+theta[1]*x))/e
return np.sum(dy**2/2)
theta = optimize.fmin(squared_loss, [0, 0], disp=False)
print('theta: ', theta)
# theta: [ 39.69978468 0.23621066]
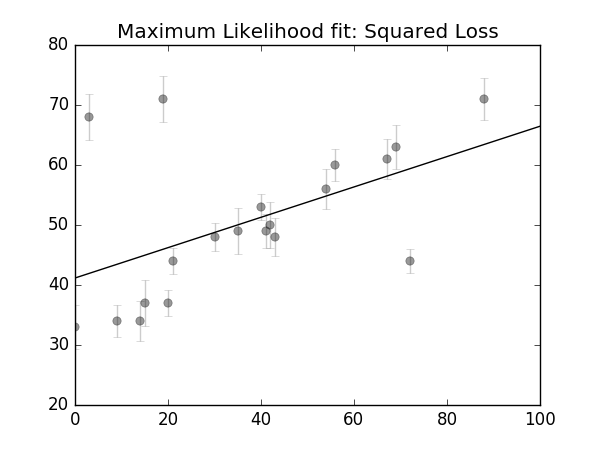
plt.figsize(figsize=(6, 4.5))
plt.errorbar(x, y, e, fmt='ok', ecolor='gray', alpha=.4)
xfit = np.linspace(0, 100)
plt.plot(xfit, theta[0]+theta[1]*fit, -k)
plt.title('Maximum Likelihood fit: Squared Loss')
plt.savefig('./imgs/linear_fit1.png')
plt.show()最终得到的 θ :theta: [ 39.69978468 0.23621066]

法二:使用矩阵运算
为了后续矩阵运算的方便,我们首先需要对输入样本矩阵(这里为一维)做一次增广(augmentation):
x_aug = np.hstack((np.ones((len(x), 1)), x.reshape((-1, 1))))考虑如下的优化问题:
L=argminθ∥y−Xθ∥22
我们可轻松地将之对 θ 求导( ∂L∂θ=0 )置零求解,以获得 θ 的解析解(analytical solution,或者叫closed-form solution):
2XT(Xθ−y)=0θ=(XTX)−1XTyθ=X†y
p_inv = np.dot(np.linalg.inv(np.dot(x_aug.T, x_aug)), x_aug.T)
theta = np.dot(p_inv, y)
print('theta:', theta)可视化的代码一如上例,显示如下:
最终得到的 θ 为,theta [ 41.16631145 0.25294549]
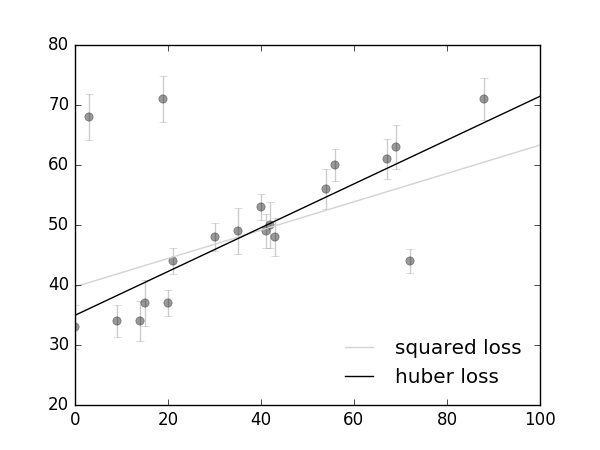
从squared loss到huber loss
从前面的可视化的拟合直线可以看出:通过最小化平方误差得到的拟合直线对离群点具有较高的敏感性,Huber loss is less sensitive to outliers in data than the squared error loss.
Lδ(y,f(x))=⎧⎩⎨12(y−f(x))2,δ⋅(|y−f(x)|−δ/2),for |y−f(x)|≤δotherwise.
def huber_loss(res, delta):
return (abs(res)<delta)*res**2/2 + (abs(res)>delta)*delta(abs(res)-delta/2)
def total_huber_loss(theta, x=x, y=y, e=e, delta=3):
return huber_loss((y-(theta[0]+theta[1]*x))/e, delta).sum()
theta1 = optimize.fmin(total_huber_loss, [0, 0], disp=False)
...

























 318
318

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










